213
tunnel:
local address: 1.1.1.1
remote address: 2.2.2.2
flow:
sour addr: 10.1.1.0/255.255.255.0 port: 0 protocol: IP
dest addr: 10.1.2.0/255.255.255.0 port: 0 protocol: IP
[inbound ESP SAs]
spi: 0x3D6D3A62(1030568546)
transform: ESP-ENCRYPT-DES ESP-AUTH-SHA1
in use setting: Tunnel
connection id: 1
sa duration (kilobytes/sec): 1843200/3600
sa remaining duration (kilobytes/sec): 1843199/3590
anti-replay detection: Enabled
anti-replay window size(counter based): 32
udp encapsulation used for nat traversal: N
[outbound ESP SAs]
spi: 0x553FAAE(89389742)
transform: ESP-ENCRYPT-DES ESP-AUTH-SHA1
in use setting: Tunnel
connection id: 2
sa duration (kilobytes/sec): 1843200/3600
sa remaining duration (kilobytes/sec): 1843199/3590
anti-replay detection: Enabled
anti-replay window size(counter based): 32
udp encapsulation used for nat traversal: N
Configuring aggressive mode IKE with NAT traversal
Network requirements
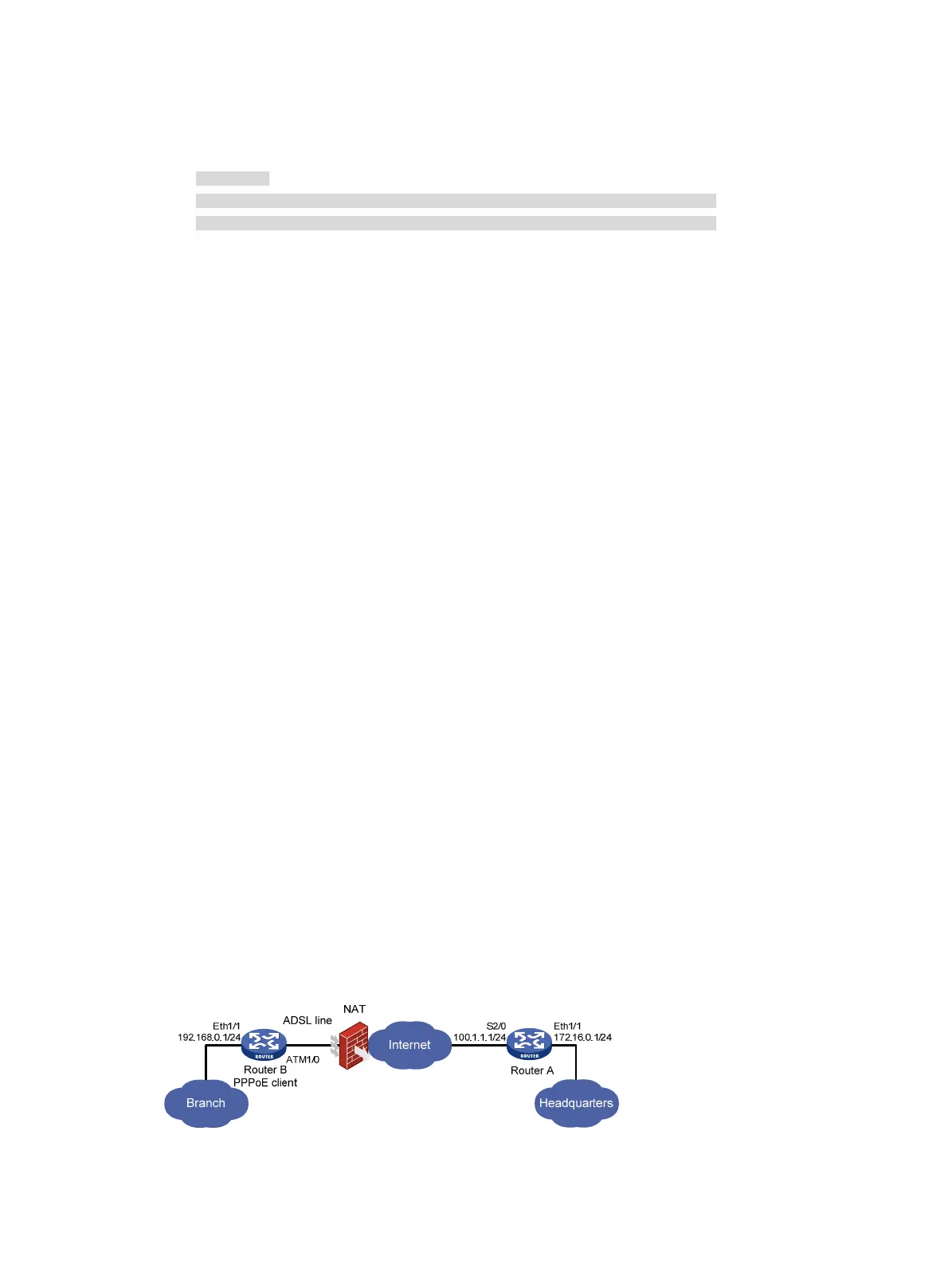
As shown in Figure 67, the branch and the headquarters connect to an ATM network through Router
B and Router A. Router B connects to the public network through an ADSL line and acts as the
PPPoE client. The interface connecting to the public network uses a private address dynamically
assigned by the ISP. Router A uses a fixed public IP address for the interface connected to the public
network.
Configure IPsec tunnels between Router A and Router B to protect traffic between the branch and its
headquarters. Use IKE to establish the IPsec tunnels.
Figure 67 Network diagram

 Loading...
Loading...




