VLAN Members: If you select “V” from the pull-down menu, it denotes that the port selected
belongs to VLAN.
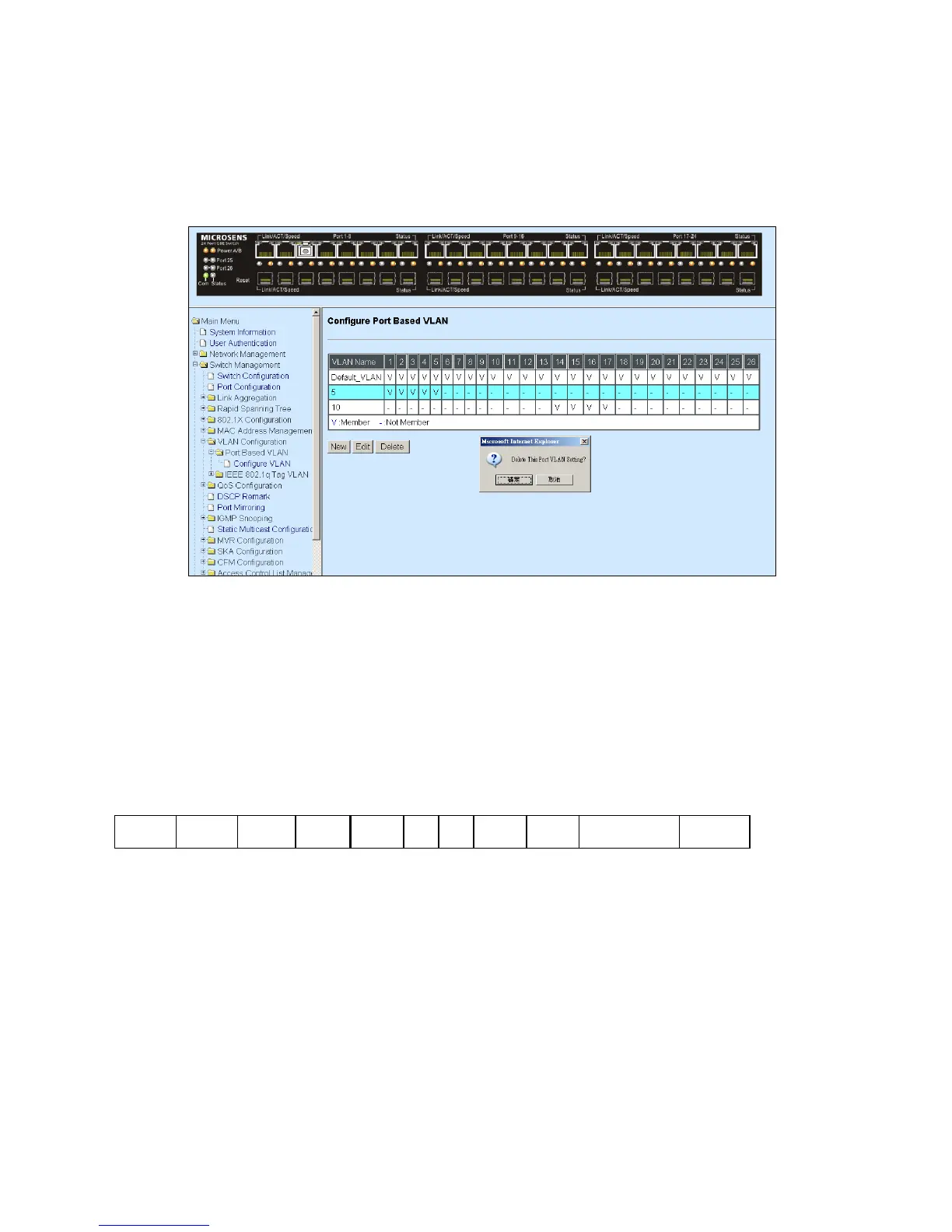
Click Delete to remove the selected Port-Based VLAN rule and then the following screen
page appears.
4.4.7.2 802.1Q VLAN Concept
Port-Based VLAN is simple to implement and use, but it cannot deploy cross switches
VLAN. The 802.1Q protocol was developed in order to provide the solution. By tagging
VLAN membership information to Ethernet frames, the IEEE 802.1Q can help network
administrators break large switched networks into smaller segments so that broadcast and
multicast traffic will not occupy too much available bandwidth as well as provide a higher
level security between segments of internal networks.
The 802.1Q frame format is shown below.
PRE Preamble 62 bits Used to synchronize traffic
SFD Start Frame Delimiter 2 bits Marks the beginning of the header
DA Destination Address 6 bytes The MAC address of the destination
SA Source Address 6 bytes The MAC address of the source
TCI Tag Control Info 2 bytes set to 8100 for 802.1p and Q tags
P Priority 3 bits Indicates 802.1p priority level 0-7
C Canonical Indicator 1 bit Indicates if the MAC addresses are in
Canonical format - Ethernet set to "0"
VID VLAN Identifier 12 bits Indicates the VLAN (0-4095)
T/L Type/Length Field 2 bytes Ethernet II "type" or 802.3 "length"
Payload < or = 1500 bytes User data
FCS Frame Check Sequence 4 bytes Cyclical Redundancy Check

 Loading...
Loading...