285
In direct authentication, re-DHCP authentication, and cross-subnet authentication, the client's
IP address is used for client identification. After a client passes authentication, the access
device generates an ACL for the client based on the client's IP address to permit packets from
the client to go through the access port. Because no Layer 3 devices are present between the
authentication clients and the access device in direct authentication and re-DHCP
authentication, the access device can directly learn the clients' MAC addresses, and can
control the forwarding of packets from clients in a more granular way by also using the learned
MAC addresses.
Portal support for EAP
Only Layer 3 portal authentication that uses a remote portal server supports EAP authentication.
Authentication by using the username and password is less secure. Digital certificate authentication
is usually used to ensure higher security.
The Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) supports several digital certificate-based
authentication methods, for example, EAP-TLS. Working together with EAP, portal authentication
can implement digital certificate-based user authentication.
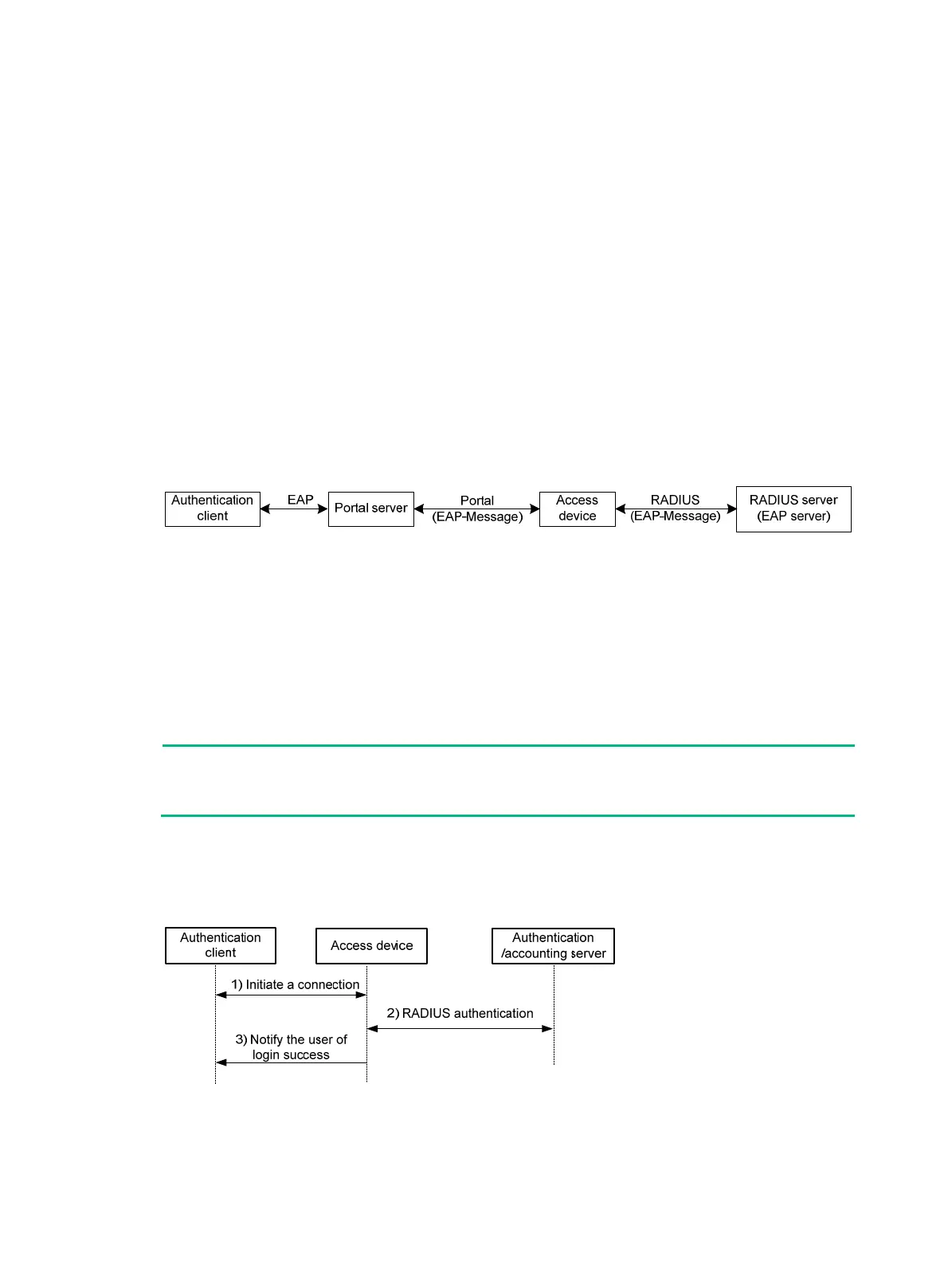
Figure 87 Portal support for EAP working flow diagram
As shown in Figure 87, the authentication client and the portal server exchange EAP authentication
packets. The portal server and the access device exchange portal authentication packets that carry
the EAP-Message attributes. The access device and the RADIUS server exchange RADIUS packets
that carry the EAP-Message attributes. The RADIUS server that supports the EAP server function
processes the EAP packets encapsulated in the EAP-Message attributes, and provides the EAP
authentication result. During the whole EAP authentication process, the access device does not
process the packets that carry the EAP-Message attributes but only transports them between the
portal server and the RADIUS server. Therefore, no additional configuration is needed on the access
device.
NOTE:
To use portal authentication that supports EAP, the portal server and client must be the HPE IMC
portal server and the HPE iNode portal client.
Layer 2 portal authentication process
Figure 88 Local Layer 2 portal authentication process

 Loading...
Loading...




