The PowerPC Core
6-30 MPC823e REFERENCE MANUAL MOTOROLA
CORE
6
6.6.9 Instruction Timing
The following table summarizes the different load/store instructions timing in the case of
zero wait state memory references on a parked bus. With external memory accesses,
pipelined external accesses are assumed.
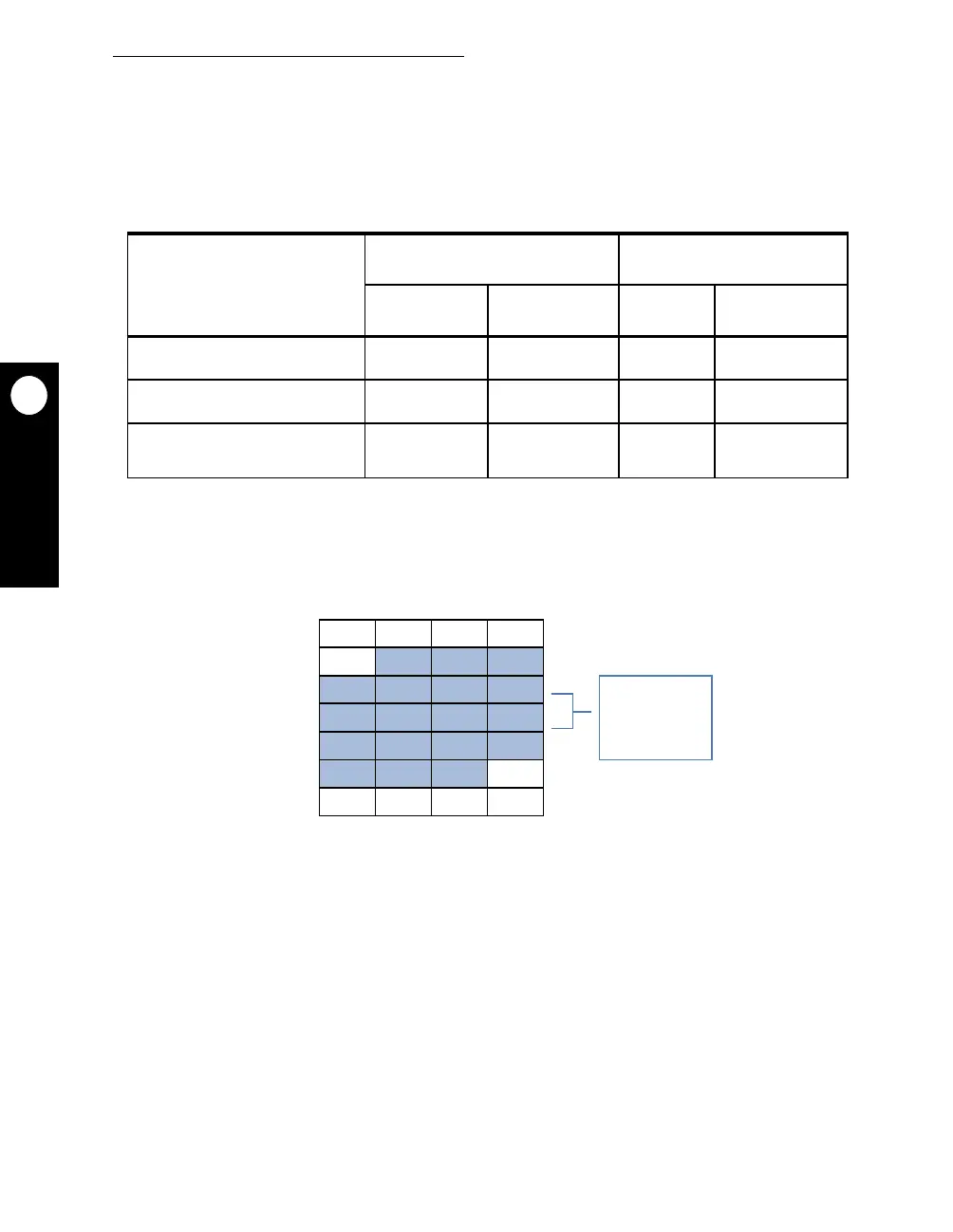
String instructions are broken into a series of aligned bus accesses. Figure 6-8 illustrates
the maximum number of bus cycles needed for string instruction execution.
6.6.10 Stalling Storage Control Instructions
A storage control instruction waits one clock before it is taken.
6.6.11 Accessing Off-Core Special Registers
Access to special registers—mtspr and mfspr—implemented off-core is executed by the
load/store unit via the internal bus using a special cycle. Refer to Section 6.4.1.1 Physical
Location of Special Registers for detailed information. If the access terminates in a bus
error, then an implementation-dependent software emulation interrupt is taken. All write
operations to off-core special registers (mtspr) are previously synchronized. In other words,
the instruction is not taken until all prior instructions terminate.
Table 6-12. Load/Store Instructions Timing
INSTRUCTION TYPE
LATENCY CLEARED FROM
LOAD/STORE UNIT
DATA CACHE EXTERNAL
MEMORY
DATA
CACHE
EXTERNAL
MEMORY
Fixed-Point Single Target
Register Load (Aligned)
2 Clocks 5 Clocks 2 Clocks 5 Clocks
Fixed-Point Single Target
Register Store (Aligned)
1 Clock 1 Clock 2 Clocks 5 Clocks
Load/Store Multiple 1 + N 1 + N
NOTE: N denotes the number of registers transferred.
00’h 00 01 02 03
04’h 04
05 06 07 2 BUS CYCLES
08’h 08 09 0A 0B WORD
TRANSFERS
3 BUS CYCLES
0C’h 0C 0D 0E 0F
10’h 10 11 12 13
14’h 14 15 16 17 2 BUS CYCLES
18’h 18 19 1A 1B
Figure 6-8. Number of Bus Cycles Needed For String Instruction Execution
3N
N1+
3
--------------
++
3N
N1+
3
--------------
++

 Loading...
Loading...