385
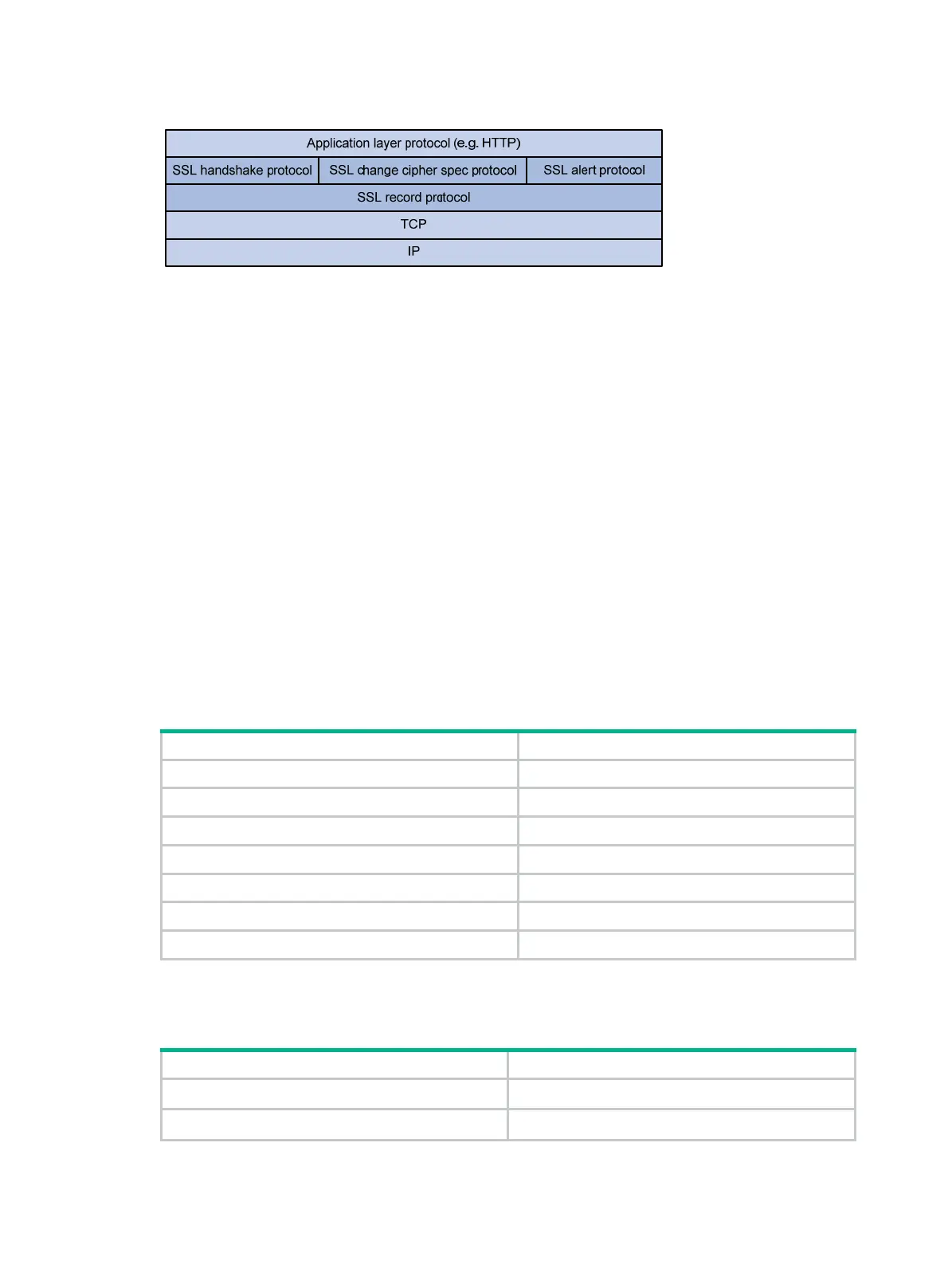
Figure 132 SSL protocol stack
• SSL record protocol—Fragments data to be transmitted, computes and adds MAC to the data,
and encrypts the data before transmitting it to the peer end.
• SSL handshake protocol—Negotiates the cipher suite to be used for secure communication
(including the symmetric encryption algorithm, key exchange algorithm, and MAC algorithm),
securely exchanges the key between the server and client, and implements identity
authentication of the server and client. Through the SSL handshake protocol, a session is
established between a client and the server. A session consists of a set of parameters, including
the session ID, peer certificate, cipher suite, and master secret.
• SSL change cipher spec protocol—Used for notification between the client and the server
that the subsequent packets are to be protected and transmitted based on the newly negotiated
cipher suite and key.
• SSL alert protocol—Enables the SSL client and server to send alert messages to each other.
An alert message contains the alert severity level and a description.
FIPS compliance
Table 20 shows the support of MSR routers for the FIPS mode that complies with NIST FIPS 140-2
requirements. Support for features, commands, and parameters might differ in FIPS mode (see
"Configuring FIPS") and non-FIPS mode.
Table 20 Hardware and FIPS mode compatibility matrix
Hardware FIPS mode compatibility
MSR900 No
MSR93X No
MSR20-1X No
MSR20 Yes
MSR30 Yes (except the MSR30-16)
MSR50 Yes
MSR1000 Yes
Configuration task list
Task Remarks
Configuring an SSL server policy
Required.
Configuring an SSL client policy
Optional.

 Loading...
Loading...




