Chapter 14: Applications 400
Note: You must enter values for æ, PV, PMT, and before computing the principal.
G
Prn(pmt1,pmt2[,roundvalue])
GInt( computes the sum of the interest during a specified period for an amortization
schedule using stored values for ¾æ,
PV, and PMT. pmt1 is the starting payment. pmt2 is
the ending payment in the range.
pmt1 and pmt2 must be positive integers < 10,000.
roundvalue specifies the internal precision the calculator uses to calculate the interest; if
you do not specify
roundvalue, the TI-84 Plus uses the current Float/Fix decimal-mode
setting.
G
Int(pmt1,pmt2[,roundvalue])
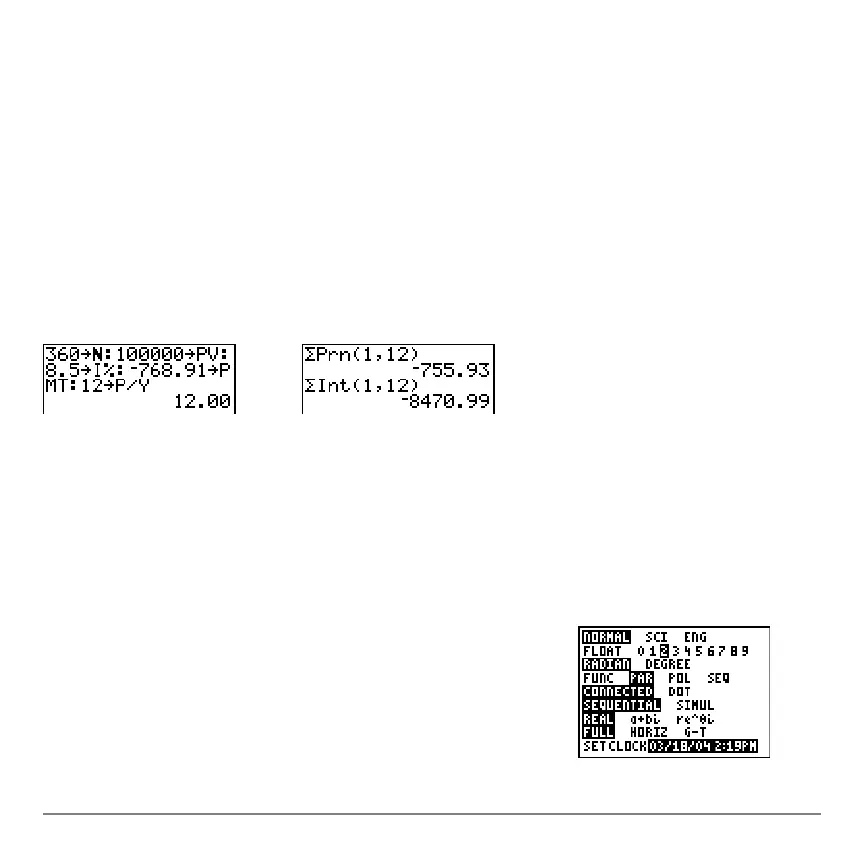
Amortization Example: Calculating an Outstanding Loan Balance
Amortization Example: Calculating an Outstanding Loan BalanceAmortization Example: Calculating an Outstanding Loan Balance
Amortization Example: Calculating an Outstanding Loan Balance
You want to buy a home with a 30-year mortgage at 8 percent APR. Monthly payments
are 800. Calculate the outstanding loan balance after each payment and display the
results in a graph and in the table.
1. Press z. Press † ~ ~ ~ Í to set the
fixed-decimal mode setting to
2. Press † † ~ Í to
select
Par graphing mode.

 Loading...
Loading...

















