249
Before you can enable BFD for the BGP peer, establish a BGP session between the local router and
the peer.
To enable BFD for a BGP peer (IPv4):
Step Command Remarks
1. Enter system view.
system-view
N/A
2. Enter BGP view or BGP-VPN
instance view.
• Enter BGP view:
bgp as-number
• Enter BGP-VPN instance view:
a. bgp
as-number
b. ip vpn-instance
vpn-instance-name
N/A
3. Enable BFD to detect the link to the
specified BGP peer.
peer
ip-address [ mask-length ]
bfd
[
multi-hop
|
single-hop
]
By default, BFD is
not enabled.
To enable BFD for a BGP peer (IPv6):
Step Command Remarks
1. Enter system view.
system-view
N/A
2. Enter BGP view or BGP-VPN
instance view.
• Enter BGP view:
bgp as-number
• Enter BGP-VPN instance view:
a. bgp
as-number
b. ip vpn-instance
vpn-instance-name
N/A
3. Enable BFD to detect the link to the
specified IPv6 BGP peer.
peer
ipv6-address [ prefix-length ]
bfd
[
multi-hop
|
single-hop
]
By default, BFD is
not enabled.
Configuring BGP FRR
When a link fails, the packets on the link are discarded, and a routing loop might occur until BGP
completes routing convergence based on the new network topology.
You can enable BGP fast reroute (FRR) to resolve this issue.
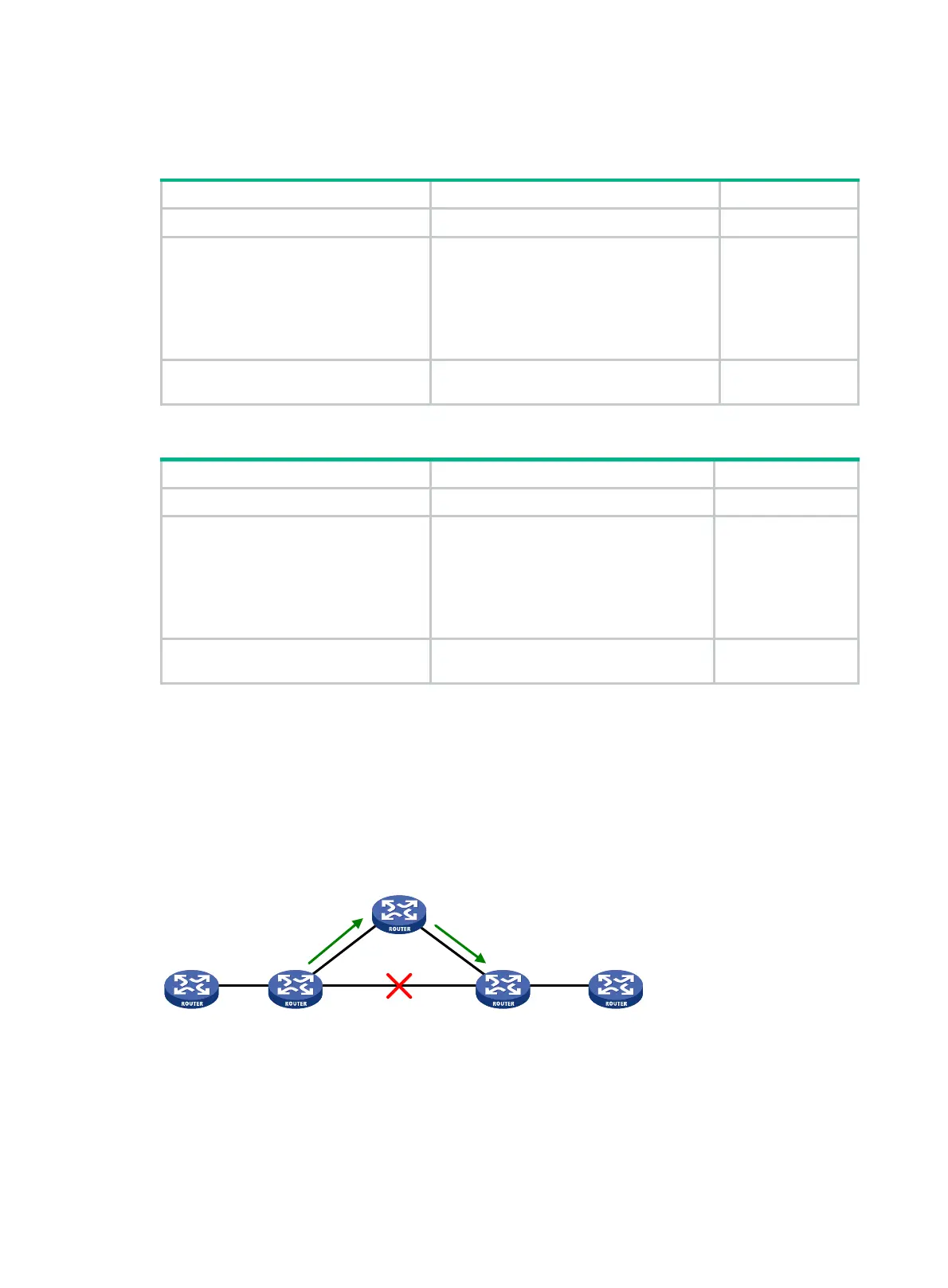
Figure 61 Network diagram for BGP FRR
After you configure FRR on Router B as shown in Figure 61, BGP generates a backup next hop
Router C for the primary route. BGP uses ARP, echo-mode BFD (for IPv4), or ND (for IPv6) to detect
the connectivity to Router D. When the link to Router D fails, BGP directs packets to the backup next
hop. At the same time, BGP calculates a new optimal route, and forwards packets over the optimal
route after route selection.
You can use the following methods to configure BGP FRR:
Backup nexthop: Router C
Router ENexthop: Router D
Router A Router B

 Loading...
Loading...



















