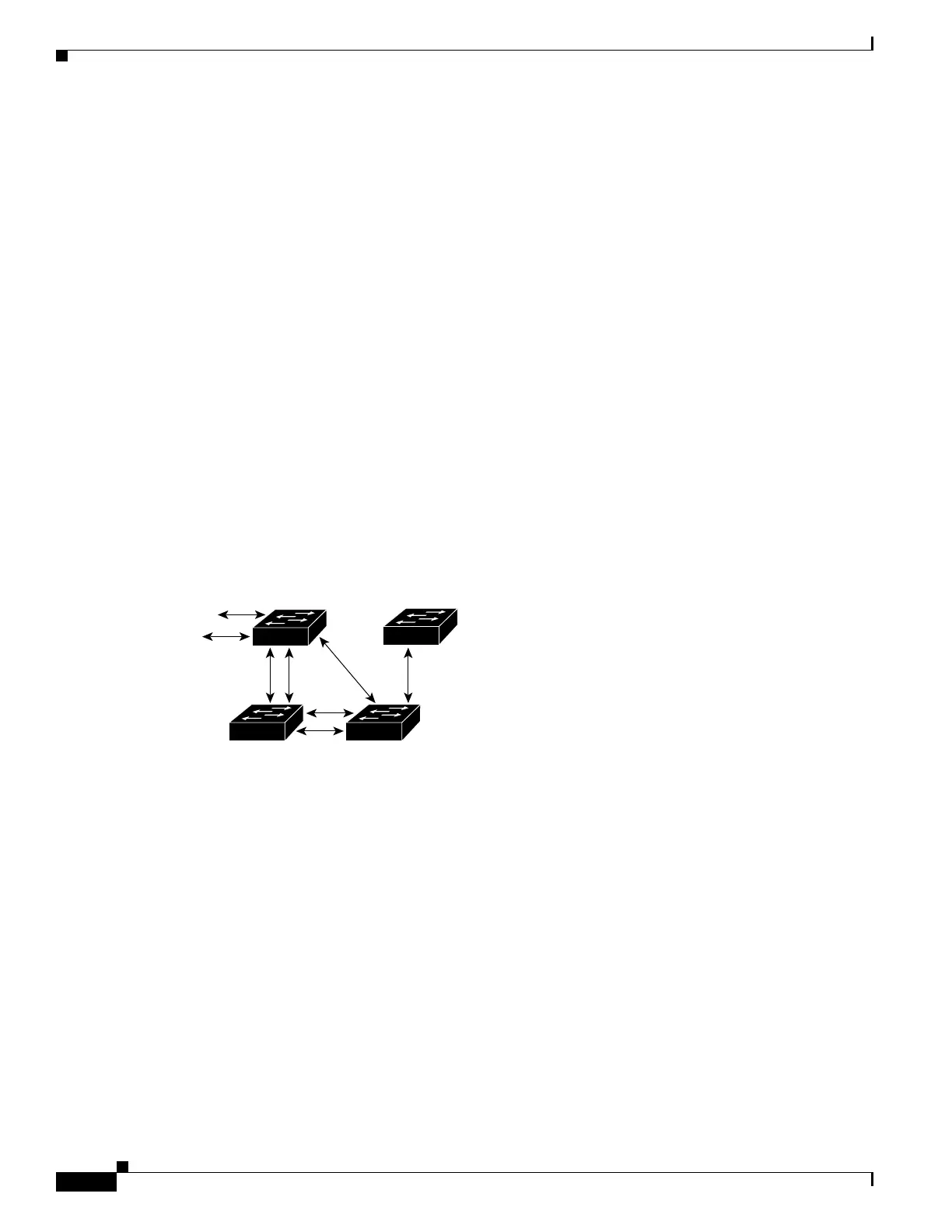1-8
Catalyst 3750-X and 3560-X Switch Software Configuration Guide
OL-25303-03
Chapter 1 Configuring STP
Understanding Spanning-Tree Features
Disabled State
A Layer 2 interface in the disabled state does not participate in frame forwarding or in the spanning tree.
An interface in the disabled state is nonoperational.
A disabled interface performs these functions:
• Discards frames received on the interface
• Discards frames switched from another interface for forwarding
• Does not learn addresses
• Does not receive BPDUs
How a Switch or Port Becomes the Root Switch or Root Port
If all switches in a network are enabled with default spanning-tree settings, the switch with the lowest
MAC address becomes the root switch. In Figure 1-3, Switch A is elected as the root switch because the
switch priority of all the switches is set to the default (32768) and Switch A has the lowest MAC address.
However, because of traffic patterns, number of forwarding interfaces, or link types, Switch A might not
be the ideal root switch. By increasing the priority (lowering the numerical value) of the ideal switch so
that it becomes the root switch, you force a spanning-tree recalculation to form a new topology with the
ideal switch as the root.
