Appendix 4 MODBUS Communication
206
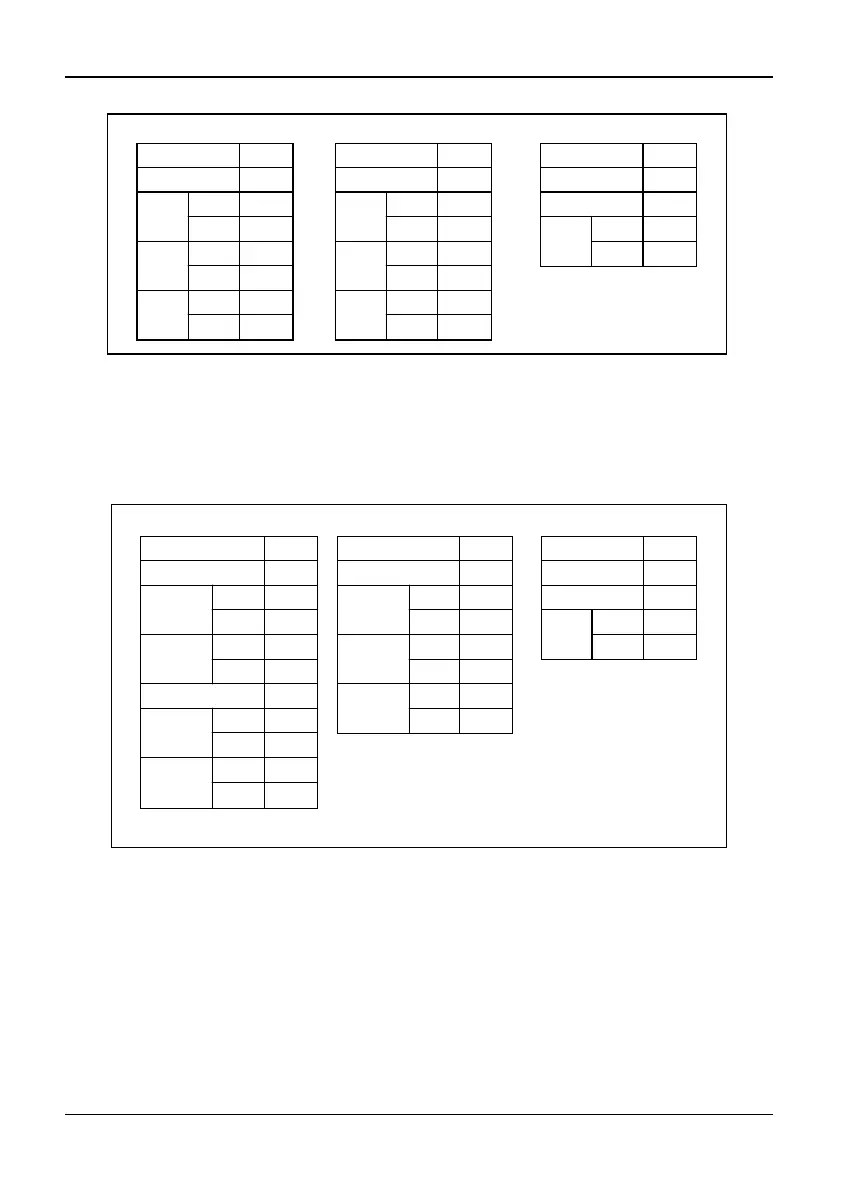
Example: Loopback test with slave 1.
Slave Address
01
Function Code
08
Test
NO.
Upper 00
Lower 00
Test
Data
Upper 12
Lower 34
CRC
Upper ED
Lower 7C
Slave Address
01
Function Code
88
Error Code 03
CRC
Upper 06
Lower 01
Slave Address
01
Function Code
08
Test
NO.
Upper 00
Lower 00
Test
Data
Upper 12
Lower 34
CRC
Upper ED
Lower 7C
Command Message
Normal Response Message AbnomalResponse Message
Write-in to specified MODBUS Register [10H]
Communications parameters are stored in special MODBUS address, data storage
address in the list must be MODBUS. It is necessary to arrange the written data items in
the holding register numbers in the order of the upper 1-byte and the lower 1-byte.
Example: frequency reference is 50.00 Hz
Slave Address 01
Function Code 10
Starting
No.
Upper 00
Lower 02
Quantity
Upper 00
Lower 01
No. of Data 02
Data
Upper 13
Lower 88
CRC
Upper AA
Lower E4
Slave Address
01
Function Code
90
Error Code 03
CRC
Upper 0C
Lower 01
Slave Address 01
Function Code 10
Starting
No.
Uppe r 00
Lower 02
Quantity
Uppe r 00
Lower 01
CRC
Uppe r A0
Lower 90
Command Message Normal Response Message
AbnomalResponse Message
Note:
No. of Data is double
Command Message
Quantity
Save the data to the EEPROM command [10H]
The address of MODBUS register, which contains the function parameters, is stored in
the private address 0x00FF and the parameters of MODBUS register are saved to the
EEPROM. It is mostly like the "Enter" key of the keyboard. The saved data will not loss
after power off. The saved data content is constructed by the 8-bit high and 8-bit low in
order. The address 0x00FF is dedicated to save data when Pb.06 = 0.
 Loading...
Loading...