Basics of communication with Industrial Ethernet
1.5 Wireless LAN
Industrial Ethernet
54 System Manual, 09/2019, C79000-G8976-C242-10
The IEEE 802.11 group
Under the project number "802", a number of working groups were given the task of
developing standards for setting up and operating networks. A known example is the "802.3"
working group that is concerned with the standards for Ethernet connections.
The "802.11" working group concentrates on the specification for wireless LAN, the IEEE
802.11 standard. The most important extensions of the standard are 802.11b, 802.11g,
802.11n, 802.11ac and 802.11ax.
"802.11" standards
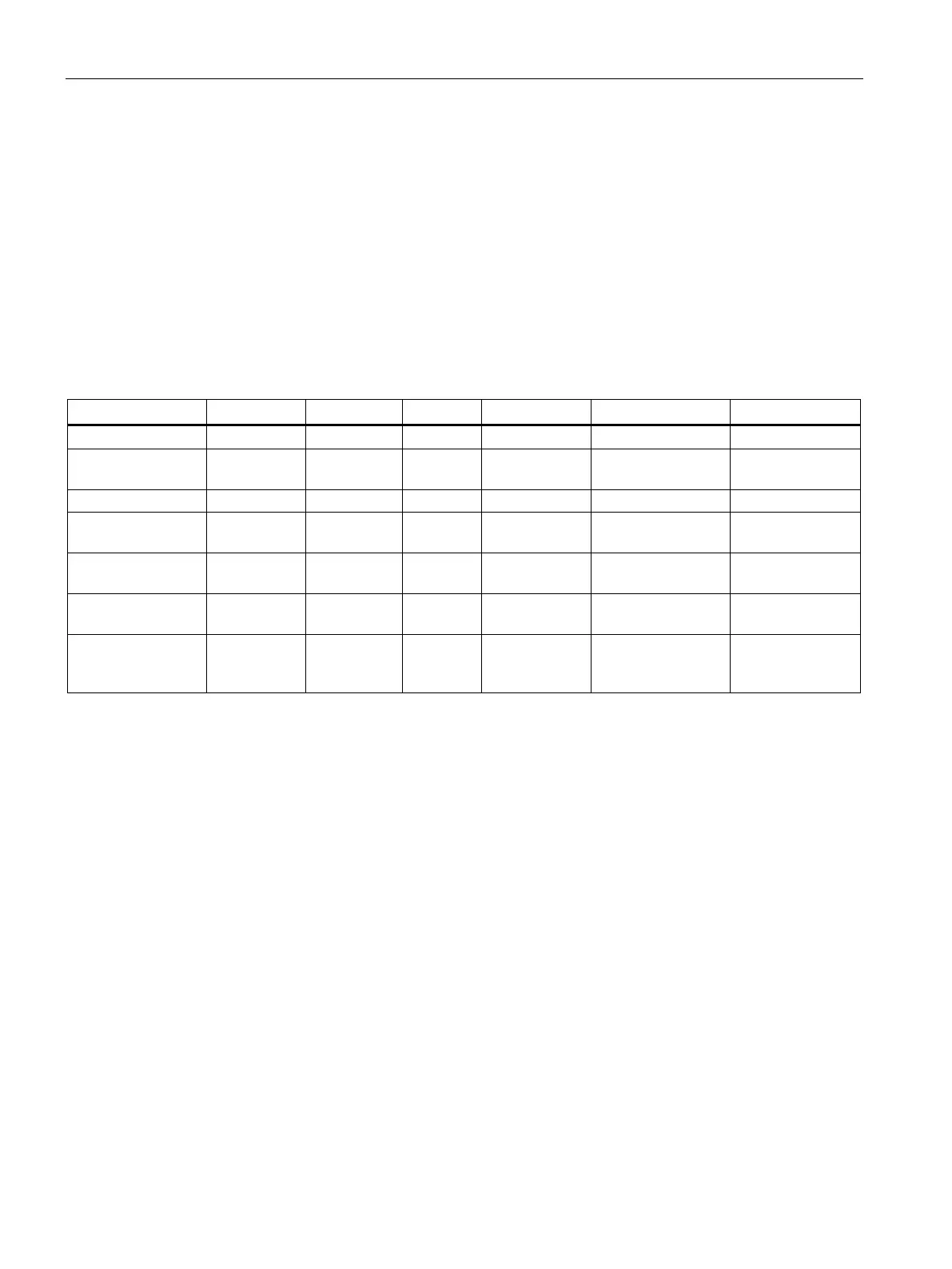
The following table provides an overview of the features of the individual standards:
Frequency band 5 GHz 2.4 GHz 2.4 GHz 2.4 GHz + 5
GHz
5 GHz 2.4 GHz + 5 GHz
Gross data rate 54 Mbps Max.
54 Mbps 600 Mbps 1733 Mbps (max.
19.2 Gbps
Modulation proce-
OFDM DSSS OFDM OFDM SC-OFDM SC-OFDMA
Transmission sys-
SISO SISO SISO SU-MIMO MU-MIMO (down-
MU-MIMO (down-
Max. number of
antennas on sender
and receiver end
1x1 1x1 1x1 4x4 8x8 4x4
- direct sequence spread spectrum
- orthogonal frequency-division multiplex
-OFDM - single carrier orthogonal frequency-division multiplex
- orthogonal frequency-division multiple access
- Single Input Single Output
- Multiple Input Multiple Output
-MIMO - Single-User MIMO
MU-MIMO - Multi-User MIMO
Expansions of the 802.11 standard include the following:
● 802.11 "e": Introduces QoS to provide better support for real-time applications (VoIP,
streaming),
● 802.11 "i": Replaces the no longer tenable WEP encryption mechanism with WPA or
WPA2.
● 802.11 "p": Introduces WLAN technology for motor vehicles with which an interface for
applications involving intelligent traffic systems is created.

 Loading...
Loading...


















