EPSON WF-C5790/WF-C5790a/WF-C5710/ET-8700/WF-C5210/WF-C5290/WF-C5290a Revision A
Configuration and operating principles Operating principles 44
Confidential
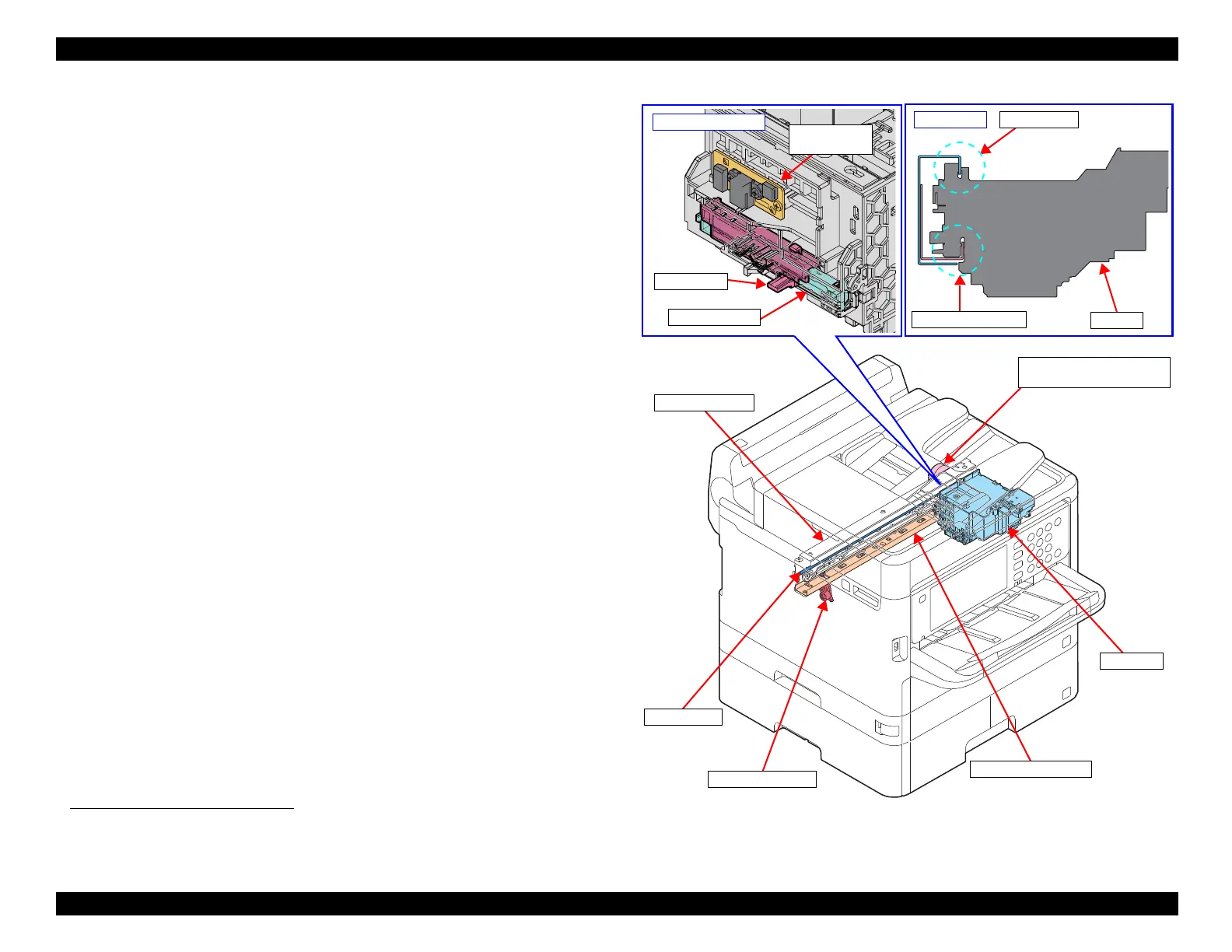
3.3.2 Carriage Mechanism
3.3.2.1 Overview
The carriage mechanism of this product consists of the CR Unit, CR Encoder Sensor,
CR Scale, CR Motor, CR Timing Belt, and etc. The Carriage Mechanism is a key
mechanism to ensure stable print quality because printing is performed by moving the
CR Unit from side to side.
As shown on the right, the CR Unit is placed on the CR Guide Frame being the
upperside of the assy held by the Main Frame. The CR Unit is attached to the CR
Timing Belt that is moved by the CR Motor so that the unit can move from side to side
to print. The position and speed of the CR Unit are always monitored by the CR
Encoder Sensor and CR Scale, and the CR Motor is controlled in accordance with the
information acquired by the CR Encoder Sensor.
The APG Mechanism adjusts the distance between the printhead nozzle and the paper
(PG: Platen Gap) as suitable, depending on the paper to be printed.
The APG Mechanism of this product is equipped with an APG Cam placed between
the CR Unit and CR Guide Frame, and simply changes PG
1
just by the movements of
the APG Trigger Lever and CR Unit.
Figure 3-23. Carriage Mechanism / APG Mechanism
1. A gap between the printhead surface and the paper surface. To ensure print quality, the two surfaces must be parallel,
and adequate control over the amount of ink fired from the printhead and the carriage movements is required based
on the PG appropriate to paper type.
Main Frame
CR Scale
APG Trigger Lever
CR Unit backside
APG Cam
CR Encoder
Sensor
APG Slider
CR Unit
CR Motor
(behind the Main Frame)
CR Guide Frame
Main Frame
CR Guide Frame
Cross-section
CR Unit
 Loading...
Loading...