189
Configuring IPsec with IPsec tunnel interfaces
Network requirements
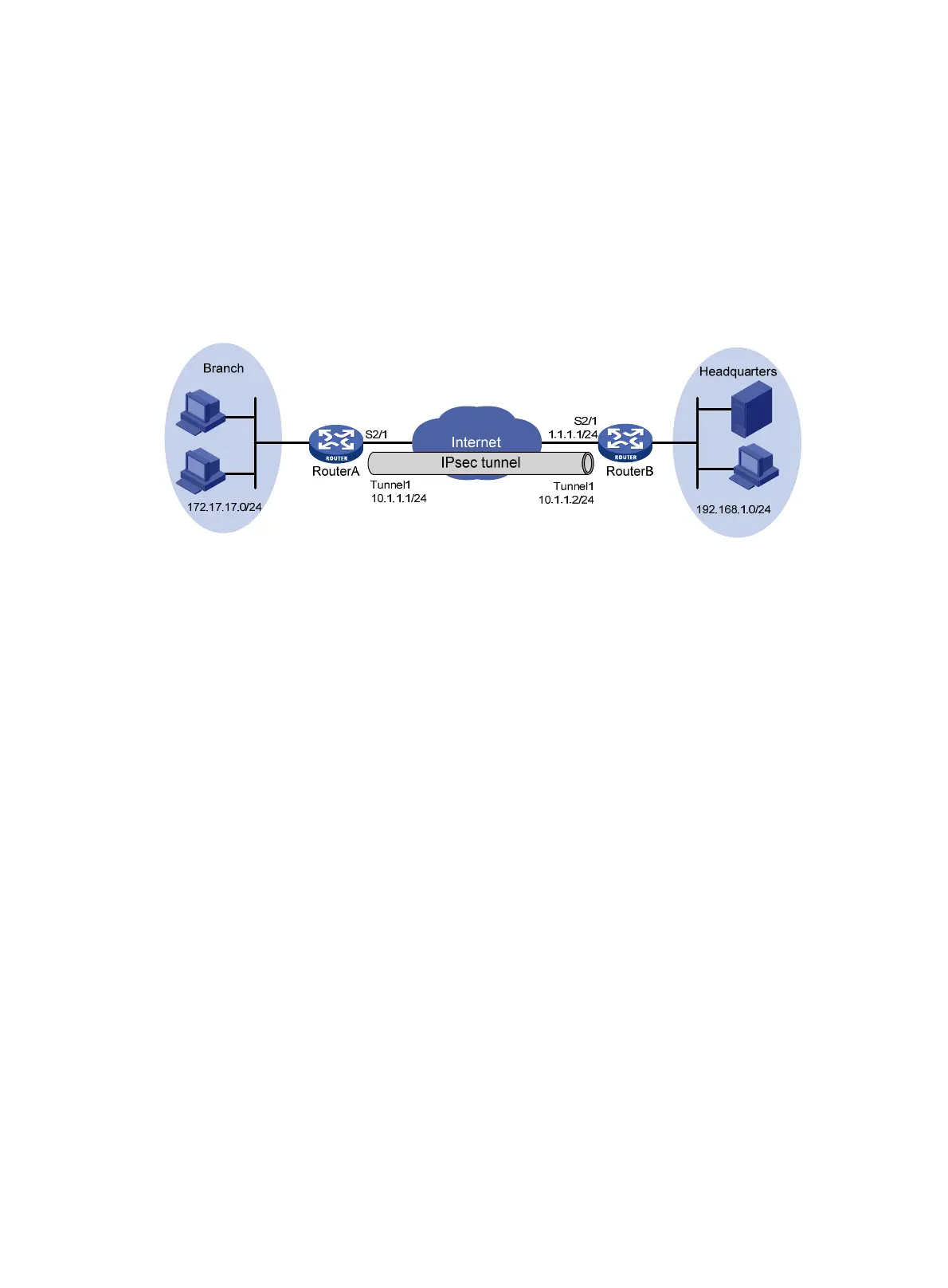
As shown in Figure 61, the gateway of the branch accesses the Internet through a dial-up line and
obtains the IP address dynamically. The headquarters accesses the Internet by using a fixed IP
address.
Configure an IPsec tunnel to protect the traffic between the branch and the headquarters. Make sure
that the IPsec configuration of the headquarters' gateway remains relatively stable despite of
changes of the branch's private IP address segment.
Figure 61 Network diagram
Configuration considerations
Configure an IPsec tunnel interface on each router and configure a static route on each router to
route the packets destined to the peer to the IPsec tunnel interface for IPsec protection.
Configuration procedure
1. Configure Router A:
# Name the local gateway routera.
<RouterA> system-view
[RouterA] ike local-name routera
# Configure an IKE peer named atob. As the local peer obtains the IP address automatically,
set the IKE negotiation mode to aggressive.
[RouterA] ike peer atob
[RouterA-ike-peer-atob] exchange-mode aggressive
[RouterA-ike-peer-atob] pre-shared-key simple aabb
[RouterA-ike-peer-atob] id-type name
[RouterA-ike-peer-atob] remote-name routerb
[RouterA-ike-peer-atob] quit
# Create an IPsec transform set named method1. This IPsec transform set uses the default
settings: the security protocol of ESP, the encryption algorithm of DES, and the authentication
algorithm of MD5.
[RouterA] ipsec transform-set method1
[RouterA-ipsec-transform-set-method1] transform esp
[RouterA-ipsec-transform-set-method1] esp encryption-algorithm des
[RouterA-ipsec-transform-set-method1] esp authentication-algorithm md5
[RouterA-ipsec-transform-set-method1] quit
# Create an IPsec profile named atob.
[RouterA] ipsec profile atob
# Configure the IPsec profile to reference the IKE peer.

 Loading...
Loading...




