ARP Configuration
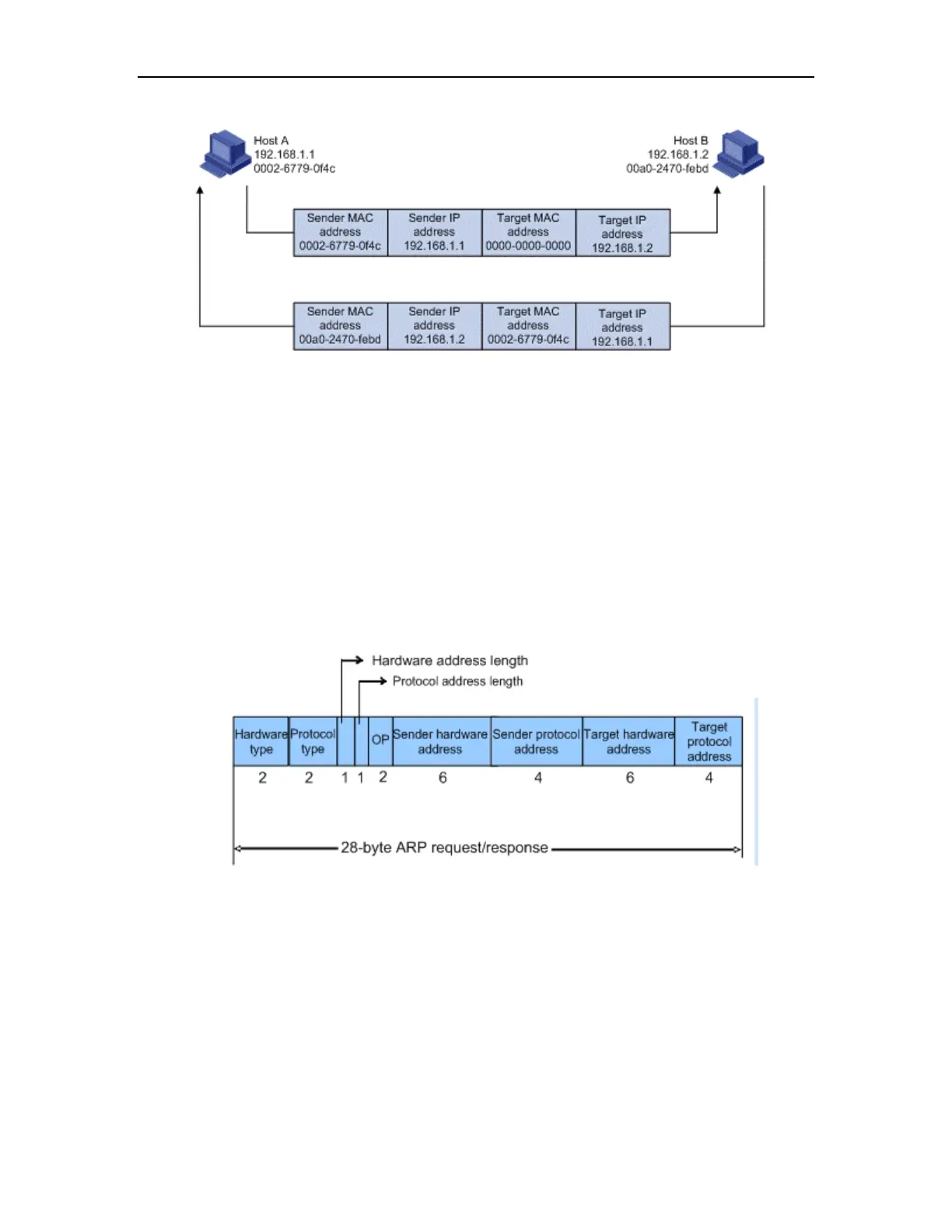
Figure 12-1 ARP address resolution process
When Host A and Host B are not on the same subnet, Host A first sends an ARP request to
the gateway. The destination IP address in the ARP request is the IP address of the gateway.
After obtaining the MAC address of the gateway from an ARP reply, Host A encapsulates the
packet and sends it to the gateway. Subsequently, the gateway broadcasts the ARP request,
in which the destination IP address is the one of Host B. After obtaining the MAC address of
Host B from another ARP reply, the gateway sends the packet to Host B.
12.1.2 ARP Message Format
Figure 12-2 ARP Message Format
The following explains the fields in Figure 12-2.
Hardware type: This field specifies the hardware address type. The value “1” represents
Ethernet.
Protocol type: This field specifies the type of the protocol address to be mapped. The
hexadecimal value “0x0800” represents IP.
Hardware address length and protocol address length: They respectively specify the
length of a hardware address and a protocol address, in bytes. For an Ethernet address, the

 Loading...
Loading...