174
Configuring an IPsec profile
An IPsec policy is uniquely identified by its name and sequence number. An IPsec policy group is a
collection of IPsec policies with the same name but different sequence numbers. In an IPsec policy
group, an IPsec policy with a smaller sequence number has a higher priority. After an IPsec policy
group is applied to an interface, for each packet arriving at the interface, the system checks the IPsec
policies of the IPsec policy group in the ascending order of sequence numbers. One IPsec tunnel will
be established for each data flow to be protected, and multiple IPsec tunnels might exist on an
interface.
An IPsec profile is similar to an IPsec policy. The difference is that an IPsec profile is uniquely
identified by its name and it does not support ACL configuration. An IPsec profile defines the IPsec
transform set to be used for protecting data flows, and specifies the parameters for IKE negotiation.
After an IPsec profile is applied to an IPsec tunnel interface, only one IPsec tunnel is set up to protect
all data flows that are routed to the tunnel.
IPsec profiles can be applied to only DVPN interfaces and IPsec tunnel interfaces. The IPsec tunnel
established using an IPsec profile protects all IP data routed to the tunnel interface.
Before configuring an IPsec profile, complete the following tasks:
• Configure the IPsec transform set for the IPsec profile to reference. For more information, see
"Configuring an IPsec profile."
• Config
ure the IKE peer for IKEv1 negotiation. For more information, see "Configuring an IKE
peer."
• Config
ure the IKEv2 profile for IKEv2 negotiation. For more information, see "Configuring an
IK
Ev2 profile."
The parameters for the local and remote ends must match.
During an IKE negotiation based on an IPsec profile, the source and destination addresses of the
IPsec tunnel interface are used as the local and remote addresses. The local-address and
remote-address commands configured for IKE negotiation do not take effect.
If you do not configure the destination address of the IPsec tunnel interface, the local peer can only
be an IKE negotiation responder; it cannot initiate an IKE negotiation.
DVPN is a technology when VPN is established between enterprise branches that use dynamic
addresses to access the public network. For more information about DVPN tunnel interface, see
HPE FlexNetwork MSR Router Series Comware 5 Layer 3
—
IP Services Configuration Guide.
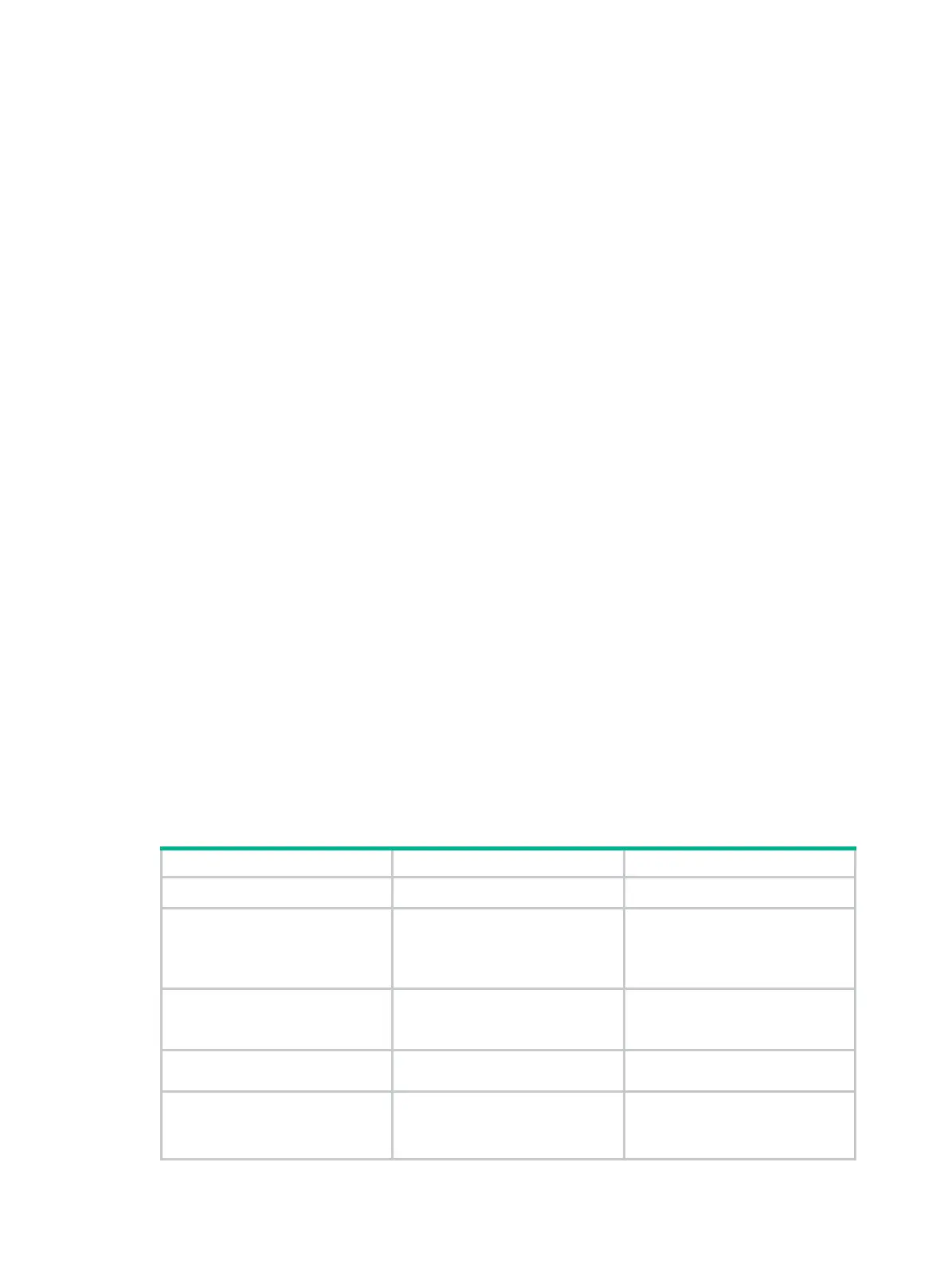
To configure an IPsec profile:
Step Command Remarks
1. Enter system view.
system-view
N/A
2. Create an IPsec profile and
enter its view.
ipsec
profile
profile-name By default, no IPsec profile exists.
3. Specify the IPsec transform
sets for the IPsec profile to
reference.
transform-set
transform-name&<1-6>
By default, an IPsec profile
references no IPsec transform
sets.
4. Specify the IKE peer for the
IPsec profile to reference.
ike-peer
peer-name [
primary
] N/A
5. Specify an IKEv2 profile for
the IPsec policy.
ikev2 profile
profile-name
Required for IKEv2 negotiation.
By default, an IPsec profile
references no IKEv2 profile.

 Loading...
Loading...




