16 FLOWSIC100 · Operating Instructions · 8012513/YSA5/V2-1/2016-07 · © SICK Engineering GmbH
Product Description
Subject to change without notice
Sound velocity
Sound velocity c can be calculated by resolving formulas 2.1 and
2.2.
(2.4)
Based on the dependencies in formulas 2.5 and 2.7, the sound velocity can be used to
determine the gas temperature and for diagnosis purposes.
(2.5)
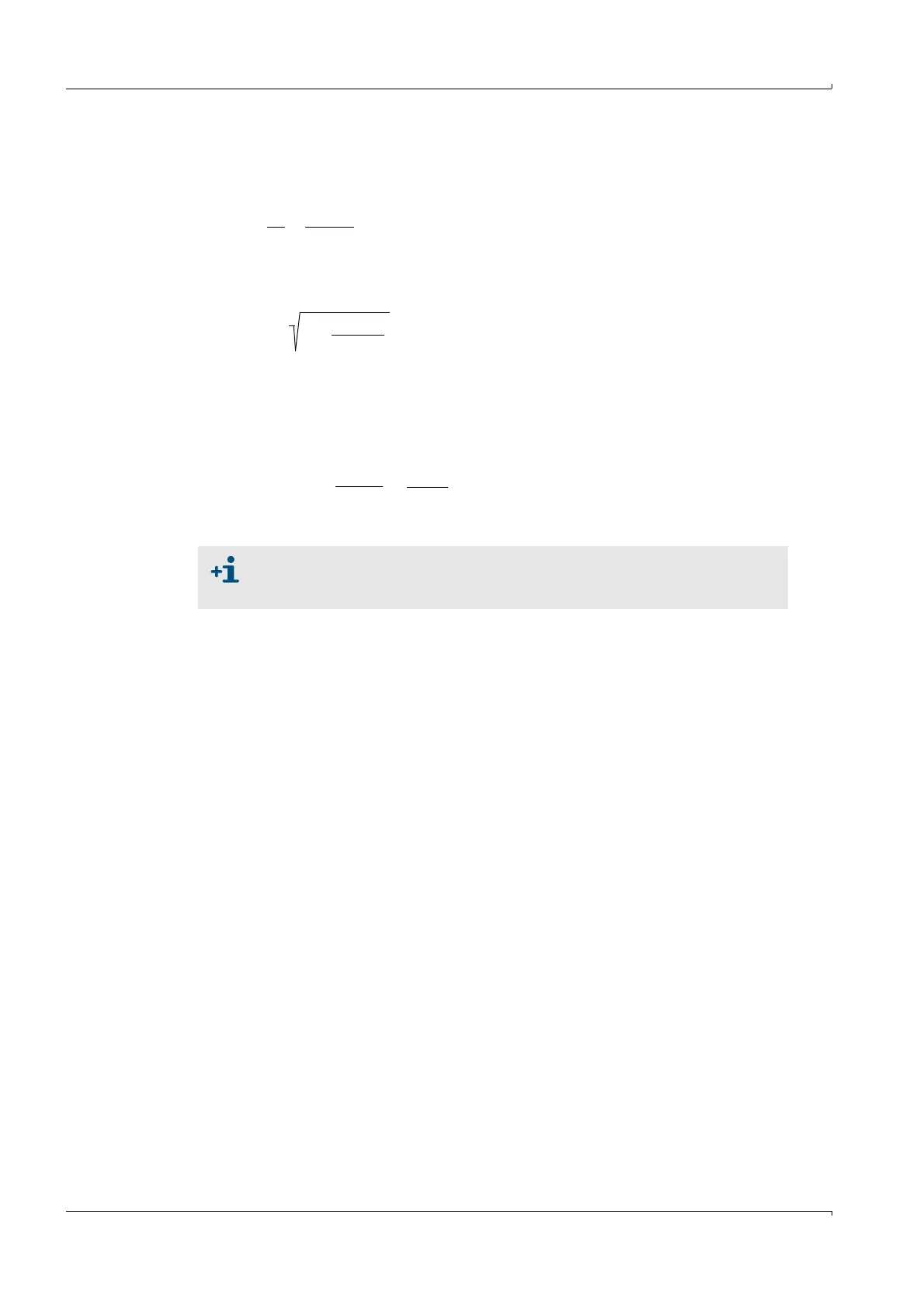
Calculating the gas temperature
Since the sound velocity is dependent on the temperature, the gas temperature can also
be calculated from the transit times (by resolving formulas 2.4 and 2.5 to derive
).
(2.6)
Formula 2.6 shows that, in addition to the measured transit times, the square of the values
of L and the standard velocity are included in the calculation.
Determining the volume flow
The volume flow in operating state is computed using the geometric constants of the duct.
The process parameters pressure, temperature and moisture content are required to
calculate the volume flow in the standard state. A detailed description is provided in
Section § 2.4, page 44.
Path compensation
When the FLOWSIC100 is operated with a 2-path configuration, the device runs with an
integrated algorithm for automatic "path compensation".
During trouble-free operation, gas and sound velocity relations between both measuring
paths are recorded and saved. Should one path then fail, the system can replace invalid
measured values from the failed path with theoretical values based on the "learned" path
relations. The system signals "Maintenance request" status at the same time.
This means a single path can be compensated temporarily and measurement continued
with a slightly higher uncertainty until the malfunction has been cleared.
This means precise temperature measurement is only possible when the gas
composition is constant, measuring path L has been measured extremely
accurately and a calibration has been carried out (see Section
p. 151, 4.3.6).
c = c
0
·
1 +
273 °C
= 273°C · ( () - 1)
4 · c
0
²
t
v
·
t
r
L
²
t
v
+ t
r
²
c = · ()
L t
v
+ t
r
2 t
v
·t
r
 Loading...
Loading...