Defining Rapid Spanning Tree 227
Defining Rapid
Spanning Tree
While Classic STP prevents Layer 2 forwarding loops in a general network
topology, convergence can take between 30-60 seconds. This time may
delay detecting possible loops and propagating status topology changes.
Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) detects and uses network topologies
that allow a faster STP convergence without creating forwarding loops.
The Global System LAG information displays the same field information
as the ports, but represent the LAG RSTP information.
To define RSTP:
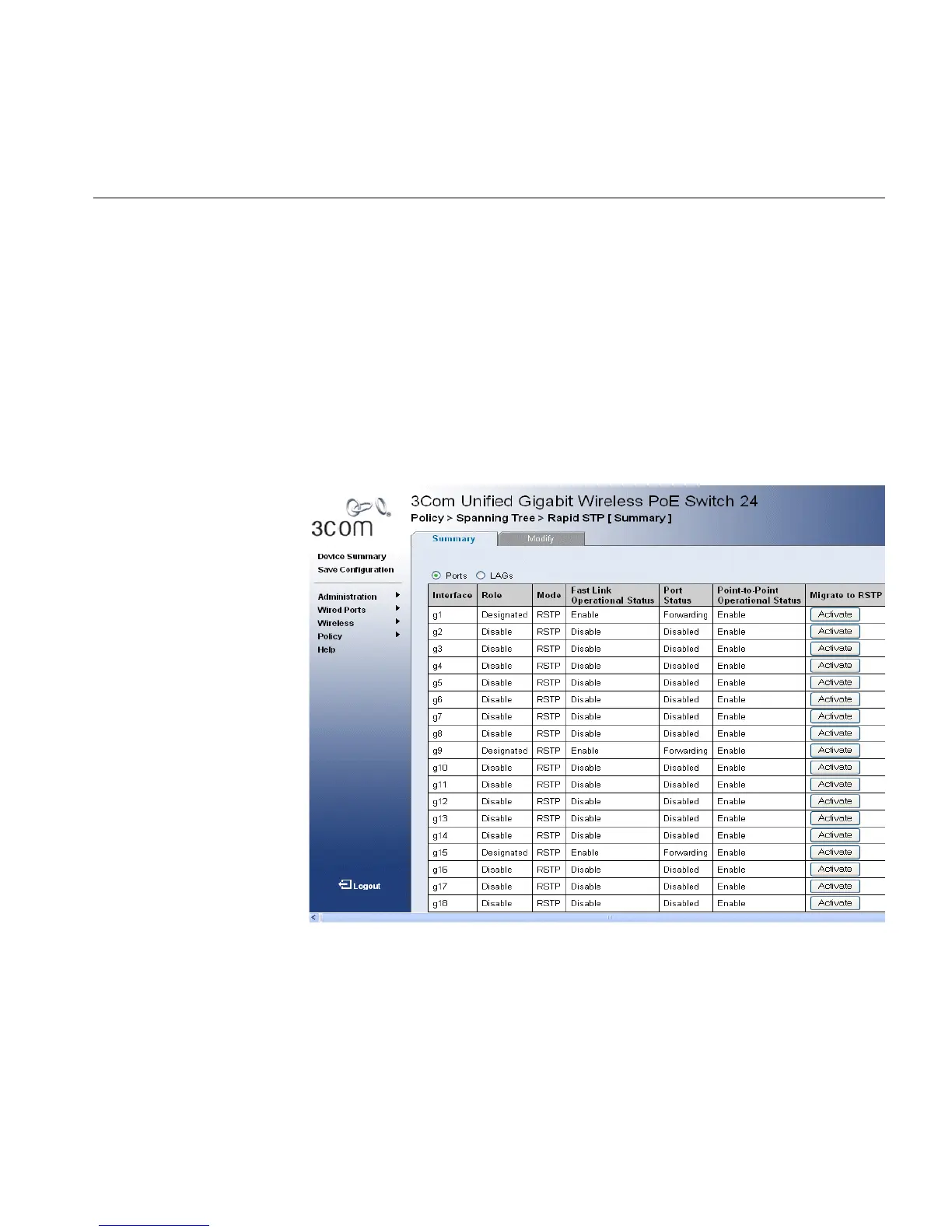
1 Click Policy > Spanning Tree > Rapid STP > Summary. The RSTP
Summary Page opens:
Figure 117 RSTP Summary Page
The RSTP Summary Page contains the following fields:
■ Interface — Displays the port or LAG on which Rapid STP is enabled.
■ Role — Displays the port role assigned by the STP algorithm to
provide to STP paths. The possible field values are:
■ Root — Provides the lowest cost path to forward packets to the
root switch.
 Loading...
Loading...











