264
Managing public keys
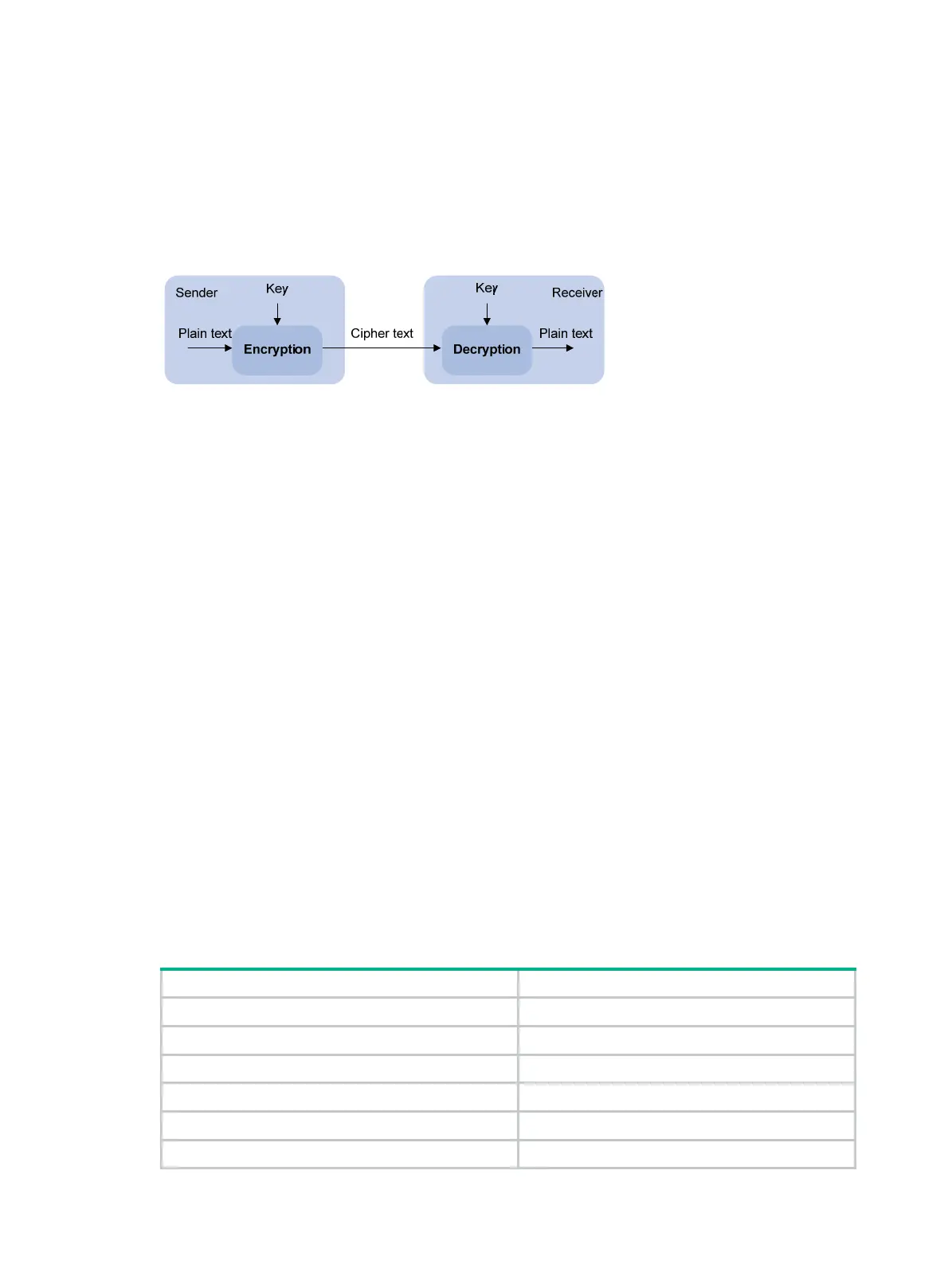
To protect data confidentiality during transmission, the data sender uses an algorithm and a key to
encrypt the plain text data before sending the data out. The receiver uses the same algorithm with
the help of a key to decrypt the data, as shown in Figure 76.
Figure 76
Encryption and decryption
The keys that participate in the conversion between plain text and cipher text can be the same or
different, dividing the encryption and decryption algorithms into the following types:
• Symmetric key algorithm—The keys for encryption and decryption are the same.
• Asymmetric key algorithm—The keys for encryption and decryption are different. One is the
public key, and the other is the private key. The information encrypted with the public key can
only be decrypted with the corresponding private key, and vice versa. The private key is kept
secret, and the public key can be distributed widely. The private key cannot be practically
derived from the public key. Asymmetric key algorithms include RSA and DSA.
The asymmetric key algorithms can be used for the following purposes:
• To encrypt and decrypt data—Any public key receiver can use the public key to encrypt
information, but only the private key owner can decrypt the information. This mechanism
ensures confidentiality. Only RSA can be used for data encryption and decryption.
• To authenticate a sender—Also called "digital signature." The key owner uses the private key
to "sign" information to be sent, and the receiver decrypts the information with the sender's
public key to verify information authenticity. RSA and DSA can be used for digital signature.
Asymmetric key algorithms are widely used in various applications. For example, SSH, SSL, and PKI
use the algorithms for digital signature. For information about SSH, SSL, and PKI, see "Configuring
SSH," "Configuring SSL," and "Configuring PKI."
FIPS compliance
Table 15 shows the support of MSR routers for the FIPS mode that complies with NIST FIPS 140-2
requirements. Support for features, commands, and parameters might differ in FIPS mode (see
"Configuring FIPS") and non-FIPS mode.
Table 15 Hardware and FIPS mode compatibility matrix
Hardware FIPS mode compatibility
MSR900 No
MSR93X No
MSR20-1X No
MSR20 Yes
MSR30 Yes (except the MSR30-16)
MSR50 Yes

 Loading...
Loading...




