use the feedback measurements of the actual controlled process value. The feedforward
control uses other measurements that have an effect on the controlled process value.
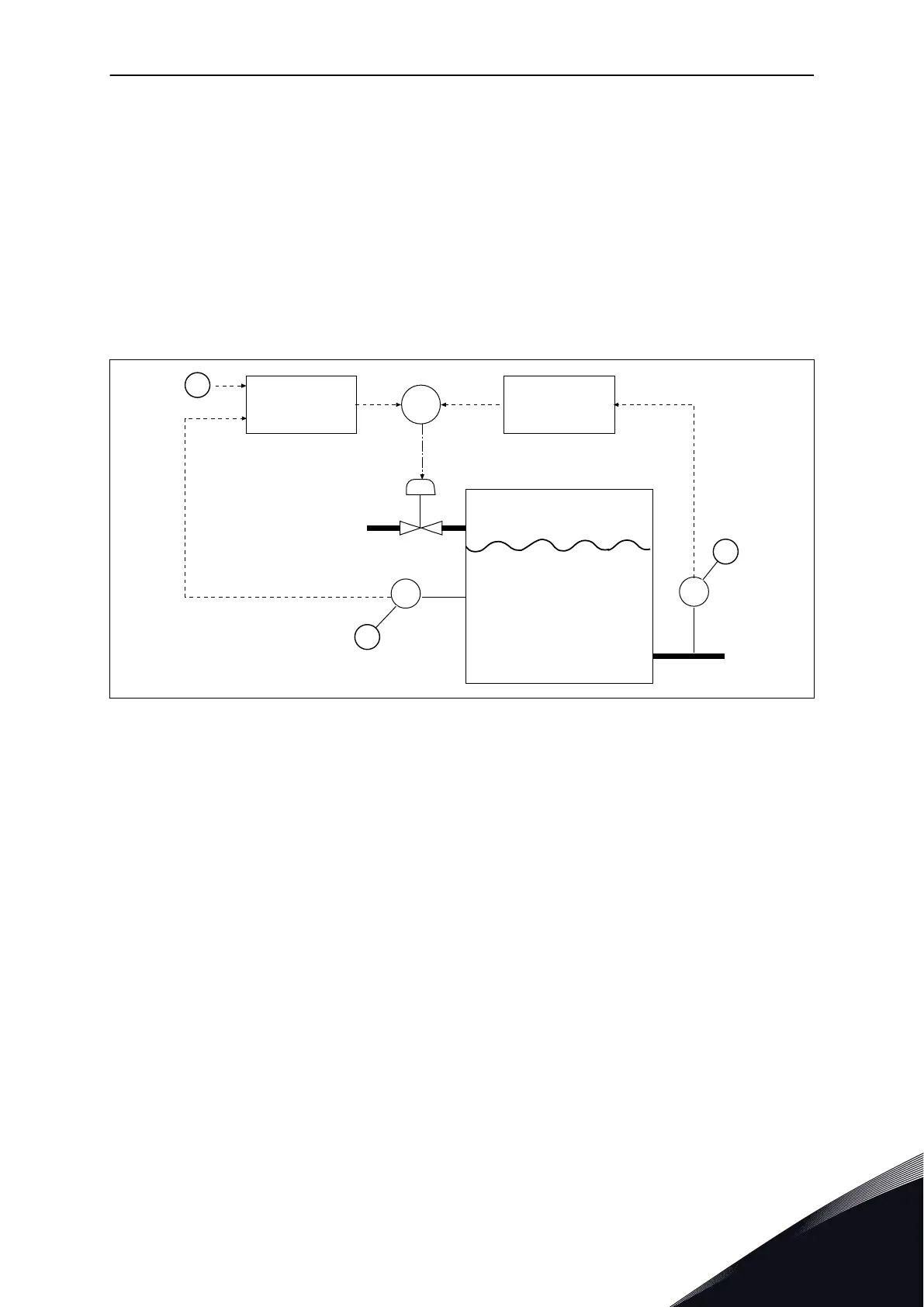
EXAMPLE 1:
You can control the water level of a tank with flow control. The target water level is set as a
setpoint, and the actual level as feedback. The control signal monitors the flow that comes
in.
The outflow is like a disturbance that you can measure. With the measurements of the
disturbance, you can try to adjust this disturbance with a feedforward control (gain and
offset) that you add to the PID output. The PID controller reacts much faster to changes in
the outflow than if you only measure the level.
Fig. 81: The feedforward control
A. Level ref
B. Level control
C. Outflow control
P3.13.4.2 FEEDFORWARD GAIN (ID 1060)
Use this parameter to adjust the gain of the feedforward signal.
P3.13.4.3 FEEDFORWARD 1 SOURCE SELECTION (ID 1061)
Use this parameter to select the source of the PID feedforward signal.
P3.13.4.4 FEEDFORWARD 1 MINIMUM (ID 1062)
Use this parameter to set the minimum value of the feedforward signal.
P3.13.4.5 FEEDFORWARD 1 MAXIMUM (ID 1063)
Use this parameter to set the maximum value of the feedforward signal.
PARAMETER DESCRIPTIONS VACON · 307
LOCAL CONTACTS: HTTP://DRIVES.DANFOSS.COM/DANFOSS-DRIVES/LOCAL-CONTACTS/
10

 Loading...
Loading...