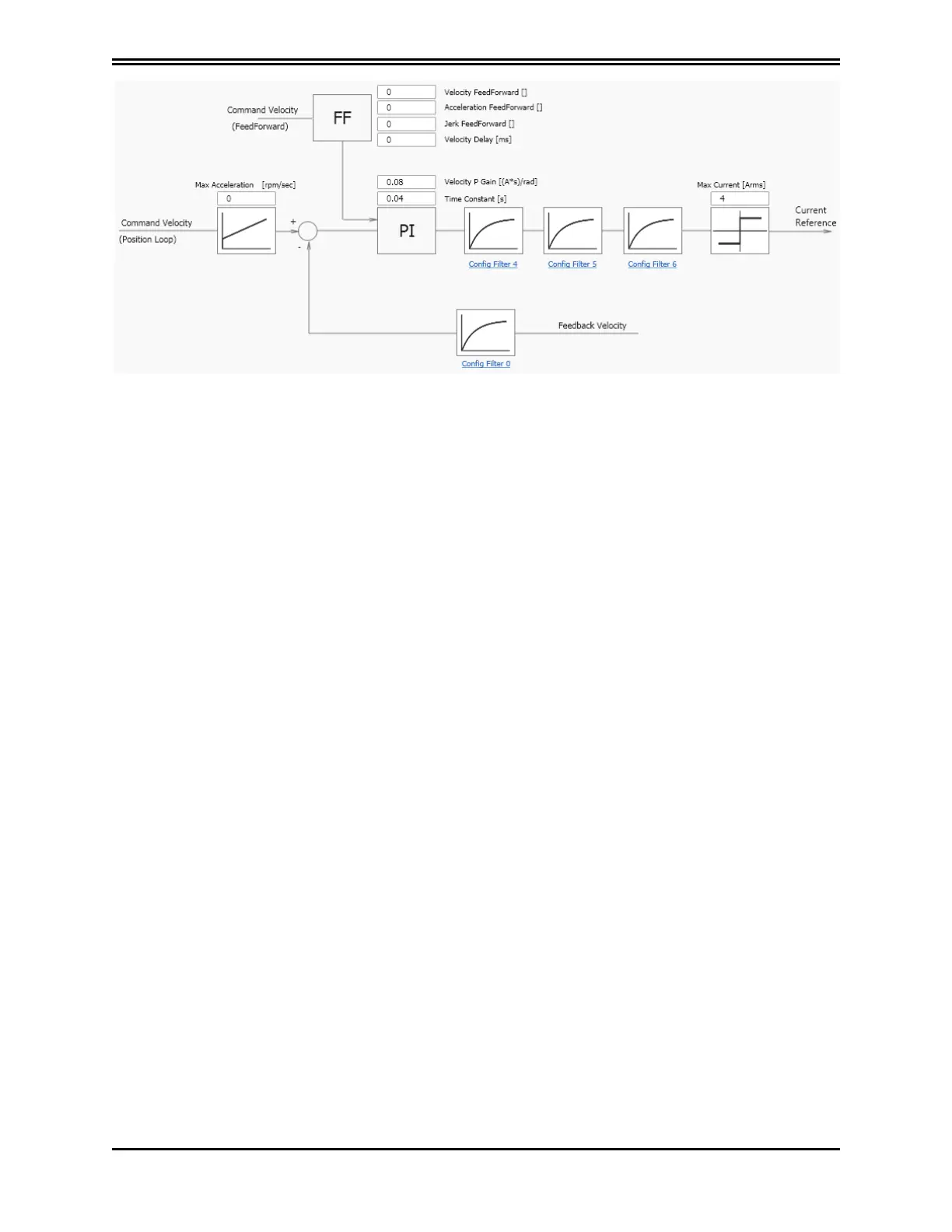
A standard correcting block (PI in the above image) is characterized by two parameters. It is followed
by a sequence of filters, and a filter on the feedback chain. This allows the implementation of more
complex control structures as well as filtering of known disturbances (Notch filter).
Filter configuration
The four filters all have the same basic structure (IIR 2nd order). it is possible to configure them as
needed (to access the Configuration menu of each filter, click the link placed under each block). You
can choose between the following types:
l
Lag: The filter consists of a real pole and a real zero. Put the pole and zero frequency that must
be positive or null.
l
Bq: It is a standard biquadratic filter, with a pair of complex conjugate zeros and a pair of
complex conjugate poles. The parameters are:
l
Zero frequency
l
Zero damping
l
Pole frequency
l
Pole damping
Frequencies must be positive or null. The damping must be between -1 and 1.
l
Pole: The filter has a single real pole. The parameter specified is the frequency of the pole,
which will be positive or null.
l
DbPole: The filter has two complex conjugate poles. The parameters are:
l
Pole frequency
l
Pole damping
Frequencies must be positive or null. The damping must be between -1 and 1.
l
Dircoef: insert the coefficients of the numerator and denominator of the filter (rarely used)
PN: L-MAM2-E-201
Moog Casella DM2020 Installation and Startup Guide
Filter configuration

 Loading...
Loading...