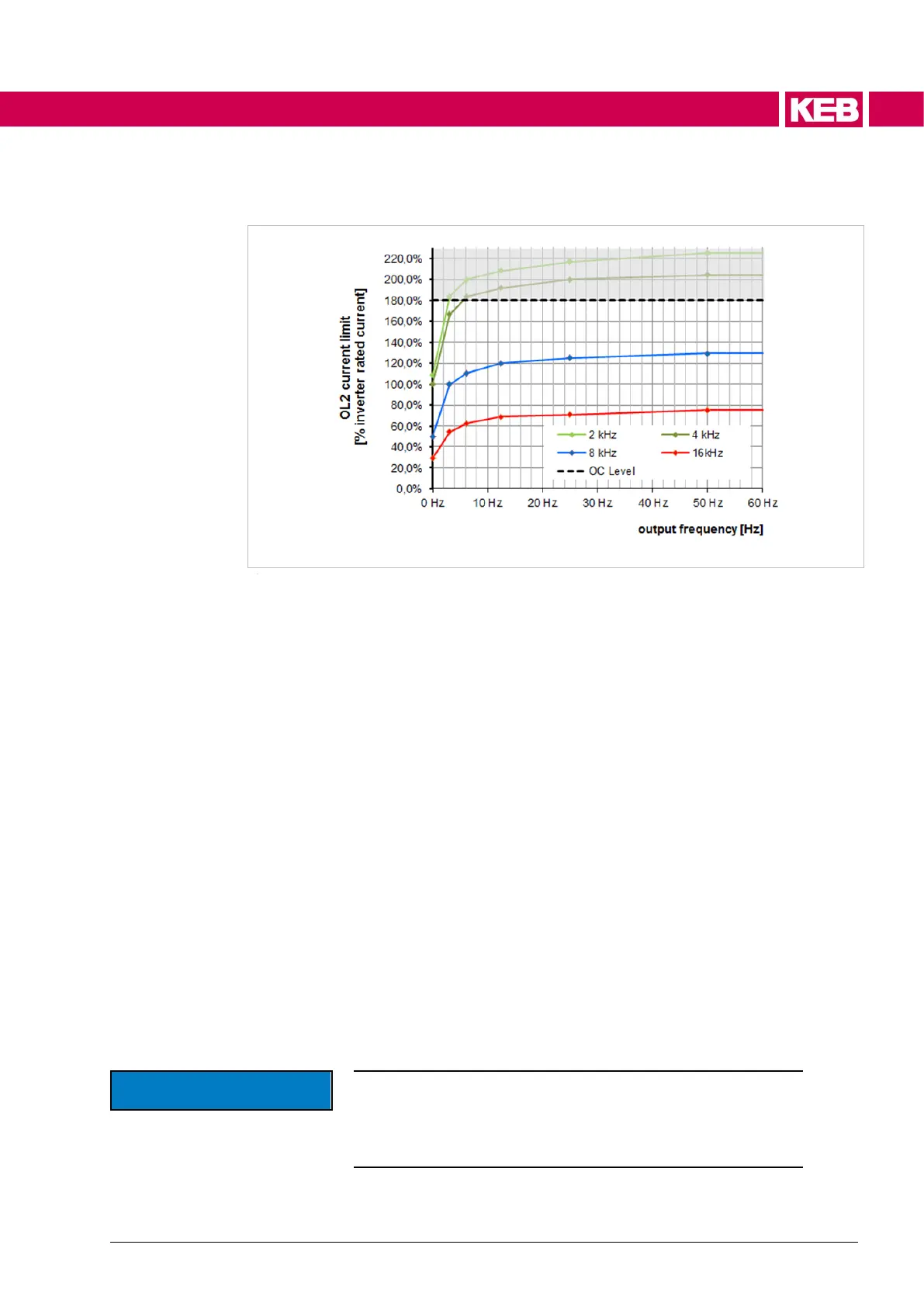
Figure 7: Overload (OL2) limiting characteristic
The ratio of the actual output current to the permissible OL2 current at this fre-
quency is controlled via PT1 element with a time constant of 200ms.
The output value of this PT1 element is displayed in parameter ru27 OL2 counter.
The drive switches off automatically on reaching the overload limit (ru27 OL2-
Counter = 100%).
ru73 Imot/ImaxOl2 displays the ratio of the actual motor current to short time cur-
rent limit.
The short-time current is dependent on the actual switching frequency.
If "Derating" (automatic switching frequency reduction if the motor current exceeds
the short-time current limit for the respective switching frequency) is used, then
ImaxOl2 is equal to the short-time current limit for the minimum switching fre-
quency that can be activated.
4.4.2.1.2 Heat sink temperature dependent OL2 current limit
If the actual heatsink temperature ru25[1] heatsink temperature 1 is below the OH
threshold, a higher current is possible without triggering an OL2 error. The maxi-
mum possible current depends on the difference between the current temperature
and the OH threshold.
The maximum current is reached at 40°C at the latest. Thereafter, a further reduc-
tion of the heat sink temperature causes no further increase of the maximum possi-
ble current.
The increase of the OL2 limit is intended for applications
when the increased current is rarely needed (e.g. heavy start-
ing after long standstill or other rarely occurring events). In-
creasing the OL2 current limit increases the load of the power
module and reduces the lifetime of it.

 Loading...
Loading...










