252
Displaying and maintaining PKI
Task Command Remarks
Display the contents or request
status of a certificate.
display pki certificate
{ {
ca
|
local
}
domain
domain-name |
request-status
} [
|
{
begin
|
exclude
|
include
}
regular-expression ]
Available in any view.
Display CRLs.
display pki crl domain
domain-name [
|
{
begin
|
exclude
|
include
}
regular-expression ]
Available in any view.
Display information about one or
all certificate attribute groups.
display pki certificate
attribute-group
{ group-name
|
all
} [
|
{
begin
|
exclude
|
include
} regular-expression ]
Available in any view.
Display information about
certificate access control policies.
display pki certificate
access-control-policy
{ policy-name |
all
} [
|
{
begin
|
exclude
|
include
}
regular-expression ]
Available in any view.
PKI configuration examples
The SCEP add-on is required when you use the Windows Server as the CA. In this case, when you
configure the PKI domain, you must use the certificate request from ra command to specify that
the entity requests a certificate from an RA.
The SCEP add-on is not required when RSA Keon is used. In this case, when configuring a PKI
domain, you need to use the certificate request from ca command to specify that the entity
requests a certificate from a CA.
Certificate request from an RSA Keon CA server
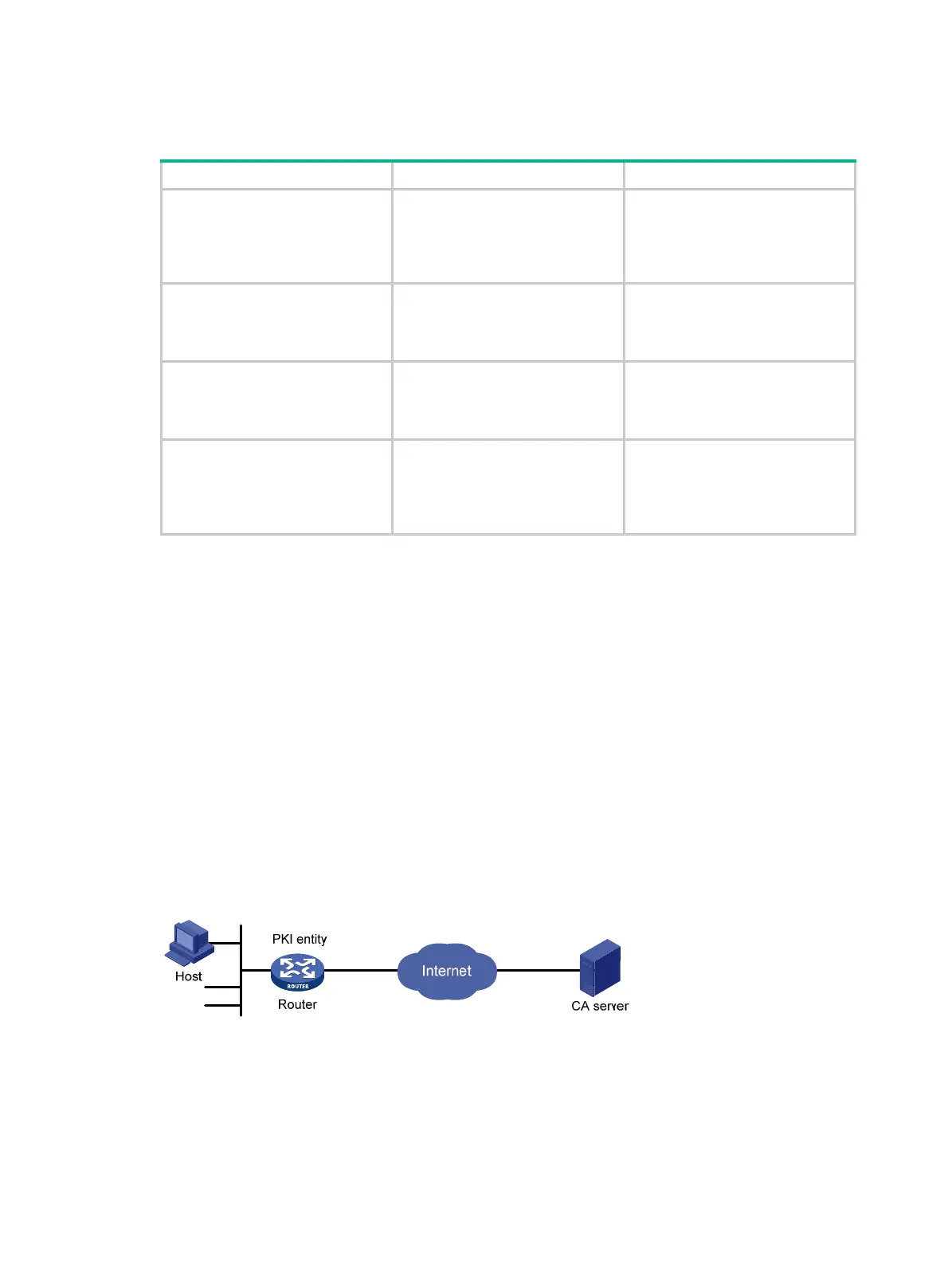
Network requirements
The device submits a local certificate request to the CA server. The device acquires the CRLs for
certificate verification.
Figure 72 Network diagram
Configuring the CA server
1. Create a CA server named myca:
In this example, you need to configure these basic attributes on the CA server at first:
{ Nickname—Name of the trusted CA.
{ Subject DN—DN information of the CA, including the Common Name (CN), Organization
Unit (OU), Organization (O), and Country (C).

 Loading...
Loading...




