12.3 Positioning
12.3.1 Acceleration/Deceleration Patterns
12-7
Asymmetric Linear Acceleration/Deceleration (Constant
Acceleration/Deceleration Rates)
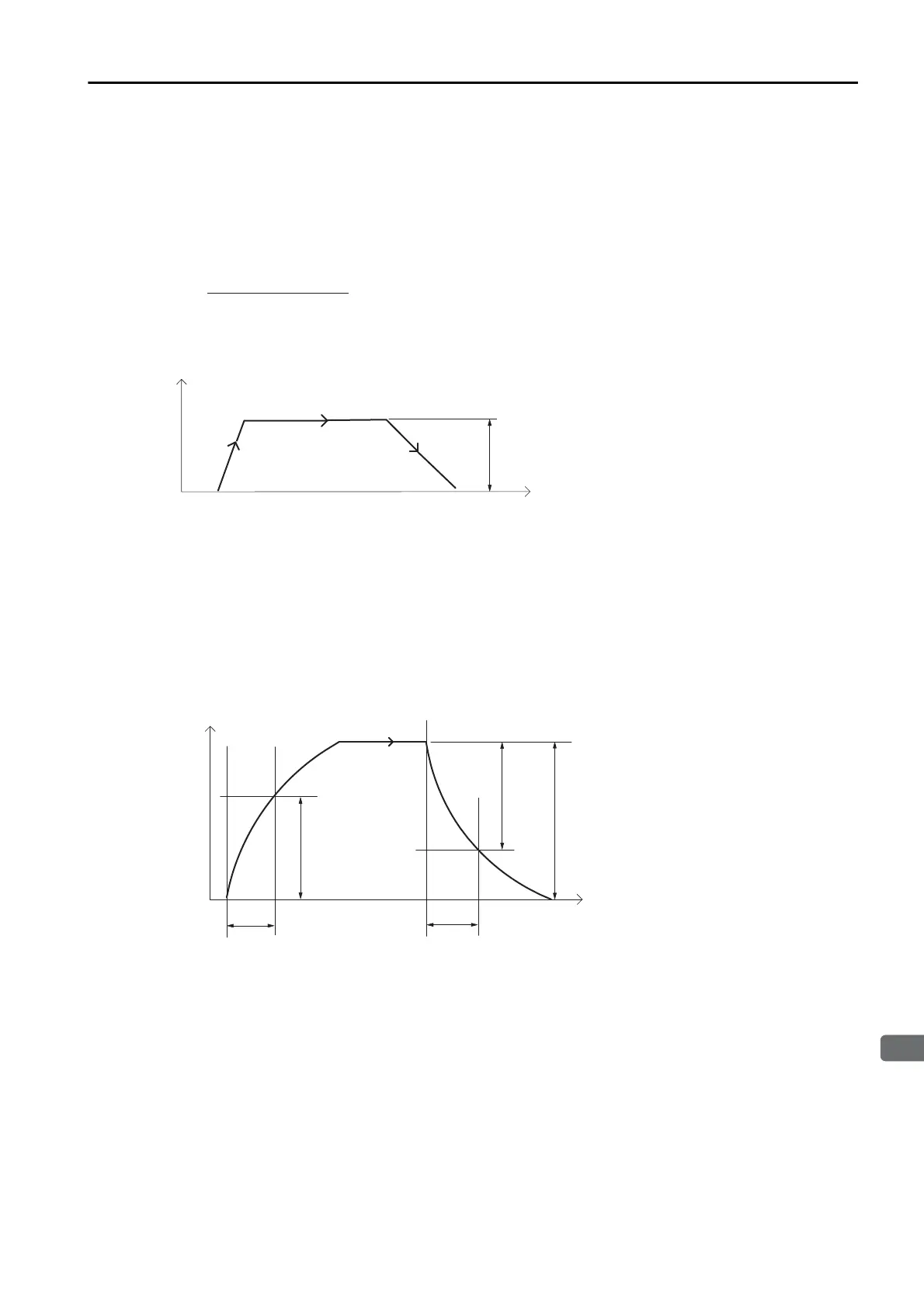
With asymmetric linear acceleration/deceleration, the acceleration and deceleration rates can
be set separately.
For example, for the deceleration rate, the time T that is required to stop during a positioning
operation from when the reference is at the feed speed set in PnB21 can be calculated as fol-
lows:
If this acceleration/deceleration pattern is used, the acceleration/deceleration rates will remain
constant even if the feed speed is changed.
Exponential Acceleration/Deceleration (Constant Accelera-
tion/Deceleration Times)
With exponential acceleration/deceleration, the acceleration/deceleration rates are determined
by two parameters, PnB21 (Feed Speed) and PnB40 (Time Constant for Exponential Accelera-
tion/Deceleration). For PnB40 (Time Constant for Exponential Acceleration/Deceleration), set
the time that is required to reach 63.2% of the feed speed set in PnB21. The acceleration/
deceleration time will be approx. 3.91 times the value of PnB40 in milliseconds.
If this acceleration/deceleration pattern is used, the acceleration/deceleration times will remain
constant even if the feed speed in PnB21 is changed.
T [s] =
Feed Speed (PnB21)
Deceleration Rate (PnB2B)
PnB40
PnB21
Time
Speed
PnB40
63.2% of PnB21
63.2% of PnB21

 Loading...
Loading...