405
Configuring IP source guard
Overview
IP source guard is intended to improve port security by blocking illegal packets. For example, it can
prevent invalid hosts from using a valid IP address to access the network.
IP source guard can filter packets according to the packet source IP address, source MAC address,
and VLAN tag. It supports these types of binding entries:
• IP-port binding entry
• MAC-port binding entry
• IP-MAC-port binding entry
• IP-VLAN-port binding entry
• MAC-VLAN-port binding entry
• IP-MAC-VLAN-port binding entry
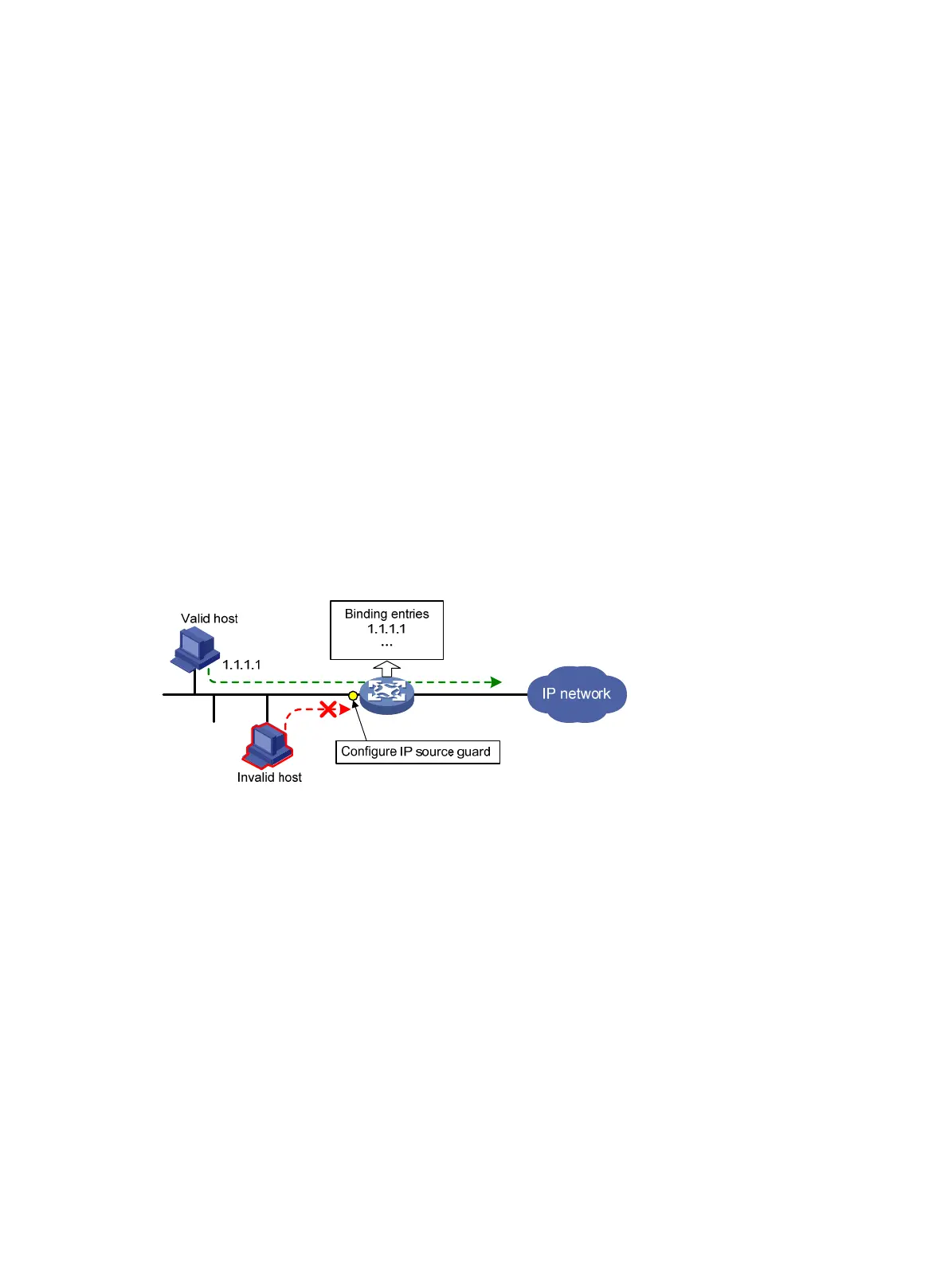
After receiving a packet, an IP source guard-enabled port obtains the key attributes (source IP
address, source MAC address and VLAN tag) of the packet and then looks them up in the IP source
guard binding entries. If there is a match, the port forwards the packet. Otherwise, the port discards
the packet, as shown in Figure 138.
Figure 138
Diagram for the IP source guard function
A binding entry can be statically configured or dynamically added.
Static IP source guard binding entries
A static IP source guard binding entry is configured manually. It is suitable for scenarios where few
hosts exist on a LAN and their IP addresses are manually configured. For example, you can
configure a static binding entry on a port that connects a server. This binding allows the port to
receive packets from and send packets to only the server.
A static IP source guard binding entry binds an IP address, MAC address, VLAN, or any combination
of the three with a port. Such an entry takes effect on only the specified port. A port forwards a packet
only when the IP address, MAC address, and VLAN tag (if any) of the packet all match those in a
static binding entry on the port. All other packets will be dropped.
IP source guard uses static IPv4 source guard binding entries on a port to filter IPv4 packets
received by the port.

 Loading...
Loading...




