Communication Processor Module
16-290
MPC823e REFERENCE MANUAL
MOTOROLA
COMMUNICATION
16
SCCs
16.9.20.3 HIGH-SPEED IRDA PROTOCOL.
The high-speed IrDA protocol is derived from
the preexisting SCCx Transparent protocol standard.
16.9.20.3.1 4PPM Data Encoding.
Pulse position modulation (PPM) encoding is achieved
by defining a data symbol duration (Dt) and subsequently subdividing Dt into a set of equal
time slices called “chips”. In PPM schemes, each chip position within a data symbol
represents one of the possible bit combinations. Each chip has a duration of Ct given by
Ct = Dt/Base.
In this formula
base
refers to the number of pulse positions or chips in each data symbol.
The base for high-speed IrDA protocol is defined as four and the resulting modulation
scheme is four-pulse position modulation (4PPM). The data rates of a IrDA PPM system are
defined as 4.0Mb/s.
The resulting values for Ct and Dt are as follows:
• Dt = 500 ns
• Ct = 125 ns
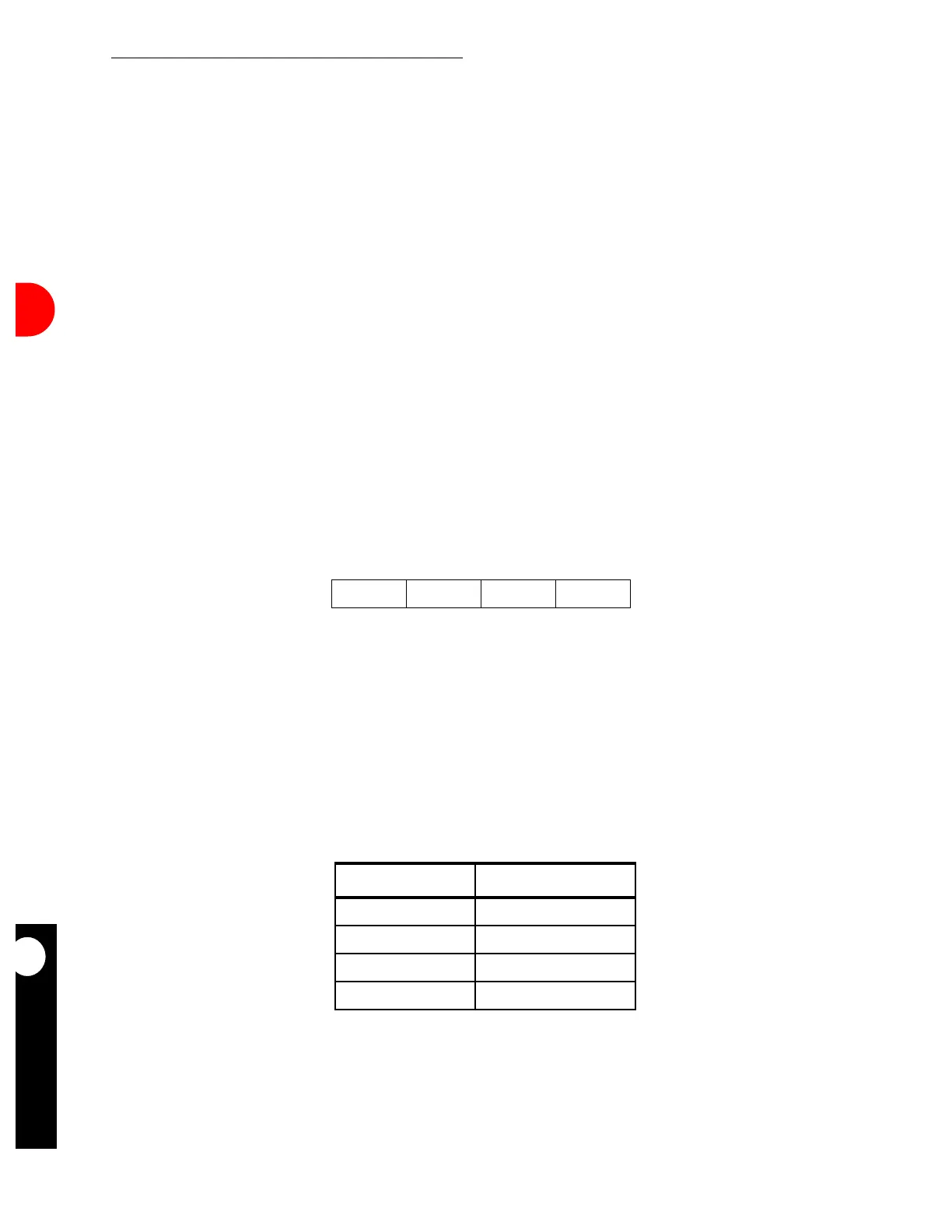
The figure below illustrates a data symbol field and its enclosed chip durations for a 4PPM
scheme.
Because there are four unique chip positions within each symbol in 4PPM, four independent
symbols exist in which only one chip is logically a “one” while other chips are logically a
“zero”. These four unique symbols are the only legal data symbols (DD) allowed in 4PPM.
Each data symbol represents two bits of payload data, or a single data bit pair (DBP), so that
a byte of payload data can be represented by four data symbols in sequence. The following
table defines the chip pattern representation of the four unique data symbols defined for
4PPM.
Figure 16-97. One Complete Symbol
DATA BIT PAIR 4PPM DATA SYMBOL
00 1000
01 0100
10 0010
11 0001
CHIP1 CHIP2 CHIP3 CHIP4

 Loading...
Loading...