11-18
Automatic Calibration
Because light absorption by hemoglobin is wavelength dependent and because the mean
wavelength of LEDs varies, a monitor must know the mean wavelength of the sensor’s red LED
to accurately measure SpO
2
. During manufacturing, the mean wavelength of the red LED is
encoded in a resistor in the sensor. During monitoring, the monitor reads this resistor and selects
coefficients that are appropriate for the wavelength of that sensor’s red LED; these coefficients
are then used to determine SpO
2
.
This resistor is read when the monitor is turned on, periodically thereafter, and each time a new
sensor is connected. Additionally, to compensate for differences in tissue thickness, the intensity
of the sensor’s LEDs is adjusted automatically.
Functional versus Fractional Saturation
This monitor measures functional saturation — oxygenated hemoglobin expressed as a
percentage of the hemoglobin that can transport oxygen. It does not detect significant amounts of
dysfunctional hemoglobin, such as carboxyhemoglobin or methemoglobin. In contrast, some
instruments report fractional saturation — oxygenated hemoglobin expressed as a percentage of
all measured hemoglobin, including measured dysfunctional hemoglobins. To compare functional
saturation measurements to those from an instrument that measures fractional saturation,
fractional measurements must be converted as follows:
Fractional saturation
Functional saturation =
100 - (%carboxyhemoglobin + %methemoglobin)
×100
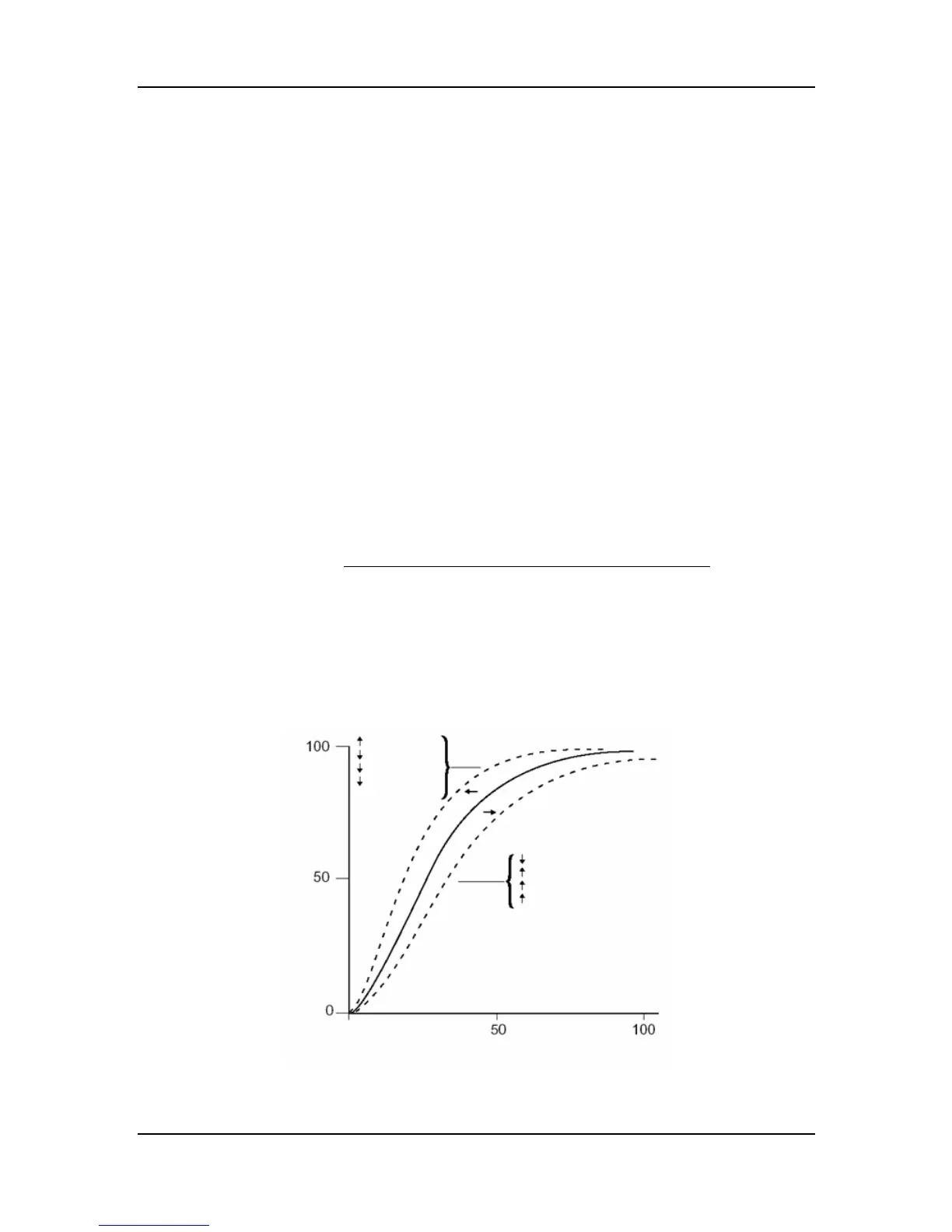
Measured versus Calculated Saturation
When saturation is calculated from a blood gas partial pressure of oxygen (PO
2
), the calculated
value may differ from the SpO
2
measurement of a monitor. This usually occurs because the
calculated saturation was not appropriately corrected for the effects of variables that shift the
relationship between PO
2
and saturation (Figure 11-8): pH, temperature, the partial pressure of
carbon dioxide (PCO
2
), 2,3-DPG, and fetal hemoglobin.
Figure 11-8 Oxyhemoglobin Dissociation Curve
Saturation (%)
SpO
2
%
Temperature
PCO2
2,3-DPG
PH
Temperature
PCO2
2,3-DPG
Fetal Hb
 Loading...
Loading...