MAN B&W 2.06
Page of
MAN Diesel
198 38 36-3.3MAN B&W ME/ME-C/ME-GI
Specic Fuel Oil Consumption, ME versus MC engines
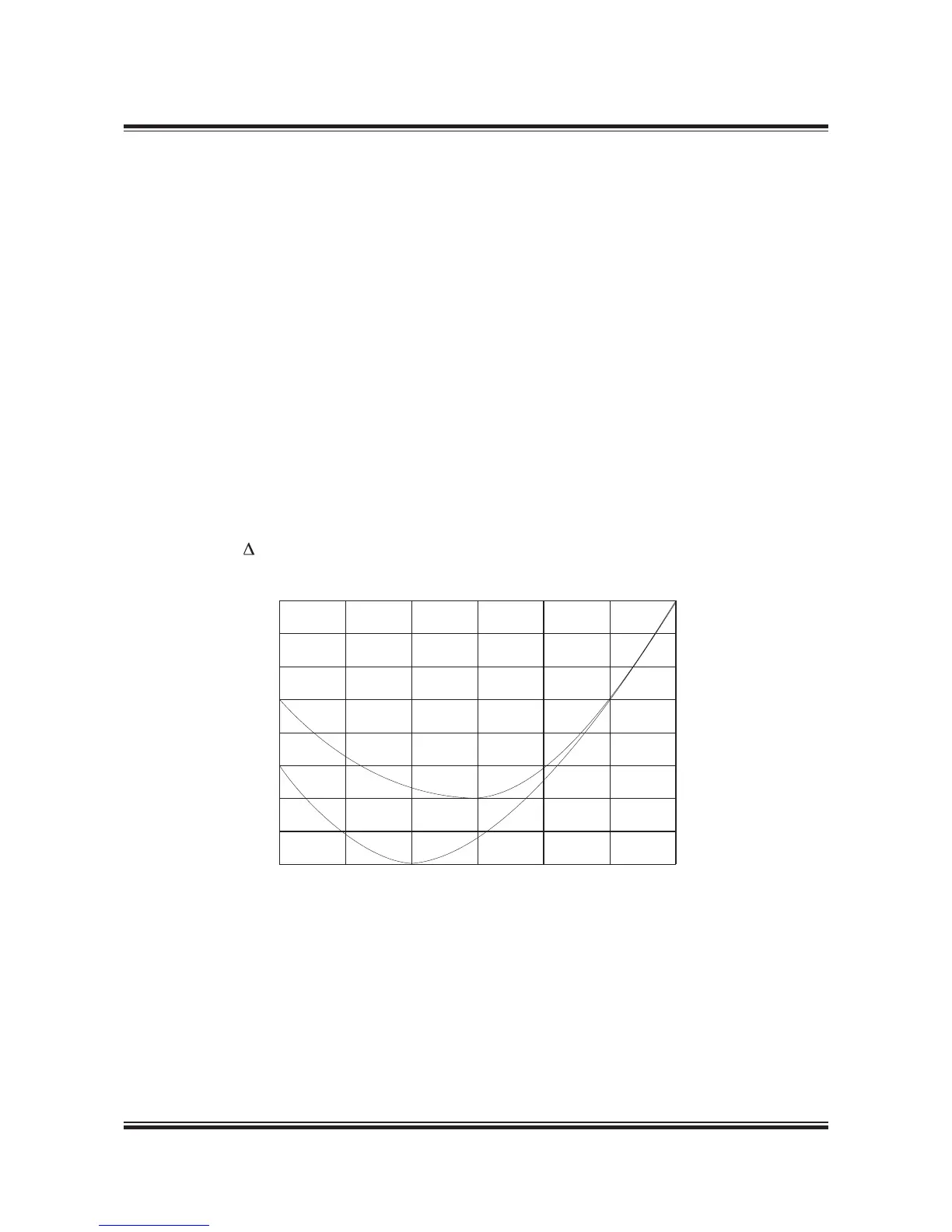
Fig. 2.06.01: Example of part load SFOC curves for ME and MC with xed pitch propeller
198 97 389.2
As previously mentioned the main feature of the
ME engine is that the fuel injection and the ex-
haust valve timing are optimised automatically
over the entire power range, and with a minimum
speed down to around 5% of the L
speed.
Comparing the specic fuel oil comsumption
(SFOC) of the ME and the MC engines, it can be
seen from the gure below that the great advan-
tage of the ME engine is a lower SFOC at part
loads.
It is also noted that the lowest SFOC for the ME
engine is at 70% of O, whereas it was at 80% of O
for the MC engine.
For the ME engine only the turbocharger matching
and the compression ratio (shims under the piston
rod) remain as variables to be determined by the
engine maker / MAN Diesel.
The calculation of the expected specic fuel oil
consumption (SFOC) can be carried out by means
of the following gures for xed pitch propel-
ler and for controllable pitch propeller, constant
speed. Throughout the whole load area the SFOC
of the engine depends on where the matching
point (O) is chosen.
 Loading...
Loading...