Description
158 Instructions for use Oxylog 3000 plus SW 1.n
During the lower pressure level phase,
spontaneous breathing can be assisted by
Pressure Support PS. The steepness of the
pressure rise to
Δ
Psupp above PEEP is also
controlled by the Slope setting.
Weaning from controlled ventilation to fully
spontaneous breathing is achieved by a gradual
reduction of inspiratory pressure Pinsp and/or the
respiratory rate RR.
AutoFlow
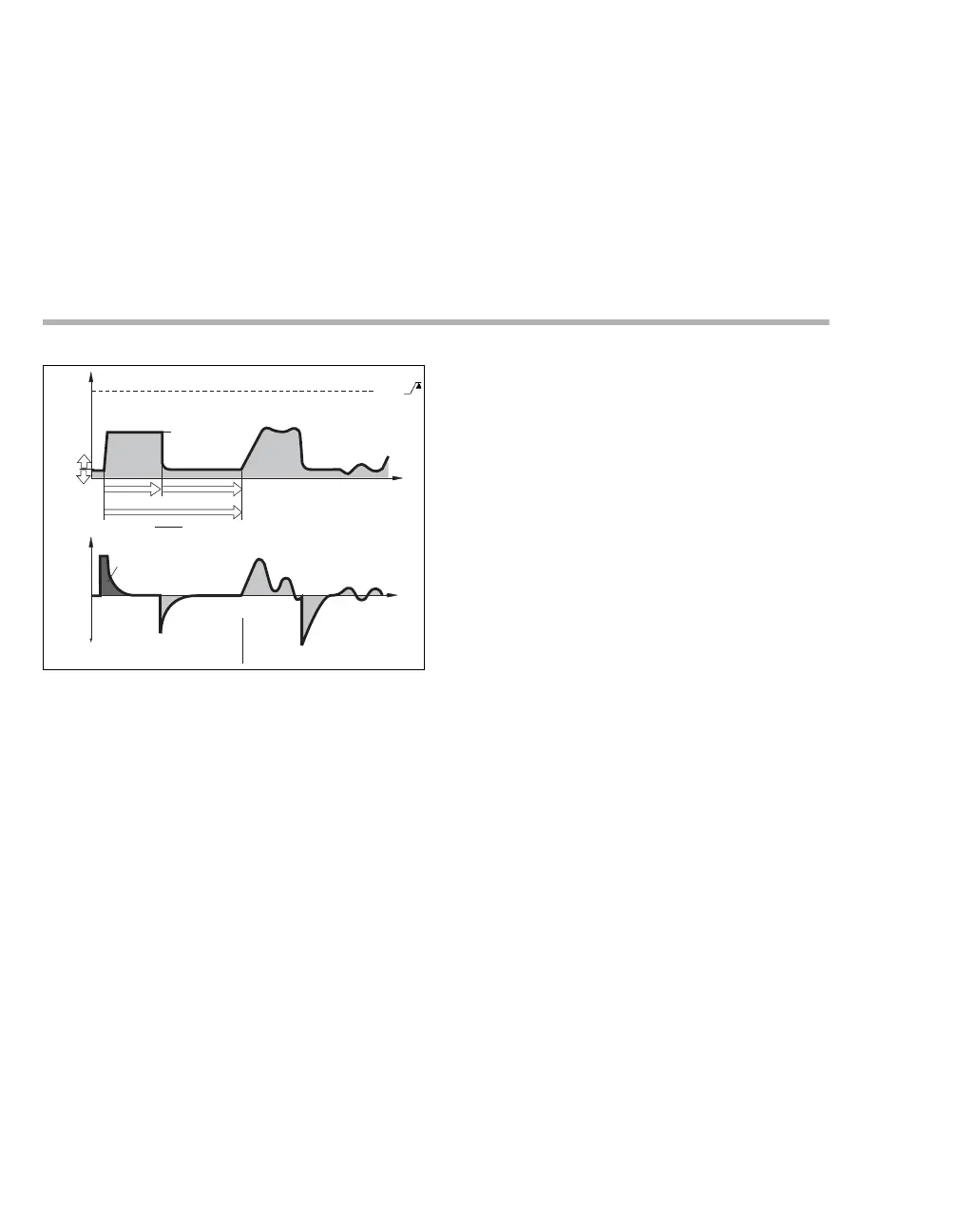
AutoFlow (AF) delivers the set tidal volume VT
using a decelerating flow pattern to achieve the
lowest peak airway pressure possible.
Oxylog 3000 plus determines the pressure
required to deliver the set tidal volume VT based on
lung characteristics such as resistance and
compliance, and the patient's spontaneous
breathing demand.
When the patient inhales, Oxylog 3000 plus
delivers an additional inspiratory flow.
The maximum inspiratory pressure in AutoFlow is
limited to:
– 5 mbar below Pmax.
The patient’s current condition must be considered
when setting Pmax, to avoid the possibility of
causing lung damage if the airway pressure
increases. Always set Pmax carefully in order to
limit the airway pressure in case of a reduced
compliance.
If the set tidal volume VT cannot be achieved and
the maximum inspiratory pressure is reached, the
alarm VT low, pressure limit is generated.
The minimum inspiratory pressure in AutoFlow is
limited to:
– 5 mbar above PEEP for non-triggered breaths;
– 0.1 mbar above PEEP for triggered breaths.
Typically, the selected inspiratory time Ti is much
longer than the lung filling time. The inspiratory
pressure Pinsp corresponds to the minimum value
calculated from the tidal volume VT and
compliance C of the lung. The inspiratory flow is
automatically controlled, so that there is no
pressure peak caused by the resistances of the
tube and the airways. With AutoFlow, the
inspiratory flow will adjust by a maximum of 3 mbar
from breath to breath.
If the tidal volume VT is reached (inspiratory
flow = 0) before the inspiratory time Ti has fully
elapsed, Oxylog 3000 plus ensures that the patient
can breathe during the remaining inspiratory time.
053
Paw
PEEP
t
t
RR
1
Tinsp Te
Pinsp = f (Vt, C)
Vt
without spontaneous breathing with spontaneous breathing
Flow
Paw

 Loading...
Loading...