482
Configuring FIPS
Overview
Federal Information Processing Standards (FIPS) was developed by the National Institute of
Standard and Technology (NIST) of the United States. FIPS specifies the requirements for
cryptographic modules. FIPS 140-2 defines four levels of security, named "Level 1" to "Level 4" from
low to high. The device supports Level 2.
Unless otherwise noted, in this document the term "FIPS" refers to FIPS 140-2.
Hardware compatibility with FIPS mode
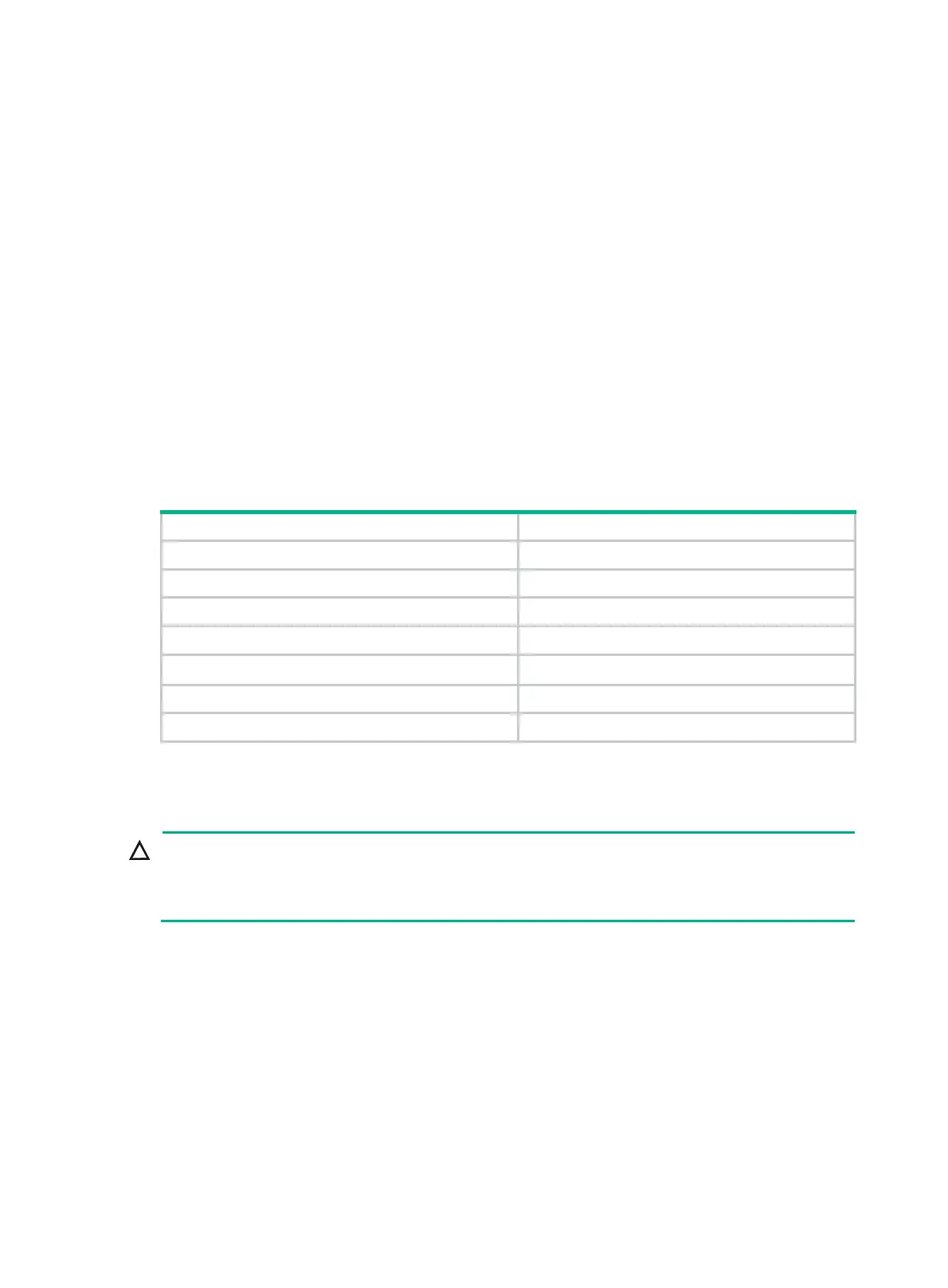
Table 24 shows the support of MSR routers for the FIPS mode that complies with NIST FIPS 140-2
requirements. Support for features, commands, and parameters might differ in FIPS mode and
non-FIPS mode.
Table 24 Hardware and FIPS mode compatibility matrix
Hardware FIPS mode compatibility
MSR900 No.
MSR93X No.
MSR20-1X No.
MSR20 Yes.
MSR30
Yes (except the MSR30-16).
MSR50 Yes.
MSR1000 Yes.
FIPS self-tests
CAUTION:
If the device reboots repeatedly, it might be caused by software failures or hardware damages.
Contact Hewlett Packard Enterprise Support to upgrade the software or repair the damaged
hardware.
When the device enters FIPS mode, power-up self-tests and conditional self-tests automatically run
to ensure the correct operation of cryptography modules. If either type of tests fails, the device will
restart.
Power-up self-tests
The power-up self-test, also called "known-answer test", examines the availability of FIPS-allowed
cryptographic algorithms. A cryptographic algorithm is run on data for which the correct output is
already known. The calculated output is compared with the known answer. If they are not identical,
the known-answer test fails.
The power-up self-test examines the cryptographic algorithms listed in Table 25:

 Loading...
Loading...




