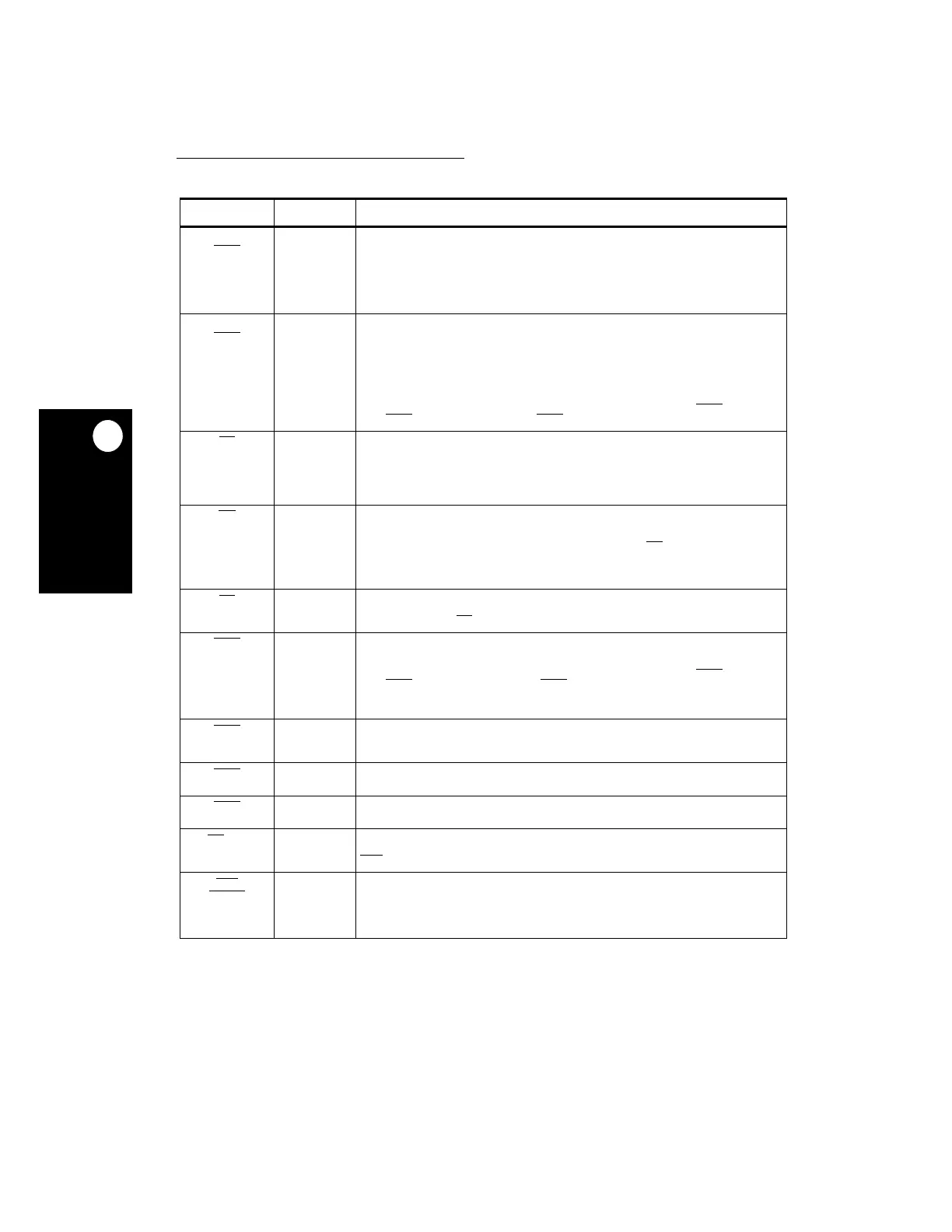
External Signals
2-4
MPC823e REFERENCE MANUAL
MOTOROLA
EXTERNAL SIGNALS
2
DP2
IRQ5
D3
Data Parity
2
—This bidirectional three-state signal provides parity generation and
checking for the data bus lane D[16:23] by transferring to a slave device initiated by
the MPC823e. The parity function can be defined independently for each one of the
addressed memory banks (if controlled by the memory controller) and for the rest of
the slaves on the external bus.
Interrupt Request 5
—This input signal is one of the eight external signals that can
request (by means of the internal interrupt controller) a service routine from the core.
DP3
IRQ6
C2
Data Parity
3
—This bidirectional three-state signal provides parity generation and
checking for the data bus lane D[24:31] by transferring to a slave device initiated by
the MPC823e. The parity function can be defined independently for each one of the
addressed memory banks (if controlled by the memory controller) and for the rest of
the slaves on the external bus.
Interrupt Request 6
—This input signal is one of the eight external signals that can
request (by means of the internal interrupt controller) a service routine from the core.
It should be noted that the interrupt request signal that is sent to the interrupt
controller is the logical AND of this signal (if defined to function as IRQ6
) and the
FRZ/IRQ6
if defined to function as IRQ6.
BR B11
Bus Request
—This bidirectional signal is asserted low when a possible master is
requesting ownership of the bus. When the MPC823e is configured to operate with
the internal arbiter, this signal is configured as an input. However, when the
MPC823e is configured to operate with an external arbiter, this signal is configured
as an output and asserted every time a new transaction is intended to be initiated
and no parking on the bus is granted.
BG
C10
Bus Grant
—This bidirectional signal is asserted low when the arbiter of the external
bus grants the specific master ownership of the bus. When the MPC823e is
configured to operate with the internal arbiter, this signal is configured as an output
and asserted every time the external master asserts the BR
signal and its priority
request is higher than any of the internal sources requiring the initiation of a bus
transfer. However, when the MPC823e is configured to operate with an external
arbiter, this signal is configured as an input.
BB
A11
Bus Busy
—This bidirectional signal is asserted low by a master to show that it owns
the bus. The MPC823e asserts this signal after the bus arbiter grants it bus
ownership and the BB
signal is negated.
IRQ6
FRZ
A10
Interrupt Request 6
—This input signal is one of the eight external signals that can
request (by means of the internal interrupt controller) a service routine from the core.
It should be noted that the interrupt request signal that is sent to the interrupt
controller is the logical AND of this signal (if defined to function as IRQ6
) and the
DP3/IRQ6
(if defined to function as IRQ6.)
Freeze
—This output signal is asserted to indicate that the internal core is in debug
mode.
IRQ0 N1
Interrupt Request 0
—This input signal is one of the eight external signals that can
request (by means of the internal interrupt controller) a service routine from the core.
It causes a non-maskable interrupt to the core.
IRQ1
N2
Interrupt Request 1
—This input signal is one of the eight external signals that can
request (by means of the internal interrupt controller) a service routine from the core.
IRQ7
N3
Interrupt Request 7
—This input signal is one of the eight external signals that can
request (by means of the internal interrupt controller) a service routine from the core.
CS
[0:5] See Table 2-2
for pin
breakout.
Chip Select
—These output signals enable peripheral or memory devices at
programmed addresses if they are appropriately defined in the memory controller.
CS0
can be configured to be the global chip-select for the boot device.
CS6
CE1_B
C14
Chip Select
6
—This output signal enables a peripheral or memory device at a
programmed address if defined appropriately in the BR6 and OR6 of the memory
controller.
Card Enable 1 Slot B
—This output signal enables even byte transfers when
accesses to the PCMCIA Slot B are handled by the PCMCIA interface.
Table 2-1. Signal Descriptions (Continued)
SIGNAL PIN NUMBER DESCRIPTION
 Loading...
Loading...