450
{ If not, proceeds to step 4.
4. URPF checks whether the receiving interface matches the output interface of the matching FIB
entry:
{ If yes, the packet is forwarded.
{ If not, URPF checks whether the check mode is loose: if yes, the packet is forwarded, if not,
proceeds to step 5.
5. URPF checks whether the packet is permitted by the ACL:
{ If yes, the packet is forwarded (such a packet is displayed in the URPF information as a
"suppressed drop").
{ If not, the packet is discarded.
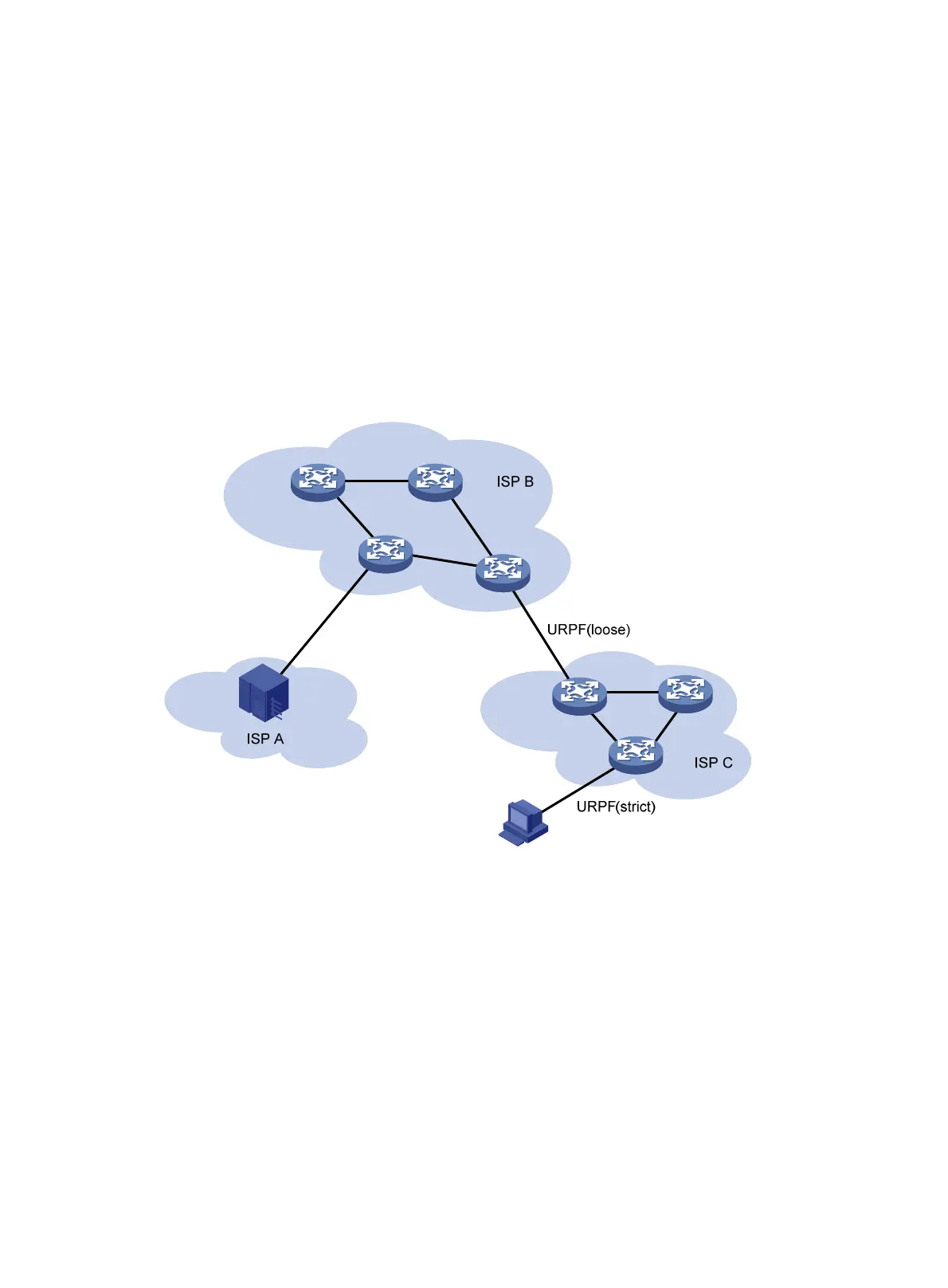
Network application
Figure 148 Network diagram
• Configure strict URPF check between an ISP network and a customer network, and loose
URPF check between ISPs.
• Configure ACLs for special packets or users.
Configuring URPF
You can configure URPF on a specific interface. URPF configured on an interface takes effect on the
interface only.
URPF checks only packets arriving at an enabled interface.
Do not configure the allow-default-route keyword for loose URPF check. Otherwise, URPF might
fail to work.
After configuring the URPF check on an interface, you can use the display ip interface command to
view statistics about packets discarded by URPF (displayed as "Drops" and "Suppressed drops").
 Loading...
Loading...




