12.3 Positioning
12.3.1 Acceleration/Deceleration Patterns
12-9
Symmetric S-Curve Acceleration/Deceleration (Constant
Acceleration/Deceleration Rates)
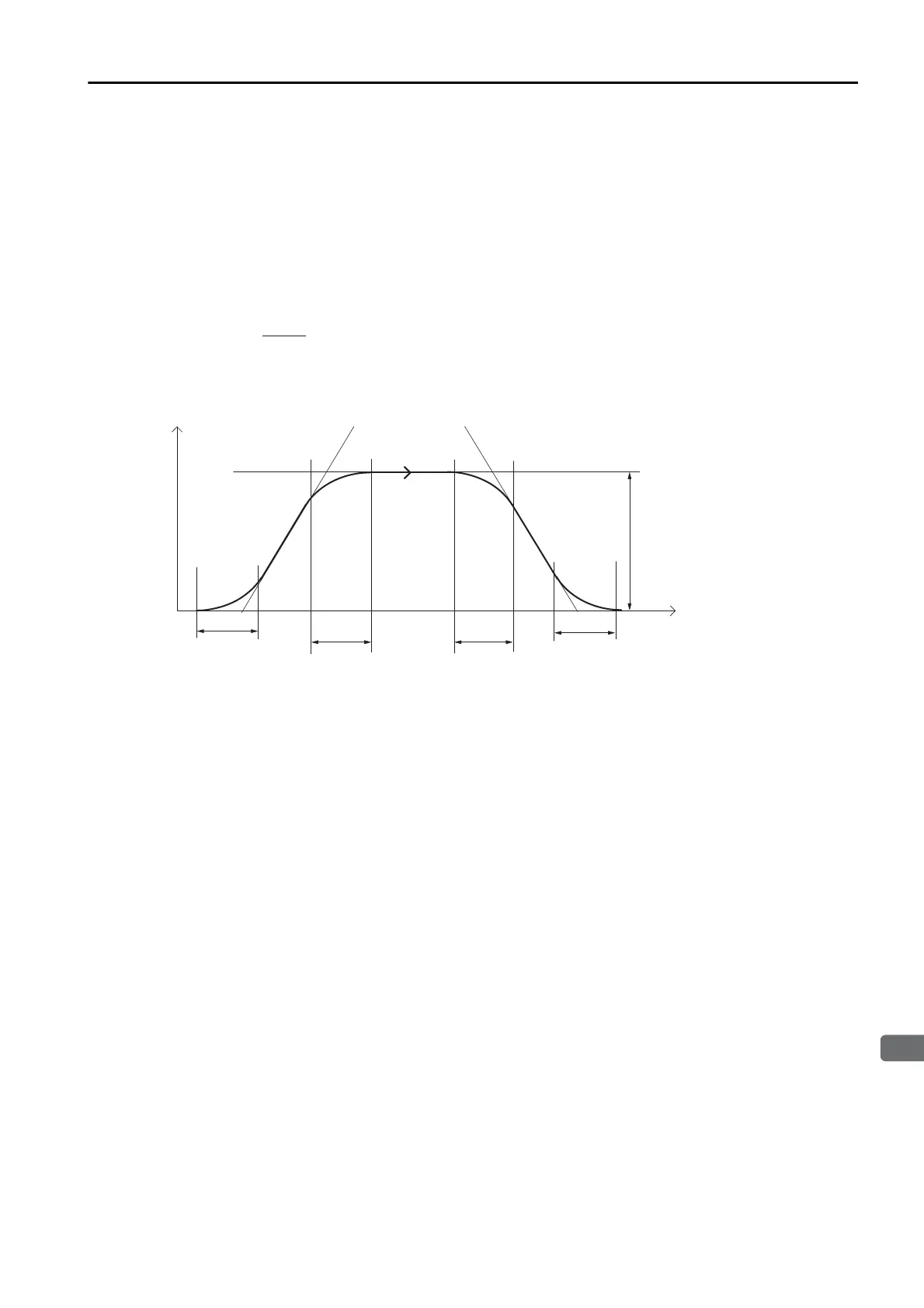
First, symmetric S-curve acceleration/deceleration is the same as symmetric linear accelera-
tion/deceleration in that the acceleration and deceleration rates are both determined by PnB2A
(Acceleration Rate). With an S-curve pattern, however, the corners when starting and just
before and after the feed speed set in PnB21 are rounded by using a filter. Set the time for
rounding off the corners in PnB42 (Average Movement Time Filter Time Constant).
The time T that is required during a positioning operation for the reference to reach the feed
speed in PnB21 is calculated as follows:
If this acceleration/deceleration pattern is used, the acceleration/deceleration rates will remain
constant even if the feed speed is changed.
T [ms] = PnB42 + ( )
×
1,000
PnB2A
PnB21
Time
PnB21
Speed
PnB42
PnB2A
PnB42
PnB42
PnB2A
PnB42

 Loading...
Loading...