Item Description Test pattern
Output sheets Type
Copy image correc-
tion
Gradation of copy images is corrected
based on the gradation density read on out-
put test pattern by the reader.
1 sheet for for error diffusion process
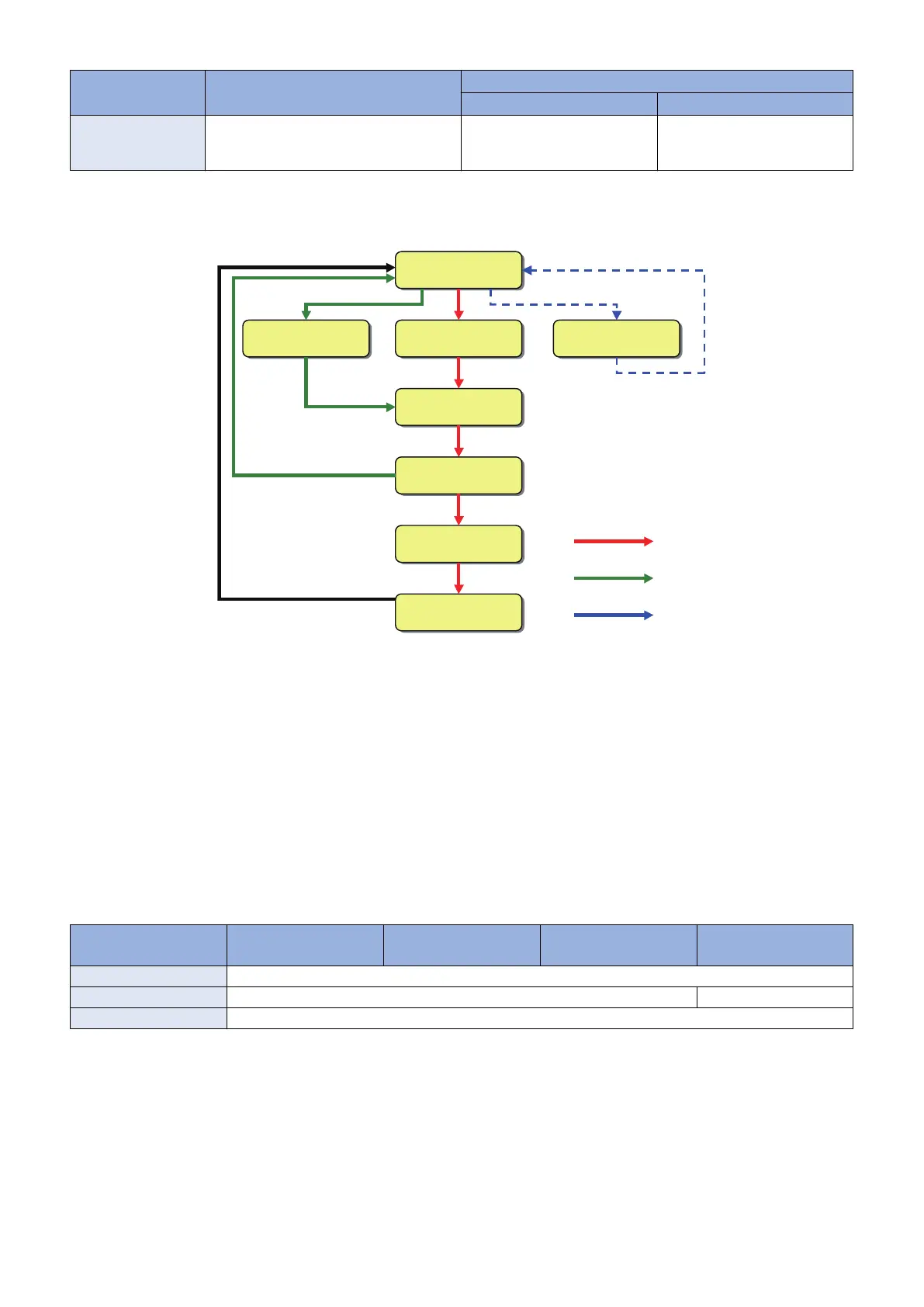
Operational flow
Gradation is corrected either in the 3 approaches above in the following flow.
⏬ീ㝵ㄪ⿵ṇ
Image gradation
correction
䝣䝹⿵ṇ
Full correction
䝁䝢䞊⏬ീ⿵ṇ
Copy image
correction
䜽䜲䝑䜽⿵ṇ
Quick correction
䝔䝇䝖䝥䝸䞁䝖䠍
Test print 1
䝇䜻䝱䞁䠍
Scan 1
䝔䝇䝖䝥䝸䞁䝖䠎
Test print 2
䝇䜻䝱䞁䠎
Scan 2
Full correction
Copy image correction
Quick correction
■ Toner cartridges
● Developing cylinder contact control
The control makes the developing cylinder engagement / disengagement to the photosensitive drum as required in the specified
print mode (full color or monochrome).
By controlling the developing cylinder engagement to the photosensitive drum only when needed, this control effectively prevents
the photosensitive drums from being deteriorated to maximize the service life.
The DC controller actuates the motor (MF8500: Developing motor, MF8200: Main motor) to switch the direction of the
engagement / disengagement cam to contact / separate the developing cylinder to / from the photosensitive drum.
The DC controller controls the developing cylinder (engagement / disengagement) by regulating the main motor rotation upon
detecting signals from the development home position sensor.
The state of the Developing Cylinder for each color (engagement / disengagement) differs depending on the condition of the Main
Body.
Condition of the Main
Body
Y M C Bk
Power OFF/Standby Disengagement
Monochrome print Disengagement Engagement
full-color print Engagement
Related Error Code
• E015-000 (Error in developing roller contact)
Failed to detect changes in developing home position sensor signals within the pre-defined time after actuating motor
(MF8500: Developing motor, MF8200: Main motor) to control the developing roller contact.
■ Transfer unit
● Pad transfer method
This product employs the pad transfer method in the primary transfer mechanism.
2. Technical Explanation
39
 Loading...
Loading...