Components and Architecture - Ethernet Open Connectivity Network
Revision 19 HC900 Process Controller Installation and User Guide 31
06/14
Connection to PC Hosts
For legacy systems, connection to PC hosts (for example, PCs that include HMI supervisory software
and/or Designer Software configuration software) can be via Modbus/TCP as well as serial Modbus RTU
over either the RS-485 or RS-232 communications ports. Both ports support Modbus RTU and are
configurable as master or slave.
For new systems, connection to PC hosts can be via Modbus/TCP as well as serial Modbus RTU over the
RS-485 communication ports.
The 5 TCP hosts can be concurrent with Modbus hosts on one or both of the other ports. Any given
controller is capable of concurrent communication with up to five PC hosts. (The meaning of the term
“host” varies, but for this definition, a PC host is any PC that is on the same LAN as the controller, or on
any LAN or WAN (Wide Area Network) that is network-connected to the controller.
Each HC900 Controller has five “sockets” (software and memory resources), each of which can service
data requests from any networked PC on a client (host)/server (controller) basis. C75 has 10 sockets. The
sockets are available on a first-come, first-served basis. Typically, when the data service for any PC Host
request is completed or times out, it allows the socket to become available to any other PC Host in the
hierarchy of networks.
Note: PDE communications, discussed previously, do not use the PC host connection sockets. PDE
communications are separate from (and are transmitted concurrent with) PC host-to-controller
communications.
The PC host can include software that closely relates to and supports controller functioning and can also
include other software that is related remotely or not at all. Closely related software can include:
Either
Designer Software – for generating and managing configuration files,
Or
HMI (Supervisory/Data Acquisition Software) or Operator Panel with Modbus/TCP driver
Or
Both configuration and HMI software (and or panel)
All communications between a controller and a PC host use Open Modbus/TCP protocol, whose
widespread use is making it an industry standard. Modbus/TCP is basically an adaptation of the Modbus
messaging structure that uses TCP/IP for a message carrier. In general, Modbus messaging is available
in two versions: ASCII, in which each eight-bit byte is sent as 2 ASCII characters, and RTU, in which
each byte is sent as two four-bit hexadecimal characters. Each Modbus message frame is embedded into
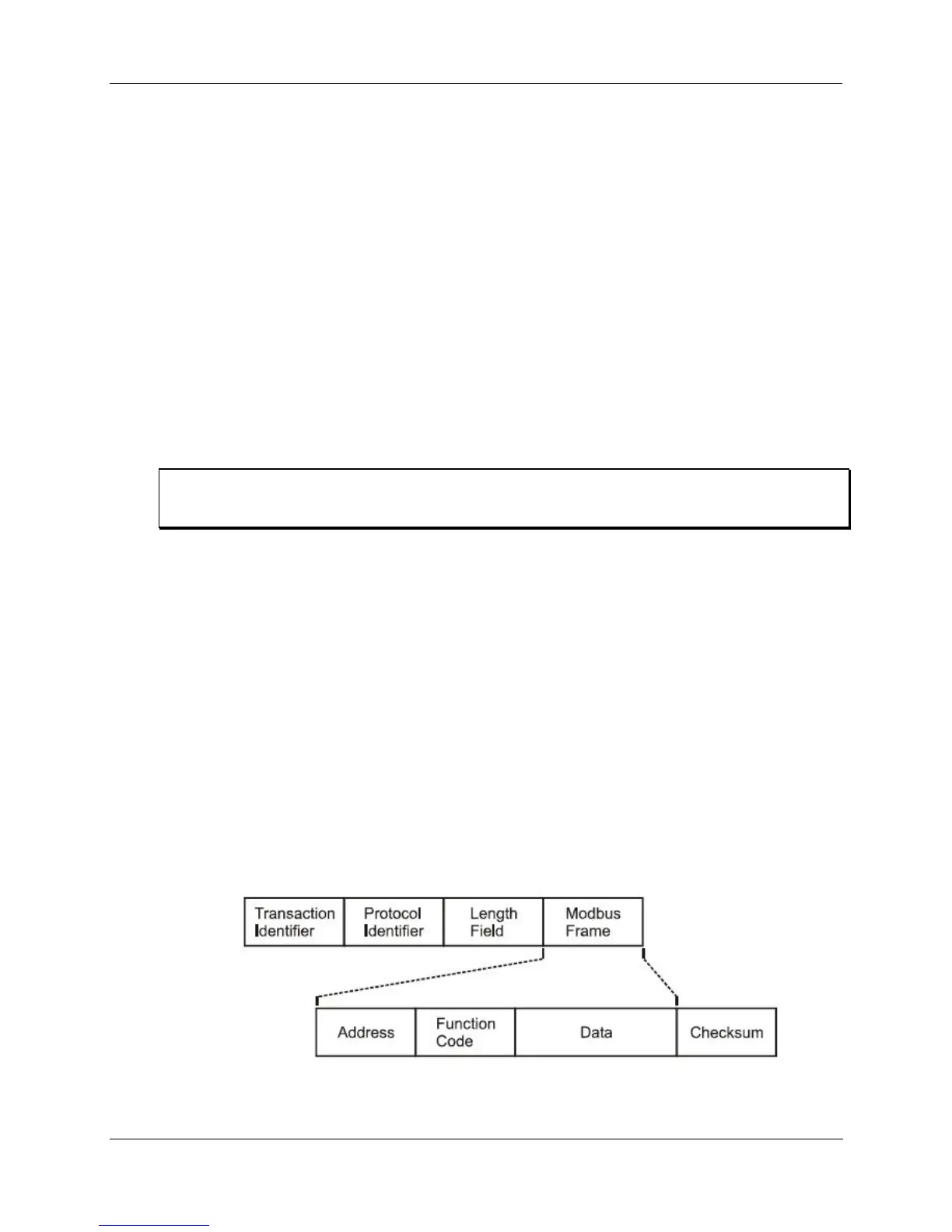
a TCP/IP datagram as indicated in Figure 20.
Figure 20 – Modbus/TCP Framing

 Loading...
Loading...