DC Electrical Characteristics
22-2
MPC823e REFERENCE MANUAL
MOTOROLA
ELECTRICAL
22
CHARACTERISTICS
This device contains circuitry protecting against damage from high-static voltage or
electrical fields. However, it is advised that precautions be taken to avoid application of any
voltages higher than the maximum-rated voltages to this high-impedance circuit. Reliability
of operation is enhanced if unused inputs are tied to an appropriate logic voltage level (either
GND or V
CC
).
22.2 THERMAL CHARACTERISTICS
22.3 POWER CONSIDERATIONS
The average chip-junction temperature
,
T
J
,
in
°
C can be obtained from
T
J
= T
A
+ (P
D
•
q
JA
) (1)
where
T
A
= Ambient Temperature
,
∞
C
q
JA
= Package Thermal Resistance
,
Junction to Ambient
,
∞
C/W
P
D
=P
INT
+ P
I/O
P
INT
=I
DD
x V
DD
,
Watts—Chip Internal Power
P
I/O
= Power Dissipation on Input and Output Pins—User Determined
For most applications P
I/O
< 0.3
•
P
INT
and can be neglected. If P
I/O
is neglected
,
an
approximate relationship between P
D
and T
J
is:
P
D
=K
∏
(T
J
+ 273
∞
C) (2)
Solving equations (1) and (2) for K gives
K = P
D
•
(T
A
+ 273
∞
C) + q
JA
• P
D
2
(3)
where K is a constant pertaining to the particular part. K can be determined from equation
(3) by measuring P
D
(at equilibrium) for a known T
A
. Using this value of K
,
the values of P
D
and T
J
can be obtained by solving equations (1) and (2) iteratively for any value of T
A
.
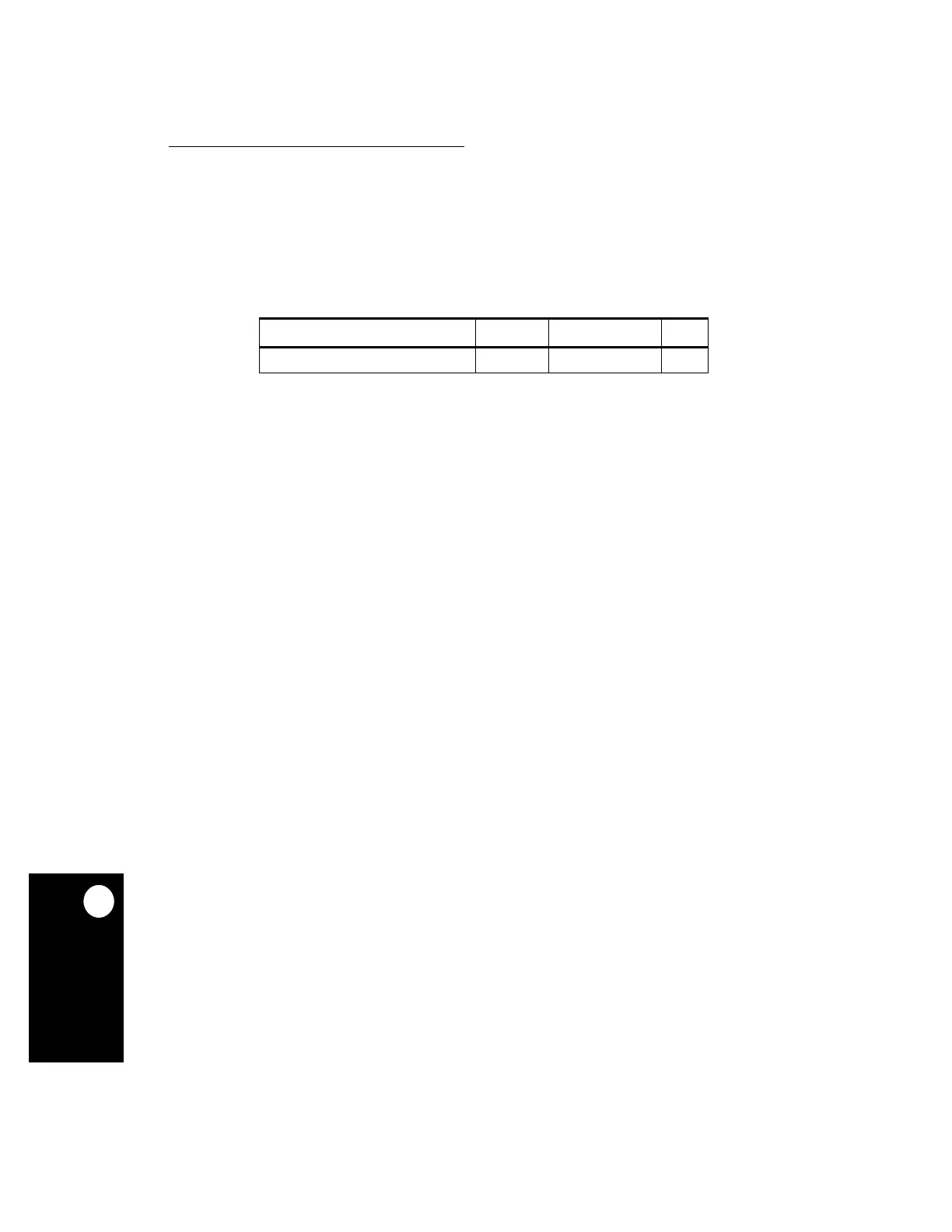
CHARACTERISTIC SYMBOL VALUE UNIT
Thermal Resistance for BGA
θ
JA
~30
°
C/W
 Loading...
Loading...