CPU Memory: Data Types and Addressing Modes
5-3
S7-200 Programmable Controller System Manual
A5E00066097-02
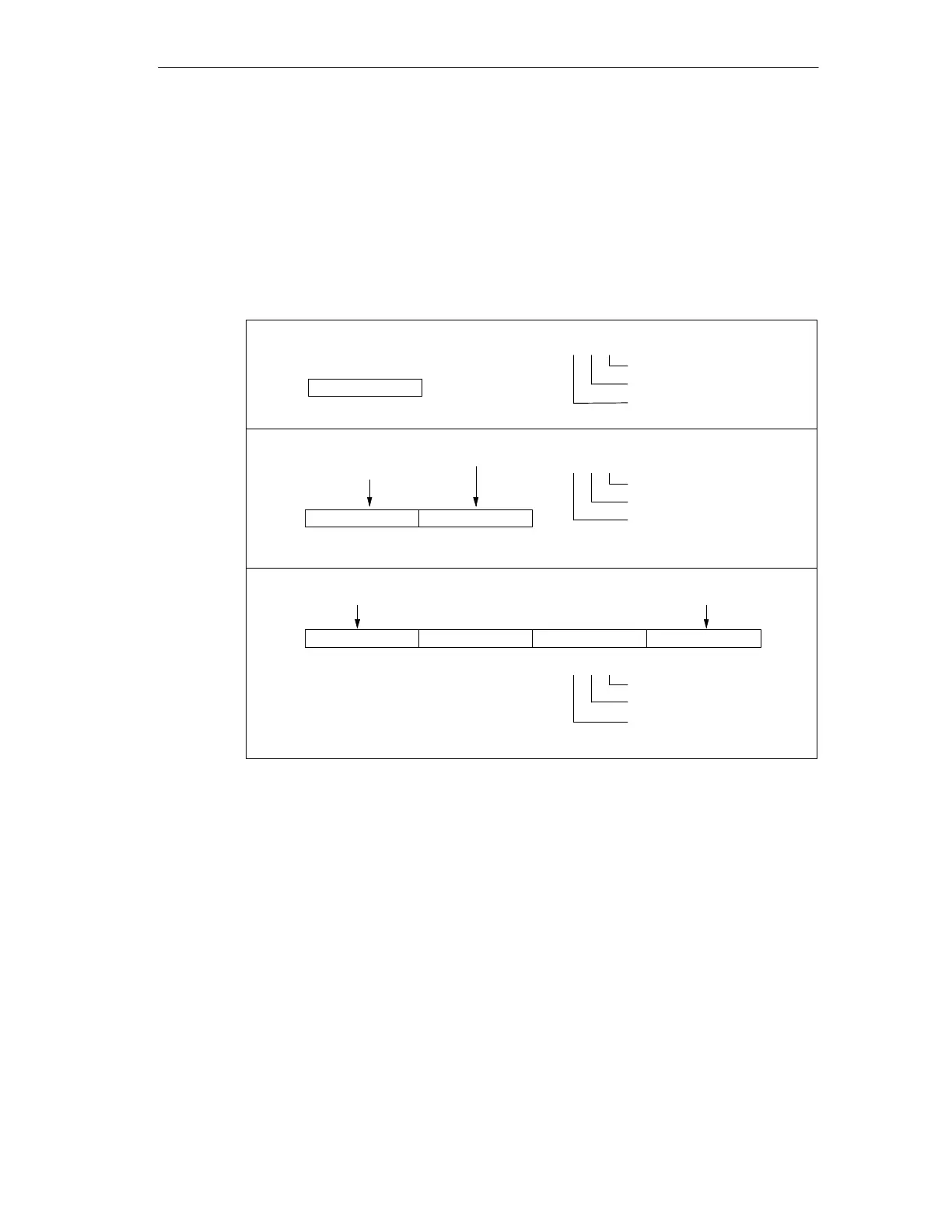
You can access data in many CPU memory areas (V, I, Q, M, S, L, and SM) as
bytes, words, or double words by using the byte-address format. To access a byte,
word, or double word of data in the CPU memory, you must specify the address in
a way similar to specifying the address for a bit. This includes an area identifier,
data size designation, and the starting byte address of the byte, word, or
double-word value, as shown in Figure 5-2. Data in other CPU memory areas
(such as T, C, HC, and the accumulators) are accessed by using an address
format that includes an area identifier and a device number.
V B 100
Area identifier (V memory)
Access to a byte size
Byte address
70
VB100
MSB
LSB
V W 100
Area identifier (V memory)
Access to a word size
Byte address
VW100 VB100 VB101
15 8
MSB
70
LSB
V D 100
Area identifier (V memory)
Access to a double word size
Byte address
VD100
Most significant byte Least significant byte
VB100 VB103VB101 VB102
31 8
MSB
70
LSB
16 1524 23
Most significant byte
Least significant byte
VB100
MSB = most significant bit
LSB = least significant bit
Figure 5-2 Comparing Byte, Word, and Double-Word Access to the Same Address

 Loading...
Loading...











