12.3 Positioning
12.3.1 Acceleration/Deceleration Patterns
12-6
12.3
Positioning
12.3.1
Acceleration/Deceleration Patterns
The following acceleration/deceleration patterns can be achieved by combining acceleration/
deceleration types with filter selections.
*1. “Constant acceleration/deceleration rates” indicates that the rate of acceleration and deceleration will be con-
stant. If the feed speed is changed, the time that is required for acceleration/deceleration will change.
*2. “Constant acceleration/deceleration times” indicates that even if the feed speed is changed, the time that is
required for acceleration/deceleration will not change and the acceleration/deceleration rates will change.
Note: Any combination that is not shown above must not be used because acceleration/deceleration will not be
performed correctly.
Symmetric Linear Acceleration/Deceleration (Constant
Acceleration/Deceleration Rates)
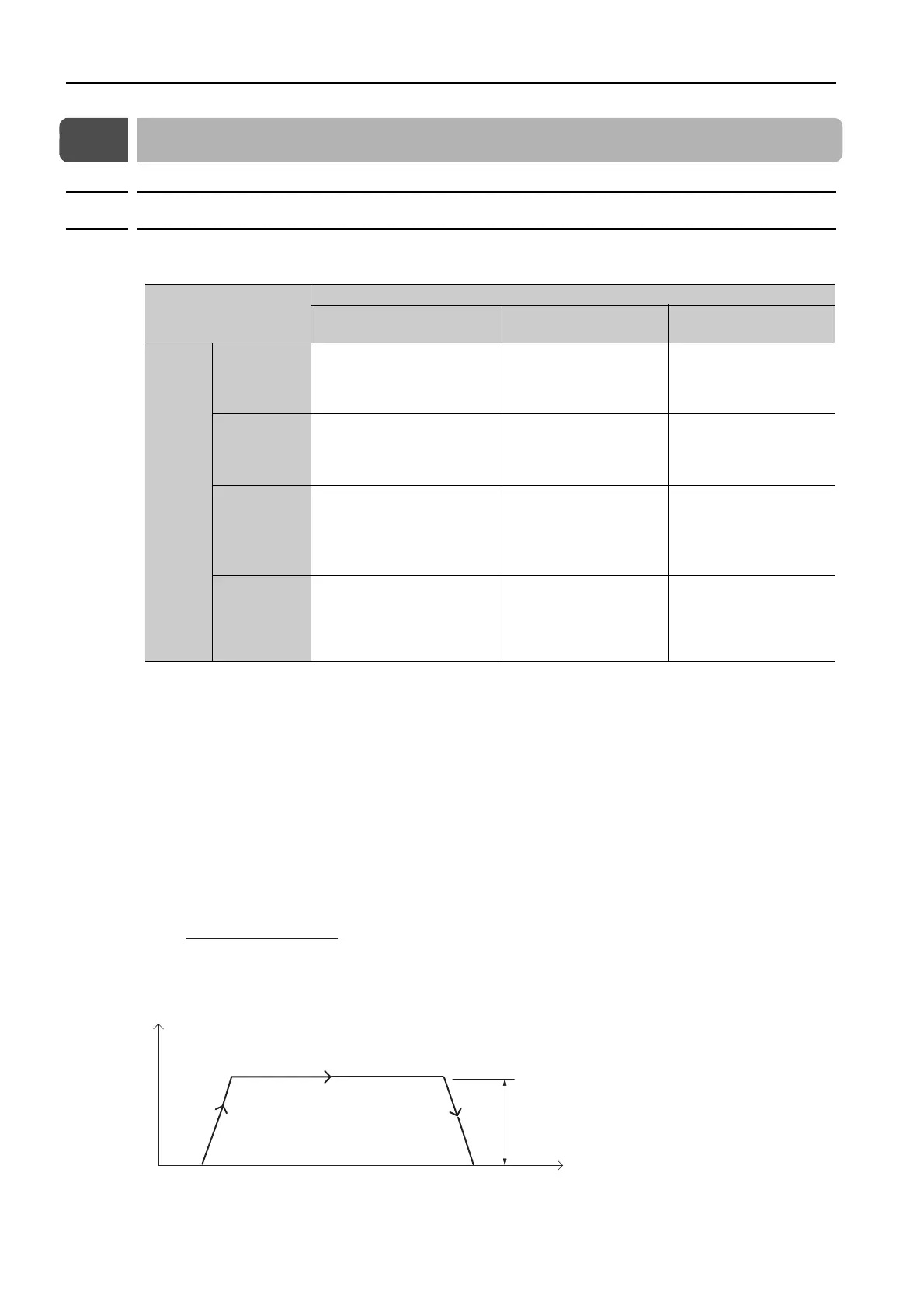
With symmetric linear acceleration/deceleration, the acceleration/deceleration rates are deter-
mined by the Acceleration Rate parameter.
The time T that is required during a positioning operation for the reference to reach the feed
speed in PnB21 is calculated as follows:
If this acceleration/deceleration pattern is used, the acceleration/deceleration rates will remain
constant even if the feed speed in PnB21 is changed.
Parameter
Acceleration/Deceleration Type (PnB26)
0000h: None.
0001h:
Symmetric Linear
0003h:
Asymmetric Linear
Filter
Selec-
tion
(PnB29)
0000h: None. No acceleration/deceleration
Symmetric linear accel-
eration/deceleration
Constant acceleration/
deceleration rates
*1
Asymmetric linear accel-
eration/deceleration
Constant acceleration/
deceleration rates
*1
0001h: Expo-
nential accel-
eration/
deceleration
Exponential acceleration/
deceleration
Constant acceleration/
deceleration times
*2
––
0002h: Expo-
nential accel-
eration/
deceleration
with bias
Exponential acceleration/
deceleration with bias
Constant acceleration/
deceleration times
*2
––
0003h: Mov-
ing
average
Symmetric linear accelera-
tion/deceleration
Constant acceleration/
deceleration times
*2
Symmetric S-curve
acceleration/decelera-
tion
Constant acceleration/
deceleration rates
*1
Asymmetric S-curve
acceleration/decelera-
tion
Constant acceleration/
deceleration rates
*1
T [s] =
Feed Speed (PnB21)
Acceleration Rate (PnB2A)
Speed
Time
PnB2APnB2A
PnB21

 Loading...
Loading...