4.8 Operating modes
The operating mode is essential for the context in which an inverter is operated.
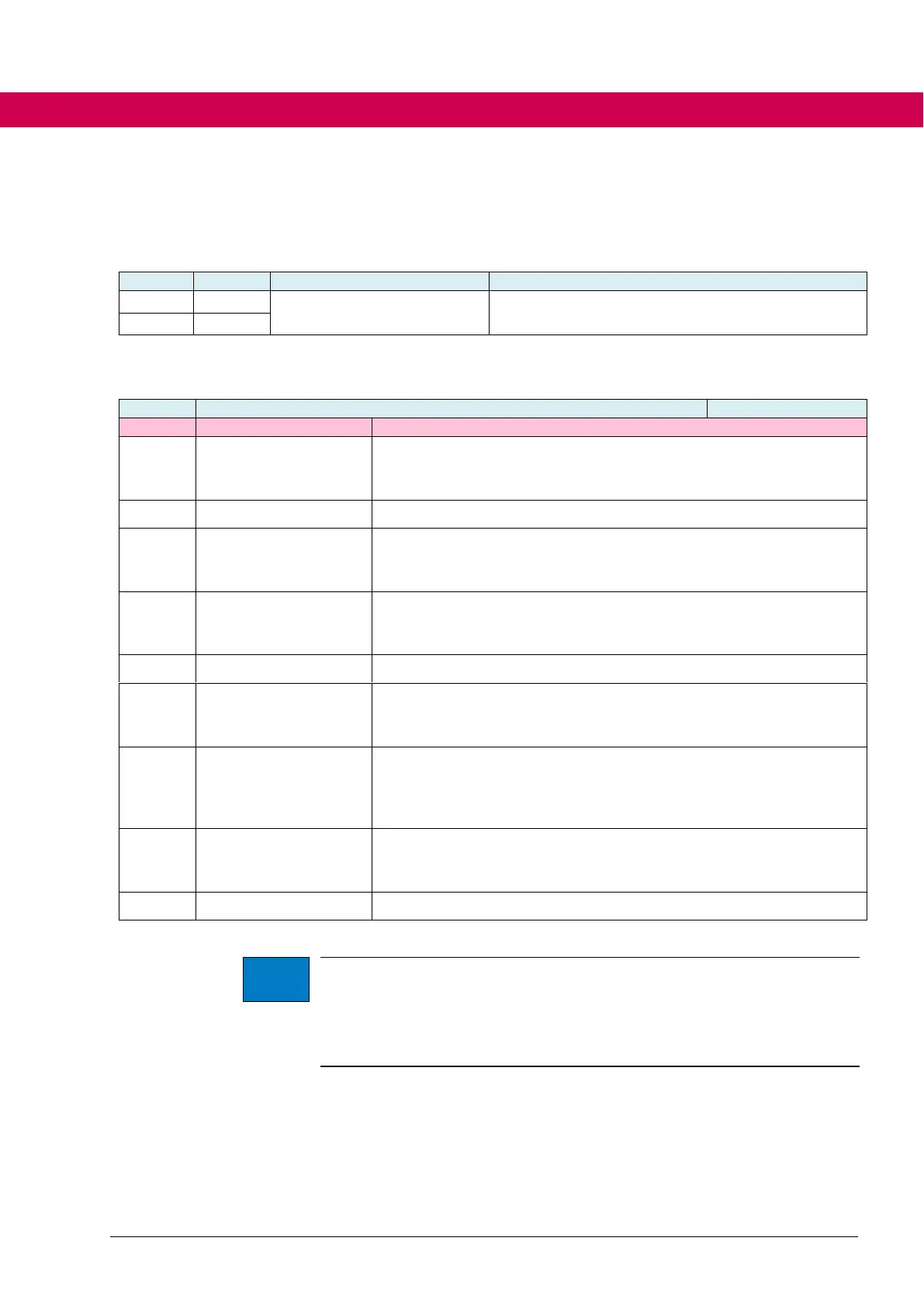
The selection occurs via object co01:
Selection of the operating mode
The single values of co01 have the following meaning:
Manufacturer-specific operating mode: the drive should be able to be
moved independently via digital inputs, e.g. in case of failure of a
higher-level control.
Presetting the target position by the control
Generation of the motion profile in the drive
Position-, speed and torque control in the drive
Presetting the target speed by the control
Generation of the speed profile in the drive
Speed- and torque control in the drive
Used to define the reference position
cyclic sync position
mode
Cyclic presetting of the set position by the control
Interpolation of the set positions in the drive
Position, speed and torque control in the drive
cyclic sync velocity
mode
Cyclic presetting of the set speed by the control
Position control circuit in the control
Interpolation of the set speed in the drive
Speed and torque control in the drive
Cyclic setting of the set torque by the control
Position and speed control circuit in the control
Interpolation of the torque and torque control in the drive
Generally distinction is made between synchronous and non-synchronous op-
erating modes. For synchronous operating modes (=> Synchronization), all
setpoints are transmitted to the drives within a fixed synchronous time grid.
The correct function of the drive is only ensured if control grid and setpoint
setting are synchronized. This is displayed with bit 8 (synchronous) in the sta-
tus word.

 Loading...
Loading...










