4-23 2000-OSM, F1
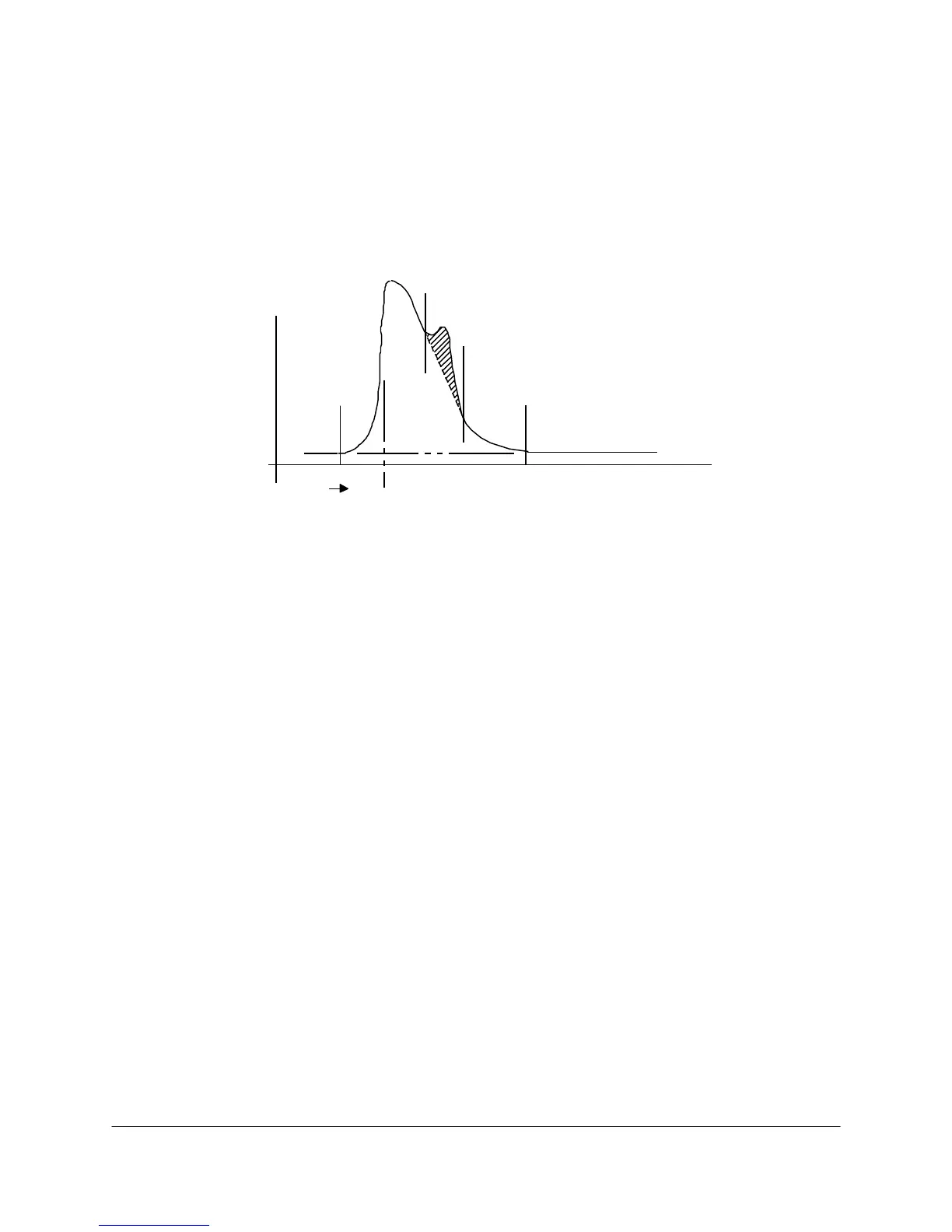
peak which begins on a valley point (see Figure 4-22). Since the tangent skim termination search
operates only during a single peak, it is activated by setting Tangent Skim at the proper time in the
method table (no On/Off is required). To use tangent skim, choose a time in the method table that
occurs at a point before the peak in question and set Tangent Skim. The search begins at the first
valley point (point B in Figure 4-22) after the request point (point A) and ends at the peak termination
point. The controller determines it has found a tangent termination point when the slope of the
chromatogram being measured at point C equals the slope of the line BC. The tangent point
identifies this second peak as being a small peak on the tail of a larger peak, rather than a separate
peak.
A
1
B
C
D
TIME
TANGENT SKIM
2
Figure 4-22. EXAMPLE OF TANGENT SKIM
Baseline definitions override the normal slope detection definition of the peak topology. This permits
you to define how the baseline is drawn for a peak or series of peaks. In the method table, the
baseline function has five commands associated with it:
Pk End =Vly
Pk End =Base
Proj Forward
Proj Reverse
Proj Term
If a specific application is such that the slope detect algorithm has difficulty determining whether a
particular point at the end of a peak is a valley or a baseline, it can provide erratic data. The
algorithm sometimes calls the point a valley and sometimes it calls it a baseline, thus providing
 Loading...
Loading...