Chapter 5
Setup and Configuration
RUGGEDCOM ROS
User Guide
122 Managing Virtual LANs
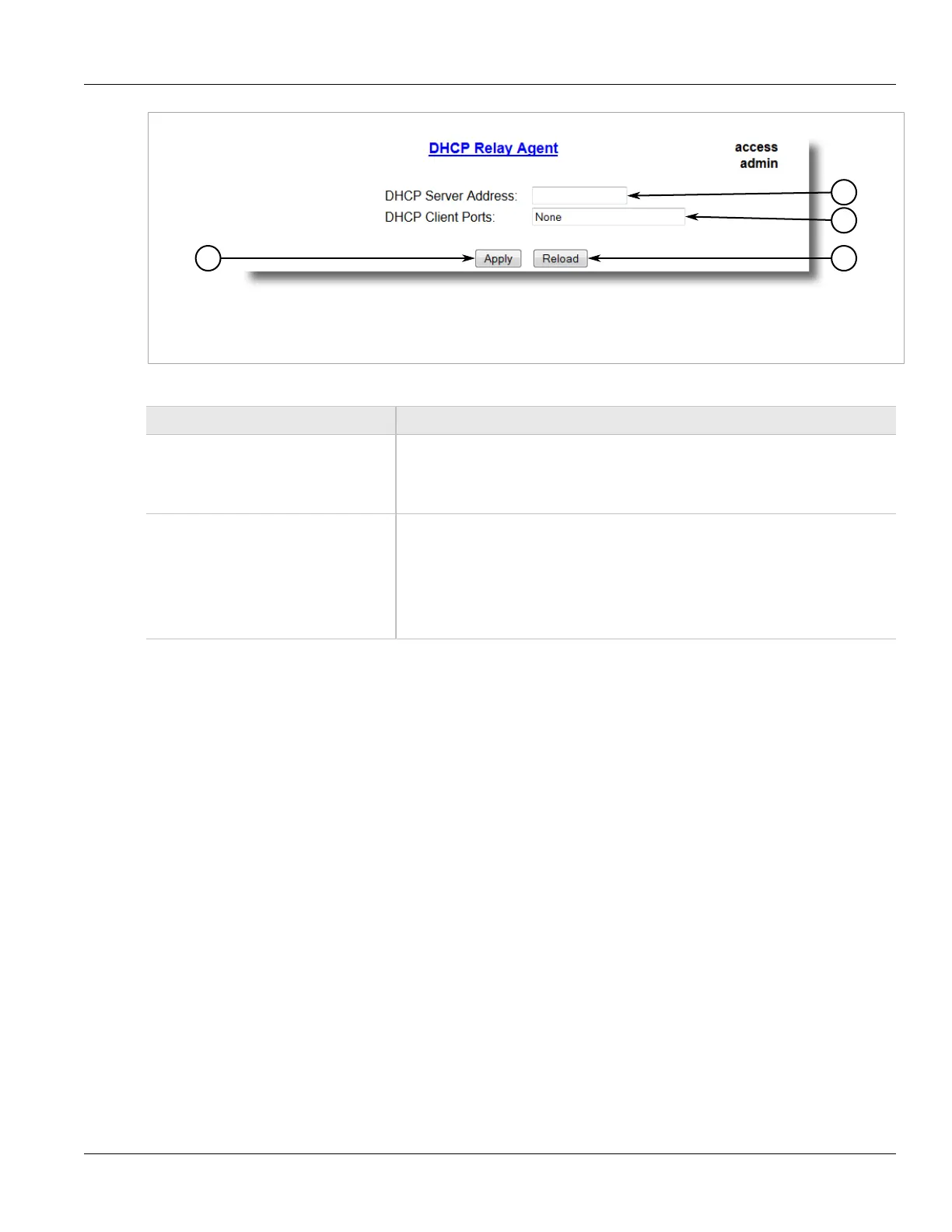
Figure 77: DHCP Relay Agent Form
1. DHCP Server Address Box 2. DHCP Client Ports 3. Apply Button 4. Reload Button
2. Configure the following parameter(s) as required:
Parameter Description
DHCP Server Address Synopsis: ###.###.###.### where ### ranges from 0 to 255
Default:
This parameter specifies the IP address of the DHCP server to which DHCP queries will
be forwarded from this relay agent.
DHCP Client Ports Synopsis: Any combination of numbers valid for this parameter
Default: None
This parameter specifies ports where DHCP clients are connected.
Examples:
• All - all ports of the switch can have DHCP clients connected.
• 2,4-6,8 - ports 2,4,5,6 and 8 can have DHCP clients connected
3. Click Apply.
Section 5.2
Managing Virtual LANs
A Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN) is a group of devices on one or more LAN segments that communicate as if
they were attached to the same physical LAN segment. VLANs are extremely flexible because they are based on
logical connections, rather than physical connections.
When VLANs are introduced, all traffic in the network must belong to one VLAN or another. Traffic on one VLAN
cannot pass to another, except through an inter-network router or Layer 3 switch.
VLANs are created in three ways:
• Explicitly
Static VLANs can be created in the switch. For more information about static VLANs, refer to Section 5.2.5,
“Managing Static VLANs”.
• Implicitly
When a VLAN ID (VID) is set for a port-based VLAN, static MAC address or IP interface, an appropriate VLAN
is automatically created if it does not yet exist.
• Dynamically
 Loading...
Loading...