363-206-305
A SONET Overview
A-14 Issue 3 June 2000
SONET Digital Multiplexing Schemes A
Asynchronous Multiplexing A
Currently, fiber optic facilities are primarily used to carry DS3 signals. The DS3
signal consists of a combination of the following payload signals:
■ 28 DS1s
■ 14 DS1Cs
■ 7 DS2s.
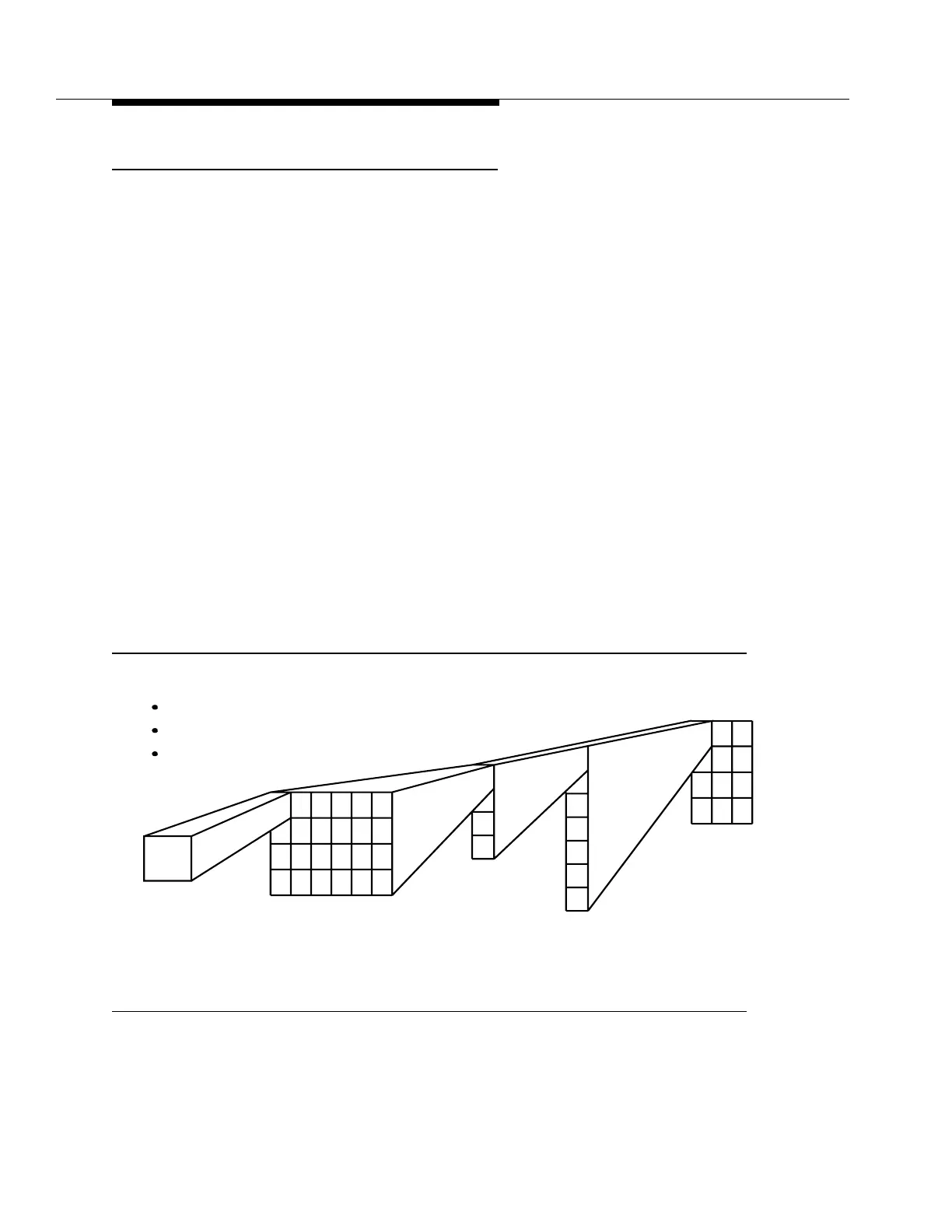
Typically, 28 DS1 signals are multiplexed into a DS3 signal, using an M13 format.
Refer to Figure A-8. M13 format is a process that includes bit-interleaving four
DS1 into a DS2 signal and then bit-interleaving seven DS2 signals into a DS3.
The DS3 rate is not a direct multiple of the DS1 or the DS2 rates due to the bit-
stuffing synchronization technique used in asynchronous multiplexing.
Identification of DS0s contained in any DS-
N
signal, except DS1, is complex and
DS0s cannot be directly extracted. Thus, an asynchronous DS3 signal must be
demultiplexed down to the DS1 level to access and cross-connect DS0 and DS1
signals.
Another disadvantage of the M13 format is there is no end-to-end overhead
channel for use by OAM&P groups.
Figure A-8. Asynchronous Multiplexing
Bit Interleaving above DS1
DS1 Not Observable above DS1
No End-To-End Overhead Channel
1 VF Circuit = 1 DSO 24 DS0s = 1 DS1 4 DS1s = 1 DS2 7 DS2s = 1 DS3 DS3 X N = Line Signal

 Loading...
Loading...