151
Configuring IS-IS FRR
A link or router failure on a path can cause packet loss and routing loop. IS-IS FRR uses BFD to
detect failures and enables fast rerouting to minimize the failover time.
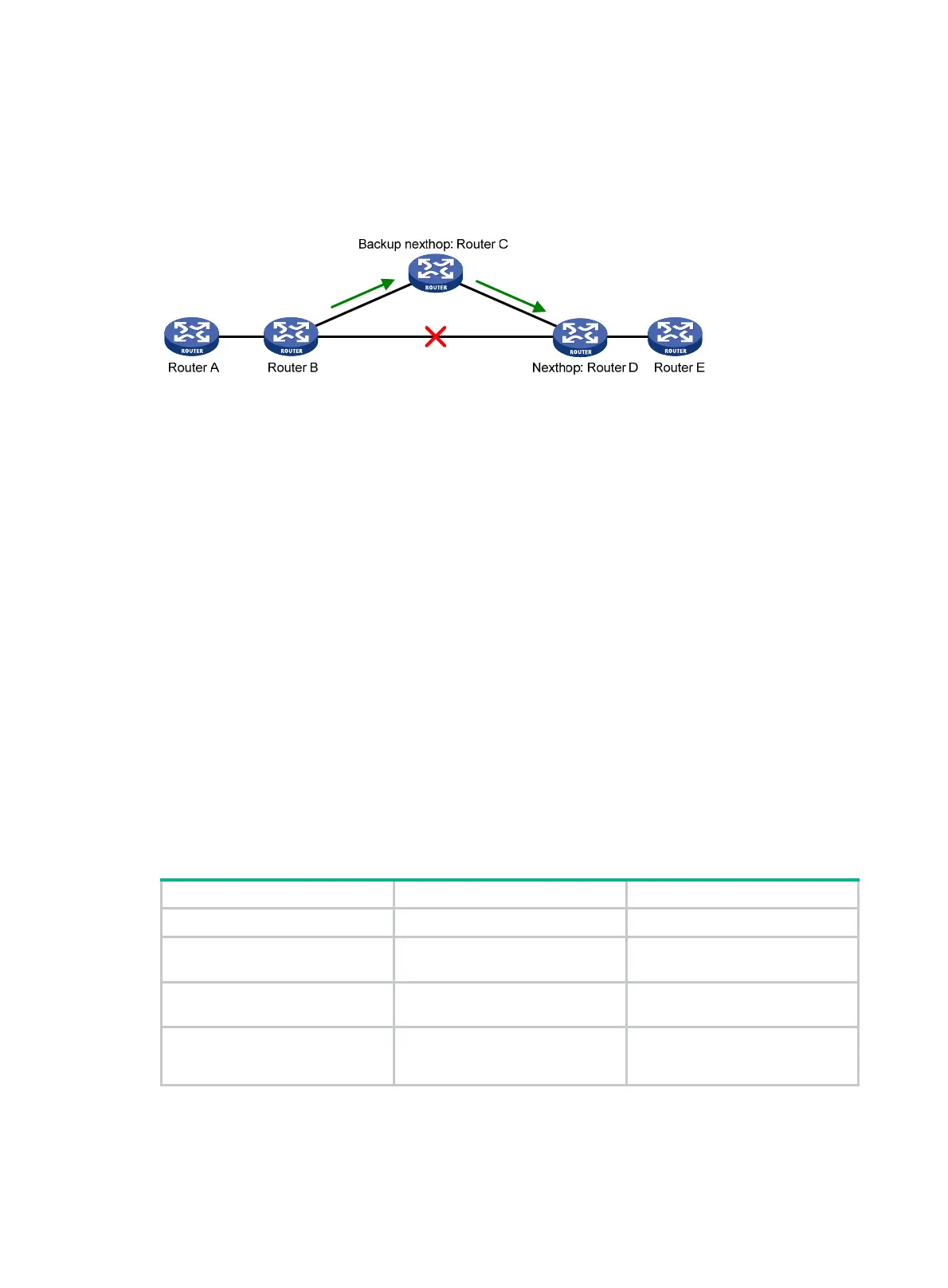
Figure 39 Network diagram for IS-IS FRR
In Figure 39, after you enable FRR on Router B, IS-IS automatically calculates or designates a
backup next hop when a link failure is detected. In this way, packets are directed to the backup next
hop to reduce traffic recovery time. Meanwhile, IS-IS calculates the shortest path based on the new
network topology, and forwards packets over the path after network convergence.
You can either enable IS-IS FRR to calculate a backup next hop automatically, or designate a backup
next hop with a routing policy for routes matching specific criteria.
Configuration prerequisites
Before you configure IS-IS FRR, complete the following tasks:
• Configure IP addresses for interfaces to ensure IP connectivity between neighboring nodes.
• Enable IS-IS.
Configuration guidelines
• Do not use FRR and BFD at the same time. Otherwise, FRR might fail to take effect.
• The automatic backup next hop calculation of FRR and that of TE are mutually exclusive.
Configuring IS-IS FRR to automatically calculate a backup
next hop
Step Command Remarks
1. Enter system view.
system-view
N/A
2. Configure the source
address of echo packets.
bfd echo-source-ip
ip-address
By default, the source address of
echo packets is not configured.
3. Enter IS-IS view.
isis
[ process-id ] [
vpn-instance
vpn-instance-name ]
N/A
4. Enable IS-IS FRR to
automatically calculate a
backup next hop.
fast-reroute
auto
By default, IS-IS FRR is disabled.

 Loading...
Loading...



















