Communication Processor Module
MOTOROLA
MPC823e REFERENCE MANUAL
16-7
RISC
COMMUNICATION
16
PROCESSOR MODULE
18.SPI RX
19.SPI TX
20.I
2
C RX
21.I
2
C TX
22.RISC timer tables
23.IDMA DREQ1 (option 3)
24.IDMA DREQ2 (option 3)
16.2.4 Executing Microcode From RAM or ROM
The microcontroller can execute microcode from a portion of 8K dual-port RAM. Depending
on the size of your microcode, you can program the ERAM field in the RCCR to protect the
first 512 bytes, 1,024 bytes, or 2,048 bytes of on-chip RAM to allow the microcontroller
exclusive access. You can execute microcode from the dual-port RAM or on-chip ROM. This
flexibility not only allows Motorola to add more protocols or enhancements to the MPC823e,
but it also allows you to obtain binary microcode. Refer to Table 16-1 for more information.
16.2.5 RISC Configuration and Control Registers
The 32-bit RISC controller configuration register (RCCR) and RISC microcode development
support control (RMDS) register are used to configure and control the RISC microcontroller.
The RCCR configures the microcontroller to run microcode from ROM or RAM and controls
the RISC internal timer. The RMDS determines the regions of the dual-port RAM that can
contain executable microcode. It is recommended that you write to these two registers as if
they were a single 32-bit register.
The ERAM4K bit is cleared in the RMDS if the RCCR’s location is accessed as either part
of a half-word or byte access. RMDS is used in conjunction with the ERAM field of the RCCR
to determine the valid address space for executable microcode. If the ERAM4K bit is to be
set, the RMDS register must be accessed as part of a word starting at IMMR+0x9C4 to
IMMR+0x9C7.
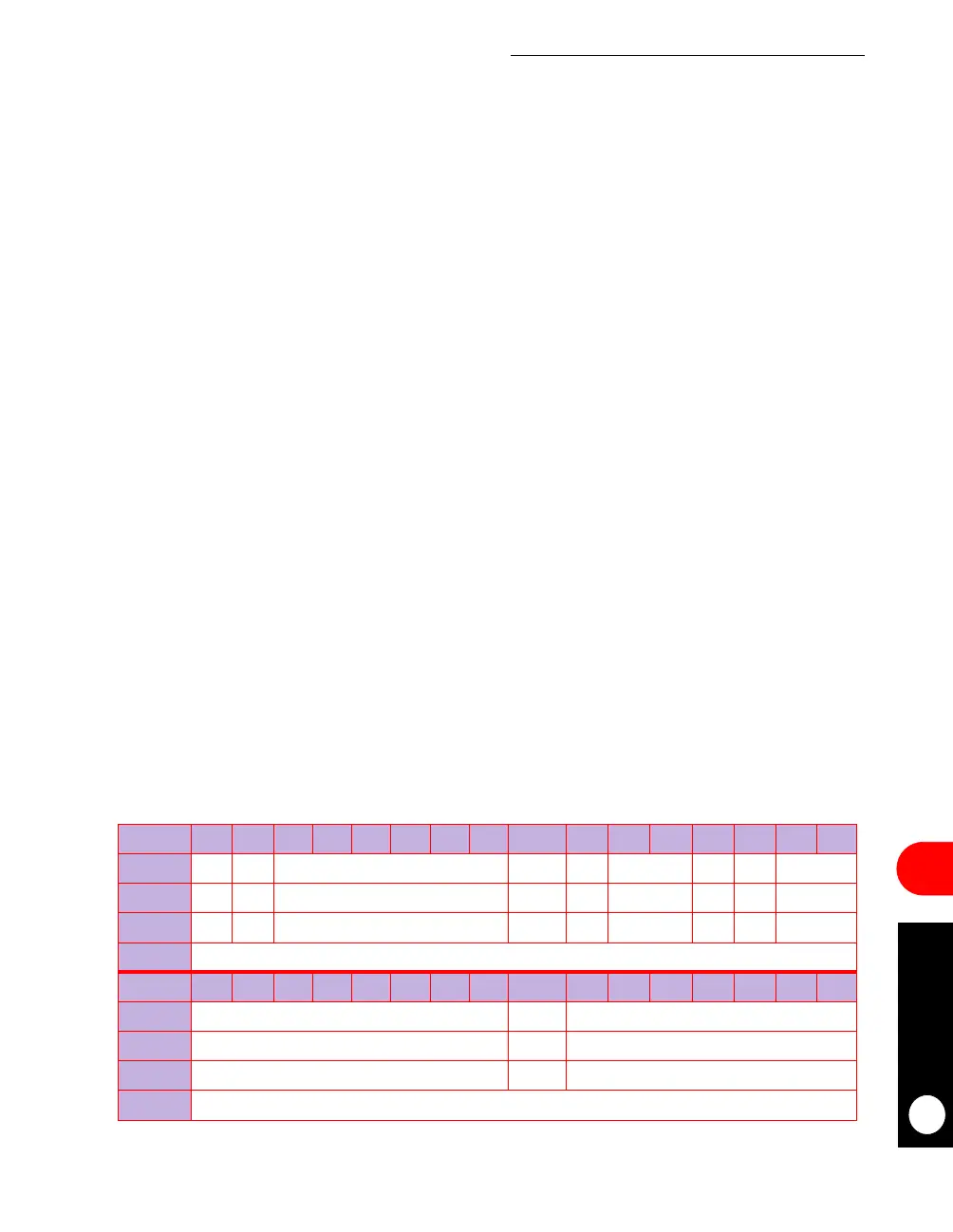
RCCR-RMDS
BIT
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
FIELD
TIME RES TIMEP DR2M DR1M DRQP EIE SCD ERAM
RESET
00 0 000000
R/W
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
ADDR
(IMMR & 0xFFFF0000) + 0x9c4
BIT
16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31
FIELD
RESERVED ERAM4K RESERVED
RESET
000
R/W
R/W R/W R/W
ADDR
(IMMR & 0xFFFF0000) + 0x9c6
 Loading...
Loading...