372 IBM Flex System V7000 Storage Node Introduction and Implementation Guide
Prepared:
The consistency group is ready to start. While in this state, the target volumes of all
FlashCopy mappings in this consistency group are not accessible.
Copying:
At least one FlashCopy mapping in the consistency group is in the Copying state and no
FlashCopy mappings are in the Suspended state.
Stopping:
At least one FlashCopy mapping in the consistency group is in the Stopping state and no
FlashCopy mappings are in the Copying or Suspended state.
Stopped:
The consistency group is stopped because either you issued a command or an I/O
error occurred.
Suspended:
At least one FlashCopy mapping in the consistency group is in the Suspended state.
Empty:
The consistency group does not have any FlashCopy mappings.
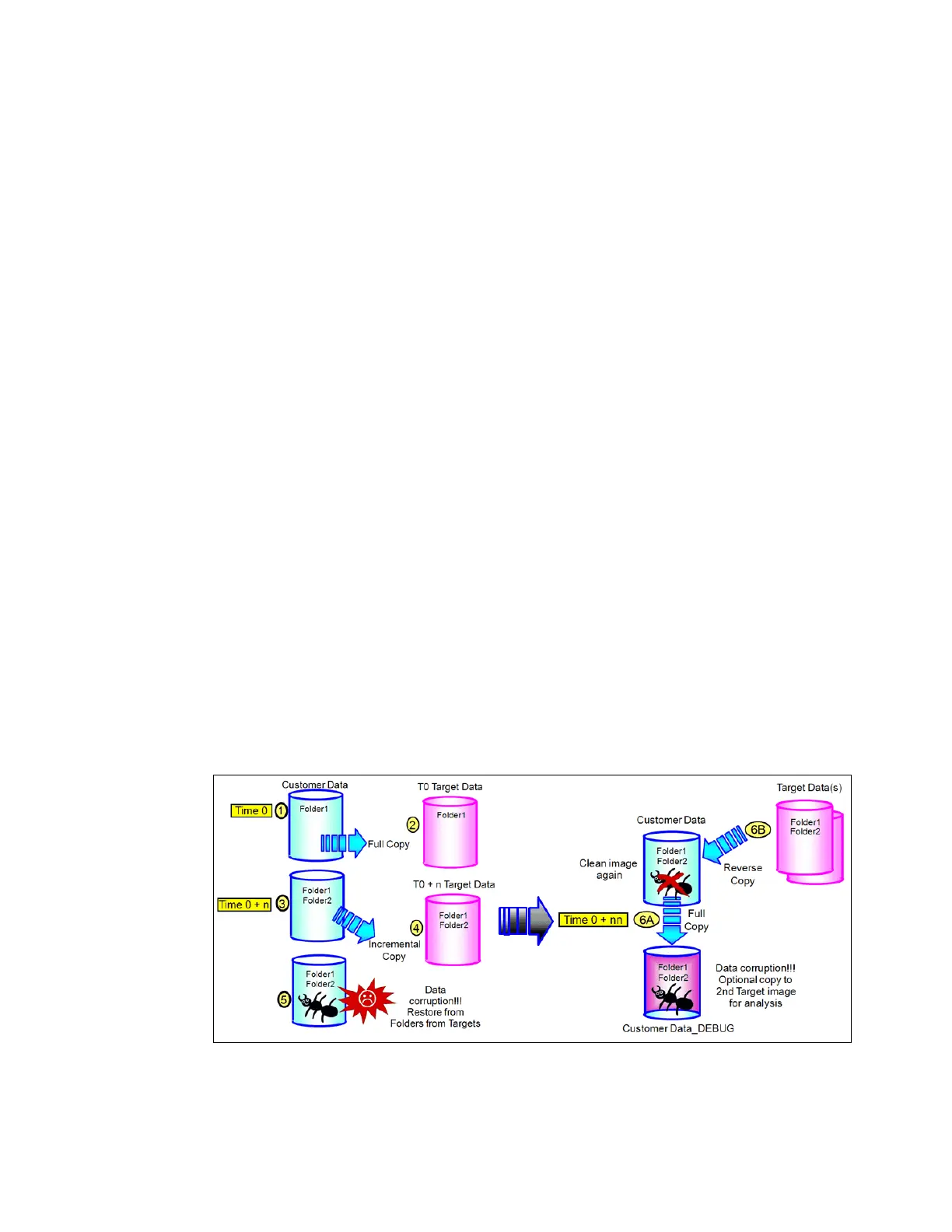
Reverse FlashCopy
Reverse FlashCopy enables FlashCopy targets to become restore points for the source
without breaking the FlashCopy relationship and without waiting for the original copy
operation to complete. It supports multiple targets and multiple rollback points.
A key advantage of Reverse FlashCopy is that it does not delete the original target, thus
allowing processes using the target, such as a tape backup, to continue uninterrupted.
You can also create an optional copy of the source volume that is made before starting the
reverse copy operation. This copy restores the original source data, which can be useful for
diagnostic purposes.
Figure 9-3 shows an example of a reverse FlashCopy scenario.
Figure 9-3 Reverse FlashCopy scenario

 Loading...
Loading...











