128
backbone in this topology. The backbone comprises all contiguous Level-2 and Level-1-2 routers in
different areas. The IS-IS backbone does not need to be a specific area.
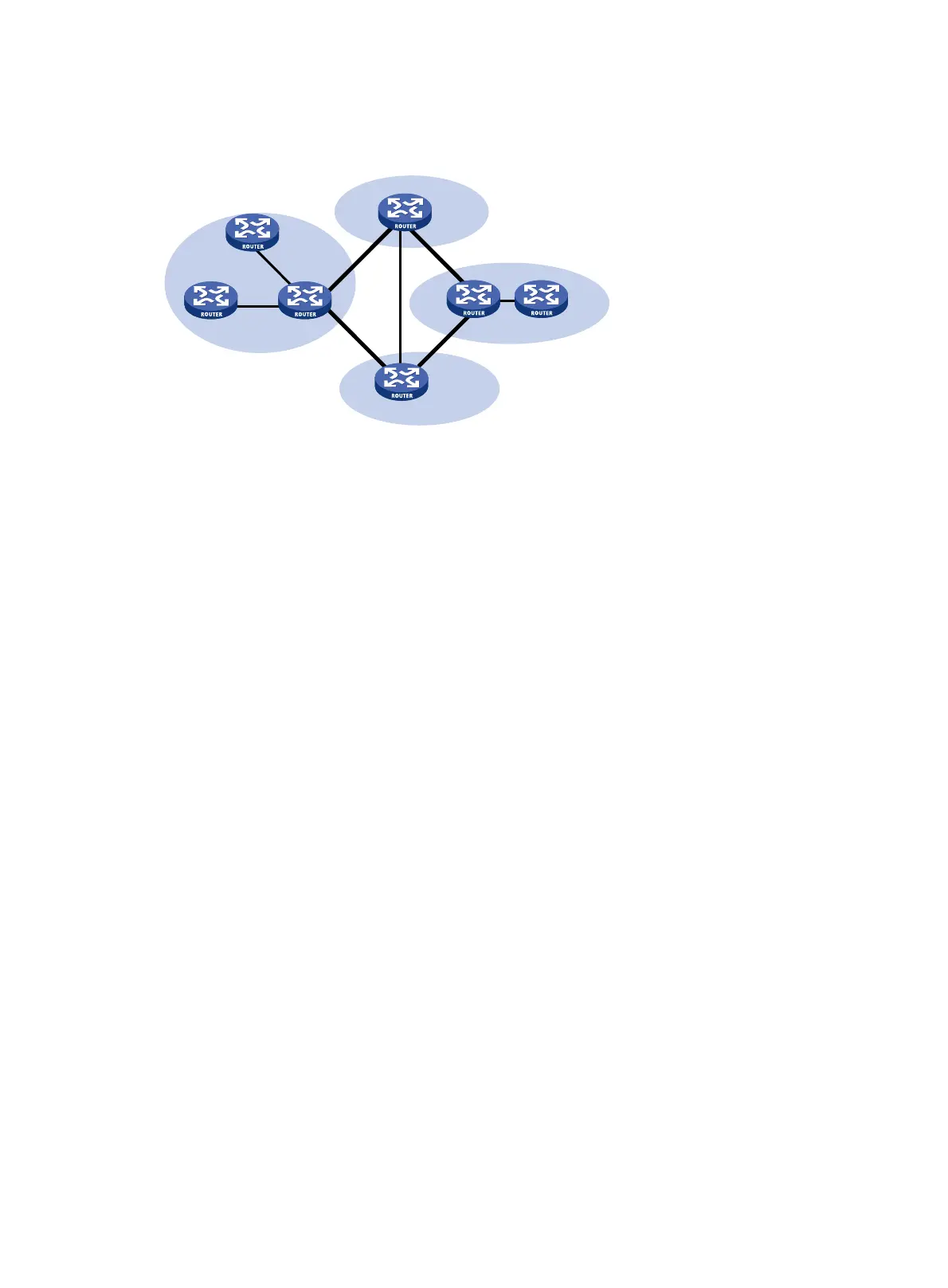
Figure 35 IS-IS topology 2
Both the Level-1 and Level-2 routers use the SPF algorithm to generate the shortest path tree.
Route leaking
Level-2 and Level-1-2 routers form a Level-2 area. An IS-IS routing domain comprises only one
Level-2 area and multiple Level-1 areas. A Level-1 area must connect to the Level-2 area rather than
another Level-1 area.
Level-1-2 routers send the routing information of Level-1 areas to the Level-2 area. Level-2 routers
know the routing information of the entire IS-IS routing domain. By default, a Level-2 router does not
advertise the routing information of other Level-1 areas and the Level-2 area to a Level-1 area, so a
Level-1 router simply sends packets destined for other areas to the nearest Level-1-2 router. The
path passing through the Level-1-2 router might not be the best. To solve this problem, IS-IS
provides the route leaking feature.
Route leaking enables a Level-1-2 router to advertise the routes of other Level-1 areas and the
Level-2 area to the connected Level-1 area so that the Level-1 routers can select the optimal routes
for packets.
IS-IS network types
Network types
IS-IS supports broadcast networks (for example, Ethernet and Token Ring) and point-to-point
networks (for example, PPP and HDLC).
DIS and pseudonodes
IS-IS routers on a broadcast network must elect a DIS.
The Level-1 and Level-2 DISs are elected separately. You can assign different priorities to a router
for different level DIS elections. The higher the router priority, the more likely the router becomes the
DIS. If multiple routers with the same highest DIS priority exist, the one with the highest Subnetwork
Point of Attachment (SNPA) address will be elected. On a broadcast network, the SNPA address is
the MAC address. A router can be the DIS for different levels.
IS-IS DIS election differs from OSPF DIS election in the following ways:
• A router with priority 0 can also participate in the DIS election.
• When a router with a higher priority is added to the network, an LSP flooding process is
performed to elect the router as the new DIS.
Area 1
L2
Area 3
Area 2
L1
L1
L1/L2
L2
L1/L2
L1
Area 4

 Loading...
Loading...



















