SUBUL ACC, loc32
6-357
SUBUL ACC, loc32 Subtract Unsigned 32-bit Value
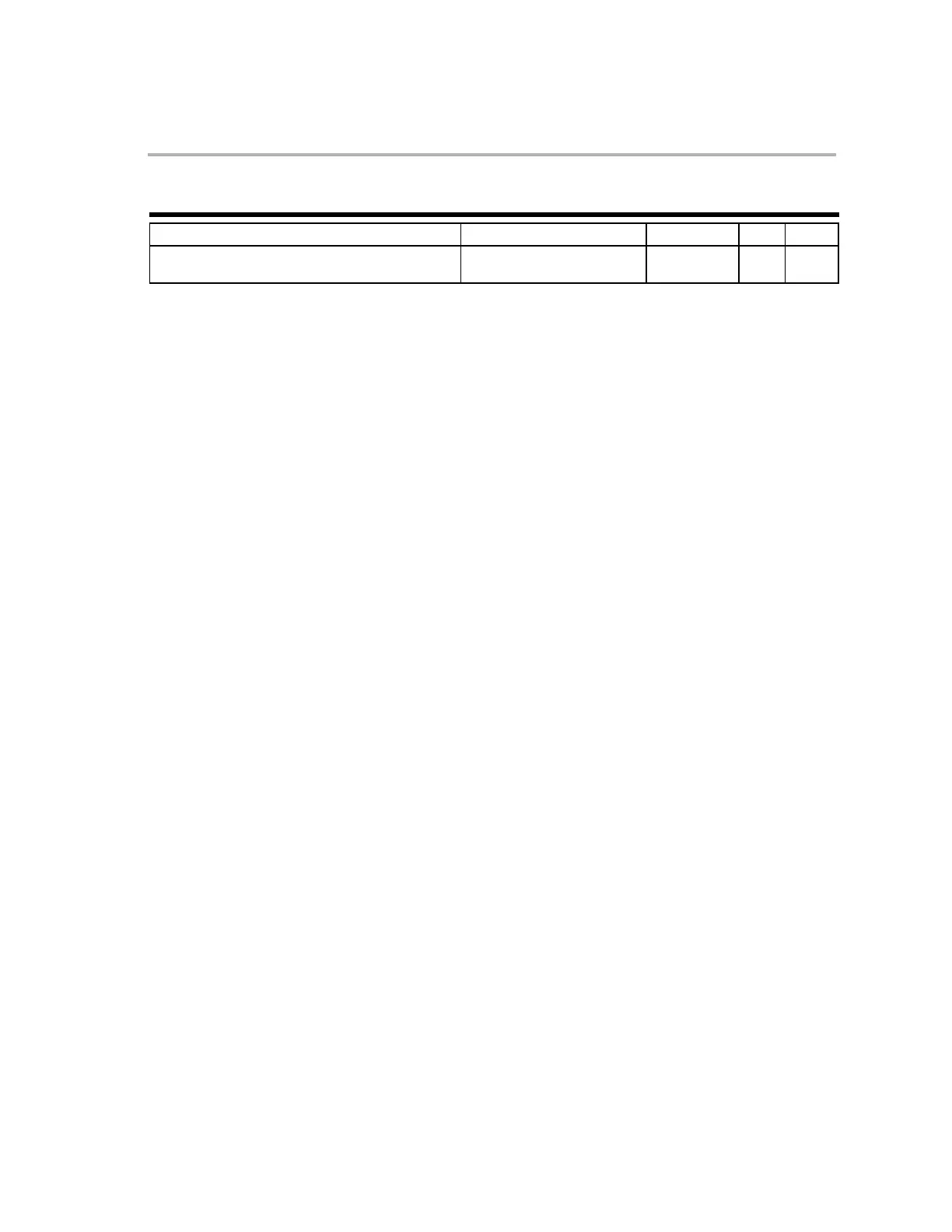
SYNTAX OPTIONS OPCODE OBJMODE RPT CYC
SUBUL ACC, loc32
0101 0110 0101 0101
0000 0000 LLLL LLLL
1 − 1
Operands loc32 Addressing mode (see Chapter 5)
ACC Accumulator register
Description Subtract from the ACC register the 32-bit the location pointed to by the
“loc32” addressing mode. The subtraction is treated as an unsigned SUBL
operation:
ACC = ACC − [loc32]; // unsigned subtraction
Note: The difference between a signed and unsigned 32-bit subtract is in the treatment of the
overflow counter (OVC). For a signed SUBL, the OVC counter monitors
positive/negative overflow. For an unsigned SUBL, the OVC unsigned (OVCU) counter
monitors the borrow.
Flags and
Modes
Z After the subtraction, the Z flag is set if the ACC value is zero, else Z is
cleared.
N After the subtraction, the N flag is set if bit 31 of the ACC is 1, else N is
cleared.
C If the subtraction generates a borrow, C is cleared; otherwise C is set.
V If an overflow occurs, V is set; otherwise V is not affected.
OVCU The overflow counter is decremented whenever a subtraction operation
generates an unsigned borrow. The OVM mode does not affect the OVCU
counter.
Repeat This instruction is not repeatable. If this instruction follows the RPT
instruction, it resets the repeat counter (RPTC) and executes only once.
Example
; Subtract two 64-bit values (VarA and VarB) and store result
; in VarC:
MOVL ACC,@VarA+0 ; Load ACC with contents of the low
; 32-bits of VarA
SUBUL ACC,@VarB+0 ; Subtract from ACC the contents of
; the low 32-bits of VarB
MOVL @VarC+0,ACC ; Store low 32-bit result into VarC
MOVL ACC,@VarA+2 ; Load ACC with contents of the high
; 32-bits of VarA
SUBBL ACC,@VarB+2 ; Subtract from ACC the contents of
; the high 32-bits of VarB with borrow
MOVL @VarC+2,ACC ; Store high 32-bit result into VarC
 Loading...
Loading...