368 IBM Flex System V7000 Storage Node Introduction and Implementation Guide
The benefit of using a FlashCopy mapping with background copy enabled is that the target
volume becomes a real independent clone of the FlashCopy mapping source volume after the
copy is complete. When the background copy is disabled, the target volume only remains a
valid copy of the source data while the FlashCopy mapping remains in place. Copying only
the changed data saves your storage capacity (assuming it is thin provisioned and -rsize has
been correctly setup.)
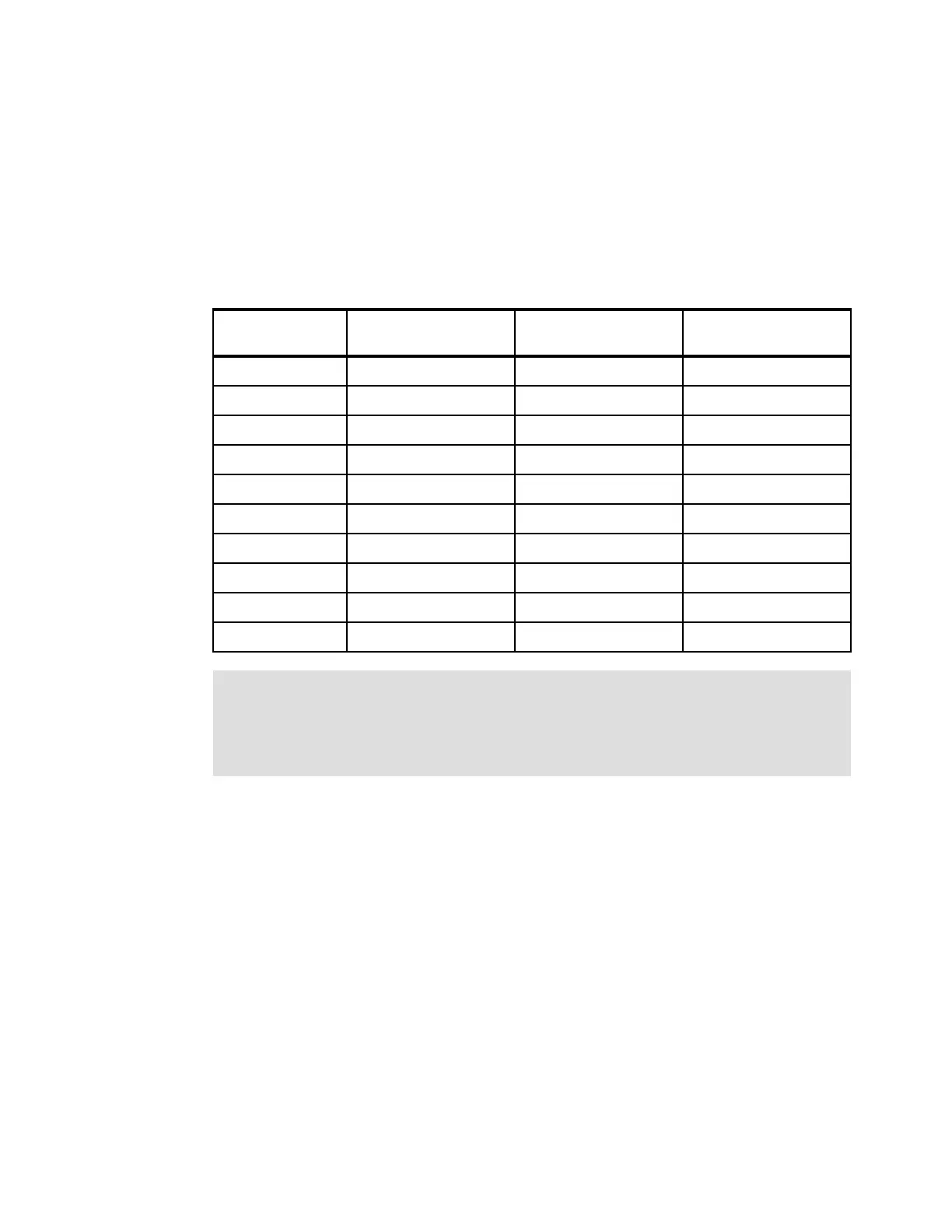
The relationship of the background copy rate value to the amount of data copied per second
is shown in Table 9-1.
Table 9-1 Background copy rate
Cleaning rate
The cleaning rate provides a method for FlashCopy copies with dependant mappings (either
multiple targets or cascaded) to be able to complete their background copies before their
source goes offline or is deleted after a stop has been issued.
When you create or modify a FlashCopy mapping, you can specify a cleaning rate for the
FlashCopy mapping that is independent of the background copy rate. The cleaning rate is
also defined as a value of 0 - 100, which has the same relationship to data copied per second
as the background copy rate (Table 9-1).
The cleaning rates controls the rate at which the cleaning process operates. The purpose of
the cleaning process is to copy (or flush) data from FlashCopy source volumes upon which
there are dependent mappings to their targets. For cascaded and multiple target FlashCopy,
the source might be a target for another FlashCopy target or even a source for a chain
(cascade) of FlashCopy mappings. The cleaning process must complete before the
FlashCopy mapping can go to the stopped state. This feature is the distinction between
stopping and stopped states which prevents data access interruption for dependent
mappings, when their source is issued a stop.
Copy / cleaning
rate values
Data copied per
second
Grains per second
(256 KB grain)
Grains per second
(64 KB grain)
1 - 10 128 KB 0.5 2
11 - 20 256 KB 1 4
21 - 30 512 KB 2 8
31 - 40 1 MB 4 16
41 - 50 2 MB 8 32
51 - 60 4 MB 16 64
61 - 70 8 MB 32 128
71 - 80 16 MB 64 256
81 - 90 32 MB 128 512
91 - 100 64 MB 256 1024
Data copy rate: The data copy rate remains the same regardless of the FlashCopy grain
size. The difference is the number of grains copied per second. The grain size can be
either 64 or 256 KB. The smaller size consumes more bitmap space and thus limits the
total amount of FlashCopy space possible, but might be more efficient regarding the
amount of data moved, depending on your environment.

 Loading...
Loading...











