Operation
9308−1/A1
Winterthur Gas & Diesel Ltd.
3/ 4
201
2.2 In-cylinder Pressure Evaluation
The compression pressure cannot be measured directly because of the combustion
and fuel injection that can occur before TDC.
In the ICC system, the compression pressure of each cycle is calculated with the
polynomial formula and the data of the piston position.
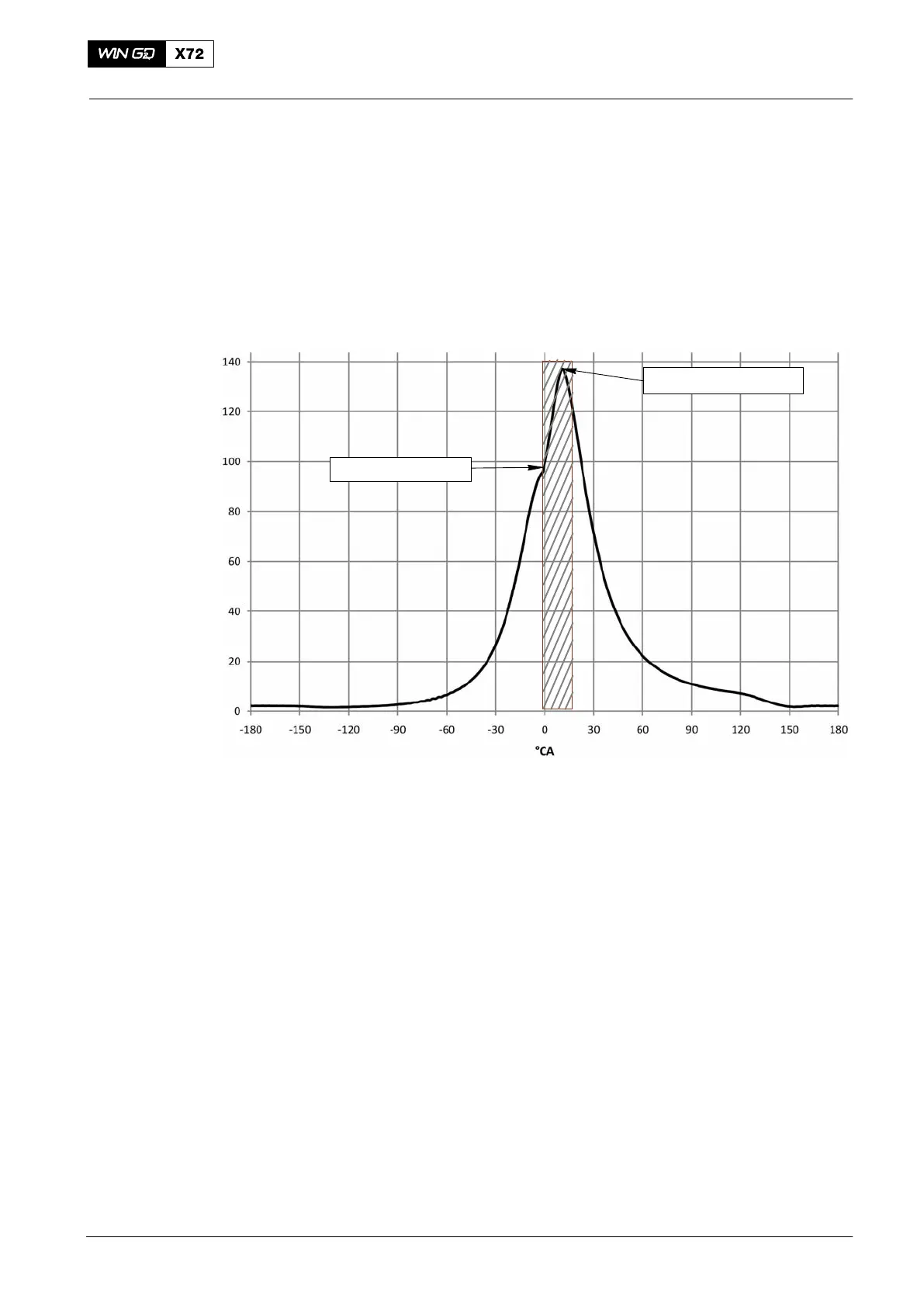
The peak firing pressure is the highest measured pressure value in the crank angle
range between the start of the injection and approximately 20°CA after TDC (see
Fig. 2).
Pressure at 0°CA
Peak Firing Pressure
Fig. 2: Cylinder Pressure Trace of a Two-stroke Engine
The pressure increase is the difference between the firing pressure and the
compression pressure (see Fig. 2). The ICC sets the pressure increase limit e.g. to
40 bar to prevent mechanical overload to the engine.
2.3 ICC - Installation and Control
The necessary firing pressure, referred to as the shop test performance, is
continuously adjusted (a reverse ISO correction) to the conditions at each operation
point of the engine. This makes sure that the firing pressure is always adjusted to the
correct value, related to the engine design. Because of the ICC, you can use the
maximum possible engine power without the risk of an overload.
The necessary temperature and pressure sensors are installed upstream of the
turbocharger compressor inlet and in the scavenge air receiver. The sensors are
connected to the IOM-10 (see Fig. 3).
Intelligent Combustion Control
2014
 Loading...
Loading...