78
802.1X overview
802.1X is a port-based network access control protocol initially proposed by the IEEE 802 LAN/WAN
committee for securing wireless LANs (WLANs), and it has also been widely used on Ethernet
networks for access control.
802.1X controls network access by authenticating the devices connected to 802.1X-enabled LAN
ports.
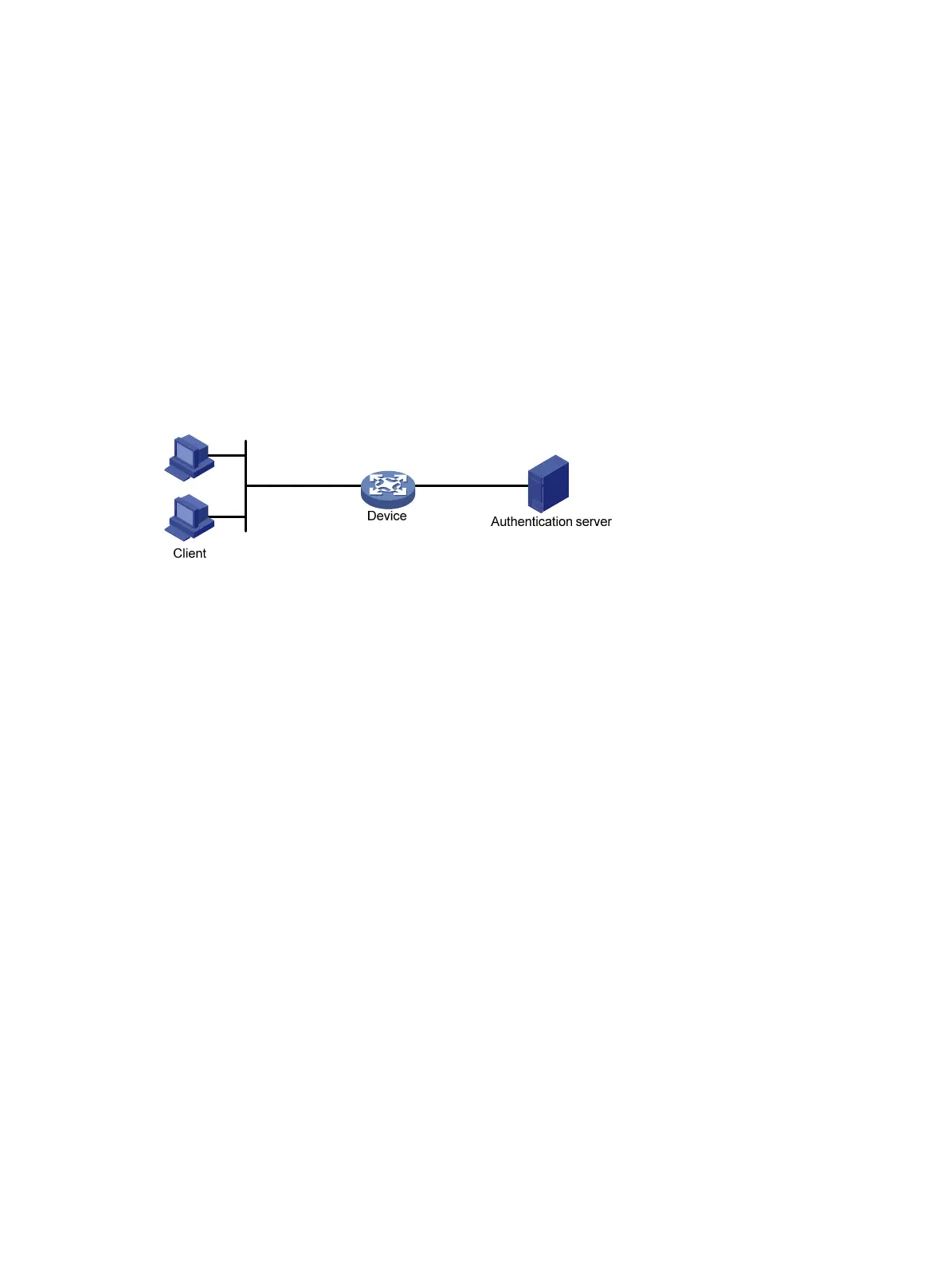
802.1X architecture
802.1X operates in the client/server model. It comprises three entities: the client (the supplicant), the
network access device (the authenticator), and the authentication server.
Figure 33 802.1X architecture
• Client—A user terminal seeking access to the LAN. It must have 802.1X software to
authenticate to the network access device.
• Network access device—Authenticates the client to control access to the LAN. In a typical
802.1X environment, the network access device uses an authentication server to perform
authentication.
• Authentication server—Provides authentication services for the network access device. The
authentication server authenticates 802.1X clients by using the data sent from the network
access device, and returns the authentication results for the network access device to make
access decisions. The authentication server is typically a Remote Authentication Dial-in User
Service (RADIUS) server. In a small LAN, you can also use the network access device as the
authentication server.
Controlled/uncontrolled port and port
authorization status
802.1X defines two logical ports for the network access port: controlled port and uncontrolled port.
Any packet arriving at the network access port is visible to both logical ports.
• Controlled port—Allows incoming and outgoing traffic to pass through when it is in the
authorized state, and denies incoming and outgoing traffic when it is in the unauthorized state,
as shown in Figure 34.
The controlled port is set in the authorized state if the client has passed
authentication, and in the unauthorized state, if the client has failed authentication.
• Uncontrolled port—Always open to receive and transmit EAPOL frames.

 Loading...
Loading...




