The general procedures for parameter adjustment in the torque mode are:
1) Initial setting of the parameters
The defaults of the parameters can be recovered by the default parameter recovering operation (see
chapter 5.2.5.3 for details).
2) Adjustment of the torque smoothing filter
In case the analog quantity serves as “torque command” input, users can adjust the analog input filter
to make the torque change smoothly.
3) Frequency division of the feedback pulse output
If the feedback pulse of the encoder needs to be outputted, the frequency division coefficient of pulse
output can be used to change the frequency of the output pulse.
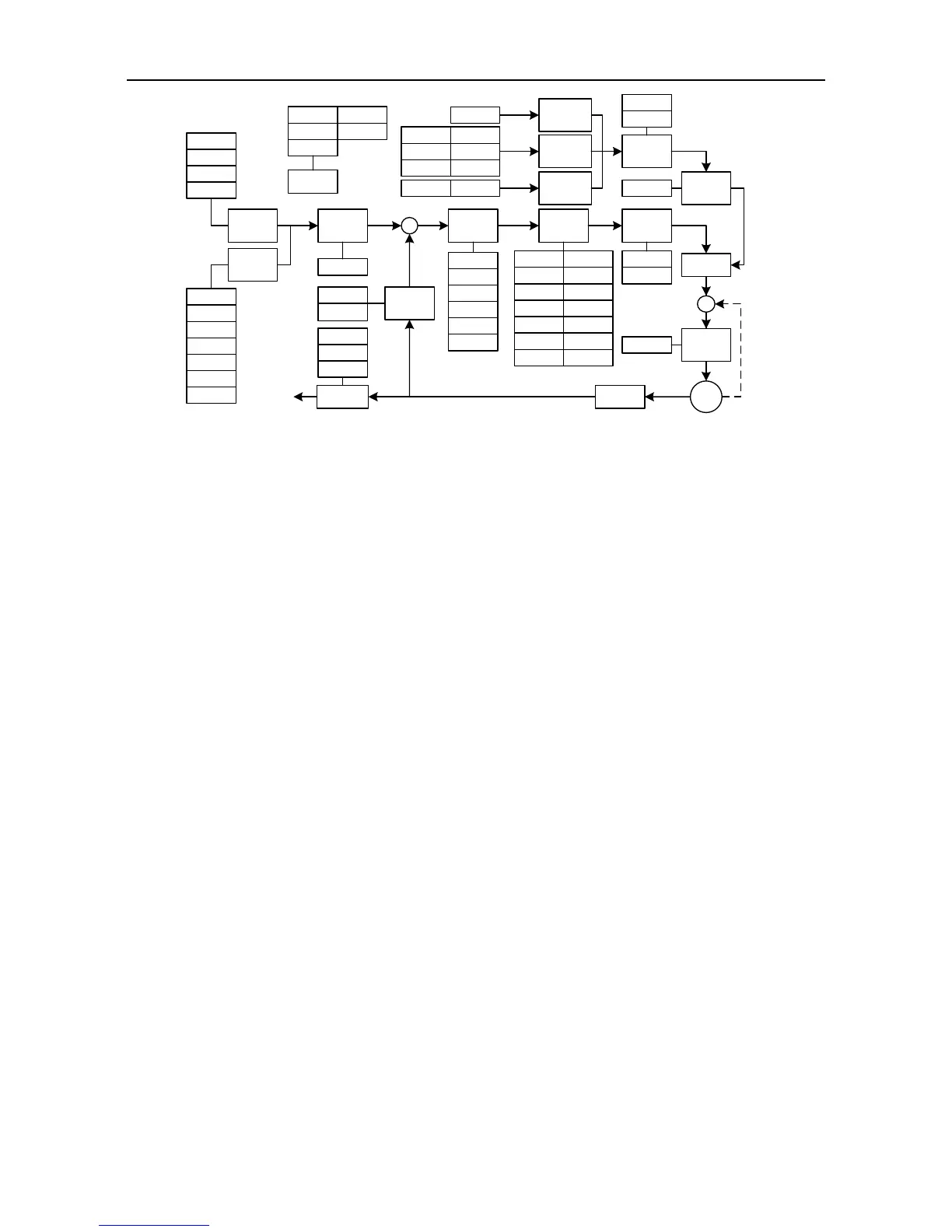
7.3 Suppression of mechanical resonance
The mechanical system has a certain resonant frequency. If the response speed of the servo is
improved, the system may resonate (oscillation and abnormal noise) near the mechanical resonant
frequency. The resonance of the mechanical system can be effectively suppressed by setting the
parameters of the notch filters.
The notch filters achieve the goal of suppressing mechanical resonance by decreasing the gain of
certain frequency. We can set the frequency to be suppressed as well as the suppression extent with
relevant parameters.
This servo drive is equipped with four notch filters which can be set by 1
st
notch filter parameter
(P1.23, P1.24, P1.25), 2
nd
notch filter parameter (P1.26, P1.27, P1.28), 3
rd
notch filter parameter
(P1.29, P1.30, P1.31) and 4
th
notch filter parameter (P1.32, P1.33, P1.34). 1
st
and 2
nd
notch filter
parameters need to be set manually; 3
rd
and 4
th
notch filter parameters can be set by online
self-adaption. The position of notch filter in speed loop is shown in the figure in chapter 7.2.2. The
setup of notch filter is shown in the diagram below.

 Loading...
Loading...