Figure 1-3 Spanning-Tree Topology
When the spanning-tree topology is calculated based on default parameters, the path between source and
destination end stations in a switched network might not be ideal. For instance, connecting higher-speed
links to an interface that has a higher number than the root port can cause a root-port change. The goal
is to make the fastest link the root port.
For example, assume that one port on Switch B is a Gigabit Ethernet link and that another port on
Switch B (a 10/100 link) is the root port. Network traffic might be more efficient over the Gigabit
Ethernet link. By changing the spanning-tree port priority on the Gigabit Ethernet port to a higher
priority (lower numerical value) than the root port, the Gigabit Ethernet port becomes the new root port.
86475
DP
DP
RP
DP
RP
DP
RP = Root Port
DP = Designated Port
DP
RP
DA
CB

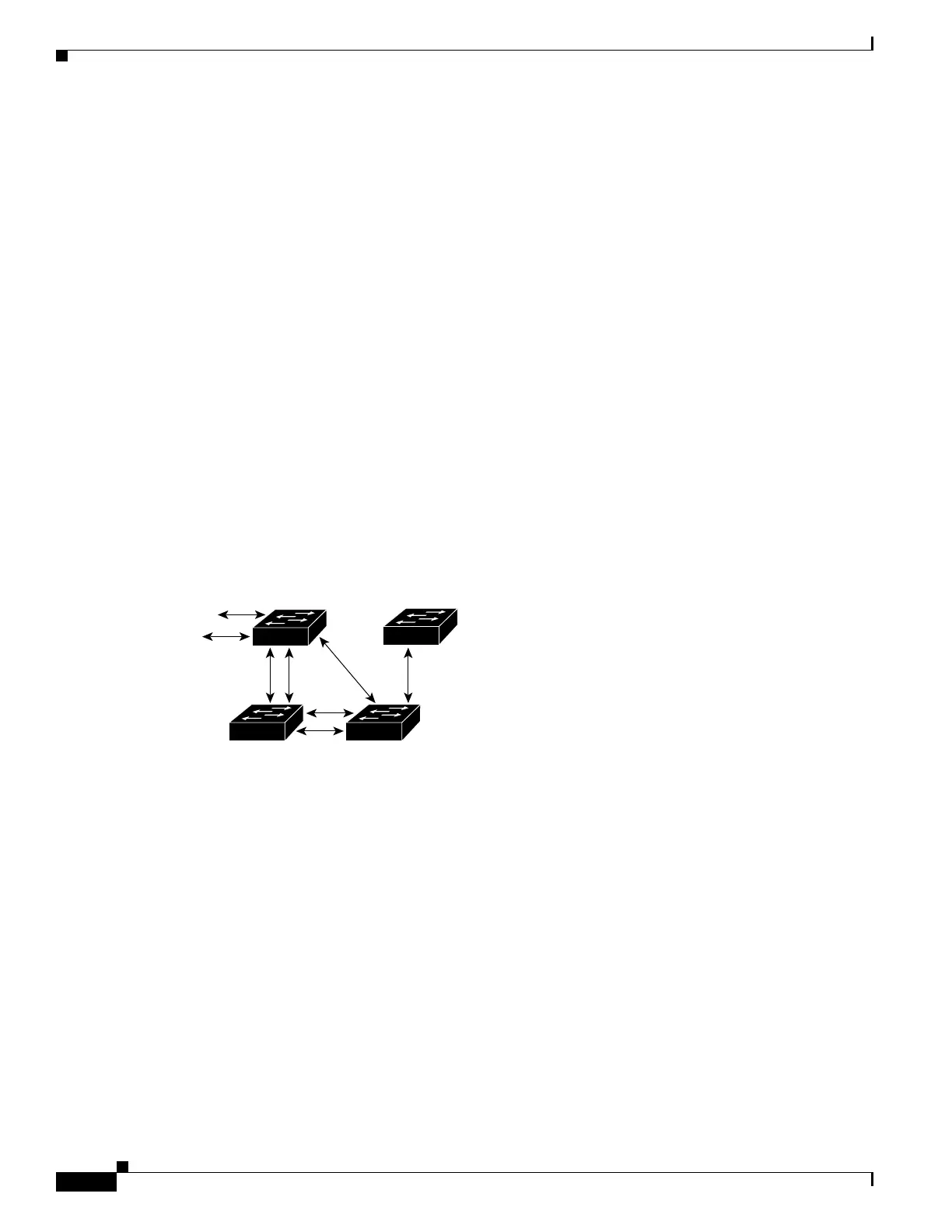 Loading...
Loading...