MAN B&W 17.01
Page of
MAN Diesel
198 41 405.2MAN B&W MC/MCC, ME/ME-B/MEC/MEGI engines
Vibration Aspects
The vibration characteristics of the twostroke low
speed diesel engines can for practical purposes
be split up into four categories, and if the adequate
countermeasures are considered from the early
project stage, the inuence of the excitation sour
ces can be minimised or fully compensated.
In general, the marine diesel engine may inuence
the hull with the following:
• External unbalanced moments
These can be classied as unbalanced st and
2nd order external moments, which need to be
considered only for certain cylinder numbers
• Guide force moments
• Axial vibrations in the shaft system
• Torsional vibrations in the shaft system.
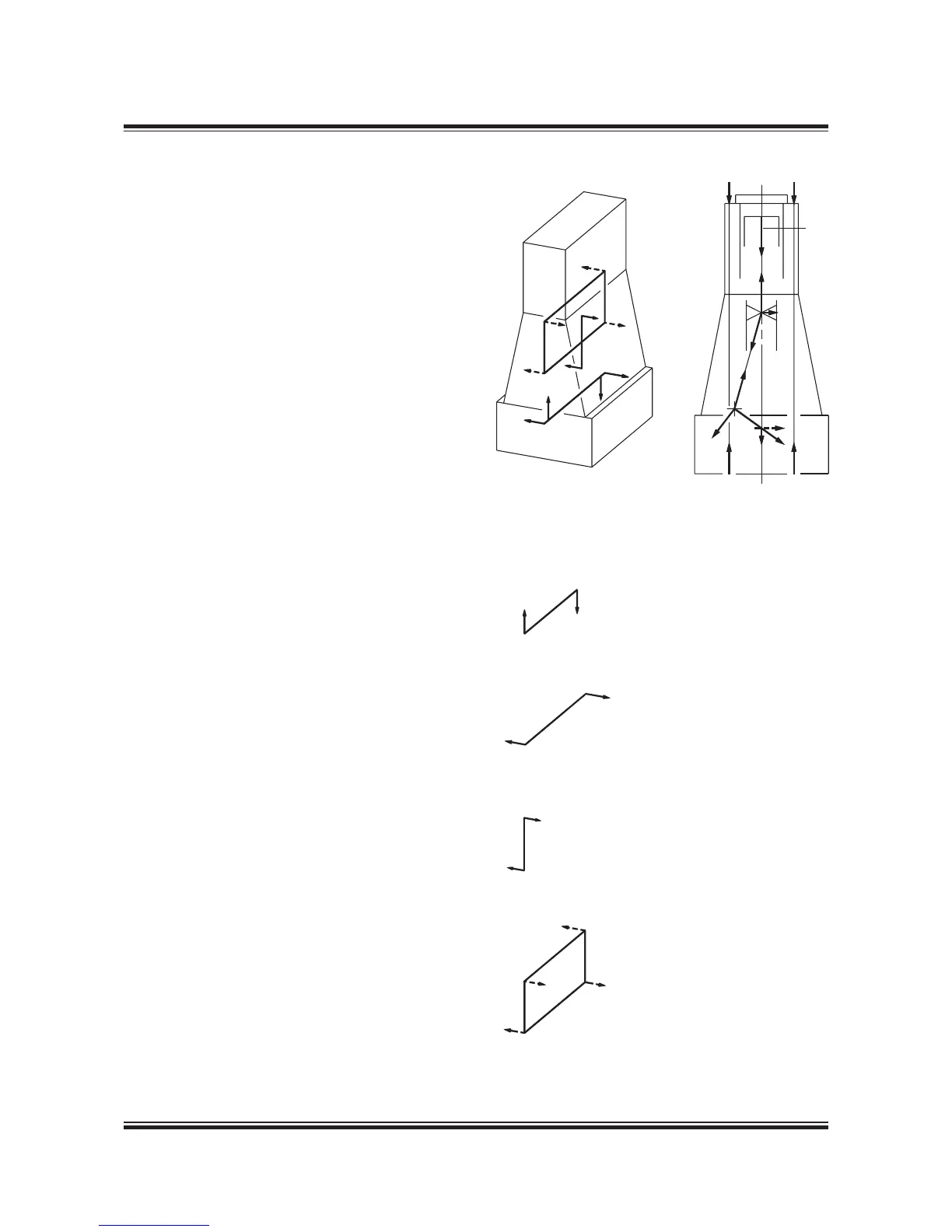
The external unbalanced moments and guide force
moments are illustrated in Fig. 7.0.0.
In the following, a brief description is given of their
origin and of the proper countermeasures needed
to render them harmless.
External unbalanced moments
The inertia forces originating from the unbalanced
rotating and reciprocating masses of the engine
create unbalanced external moments although the
external forces are zero.
Of these moments, the st order (one cycle per revo
lution) and the 2nd order (two cycles per revolution)
need to be considered for engines with a low num
ber of cylinders. On 7cylinder engines, also the 4th
order external moment may have to be examined.
The inertia forces on engines with more than 6 cylin
ders tend, more or less, to neutralise themselves.
Countermeasures have to be taken if hull resonance
occurs in the operating speed range, and if the vibra
tion level leads to higher accelerations and/or veloci
ties than the guidance values given by international
standards or recommendations (for instance related
to special agreement between shipowner and ship
yard). The natural frequency of the hull depends
on the hull’s rigidity and distribution of masses,
whereas the vibration level at resonance depends
mainly on the magnitude of the external moment
and the engine’s position in relation to the vibration
nodes of the ship.
 Loading...
Loading...